Number Systems
Short
Answers
1. What is radix of a number system?
Give example
A numbering system is a way of
representing numbers. The most commonly used numbering system in real life is
Decimal number system.
Other number systems are Binary, Octal,
and Hexadecimal Number System. Each number system is uniquely identified by its
base value or radix.
Radix or base is the count of number of
digits in each number system. Radix or base is the general idea behind
positional numbering system.
E.g.:
(123)10, (547)8, (1001)2, (25)16
2. Write note on binary number system.
There are only two digits in the Binary
system, namely, 0 and 1. The number in the binary system are represented to the
base 2 and the positional multipliers are the powers of 2.
The left most bit in the binary number
is called as the Most Significant Bit (MSB) and it has the largest positional
weight.
†The right most bit is the Least Significant
Bit (LSB) and has the smallest positional weight.
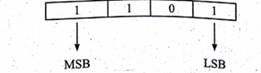
E.g.: The binary sequence (1101), has the decimal
equivalent:
(1101), = 1 x 23 + 1 x 22
+ 0 x 21+ 1 x 20
††††††††††††††††††† †††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††† †= 8 + 4 + 0 + 1 = (13)10
3. Convert (150)10† into
Binary, then convert that Binary number to Octal

4. Write short note on ISCII
ISCII is the system of handling the character
of Indian local languages. This as a 8-bit coding
system. Therefore it can handle 256 (2) characters.
†This system is formulated by the department of
Electronics in India in the year 1986-88 and recognized by Bureau of Indian
Standards (BIS). Now this coding system is integrated with Unicode.
5. Add a) -2210 +1510†††† b) 2010 +2510
(i)
-22
+ 15
The binary
equivalent of 22 is 00010110
|
††††††††††† Take 1ís complement ††††††††††† Add 1 to LSB ††††††††††† 2ís complement of -22 |
11101001 †††††††††††††††† 1 |
|
11101010 |
††††† †† †††††††† Binary addition of -22 and +15
|
Carry
bit†††††††††††† →†††††††† 111 510†††††††††††††††††††††† →††††††††††††† 1111 |
|
-710
(Result)†††† →†††† 11111001†††††††† |
(ii)
20
+ 25
Binary number for
20 = 00010100
Binary number for
25 = 00011001
|
Carry
bit†††††††††††† →††††††††††† 1 2510†††††††††††††††††††† →†††† 00011001 |
|
4510
(Result)†††† →††† 00101101 |
