Introduction
to C Programming
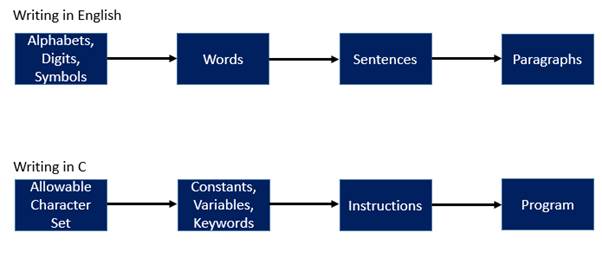
1) Analogy between C and common
English:
2) Parts of a general C program:
ü Pre-processor Commands
ü Functions
ü Variables
ü Statements &
Expressions
ü Comments

Let us look various
parts of the above program:
1.
The first line of the program #include <stdio.h> is a pre-processor command, which tells a C
compiler to include stdio.h file before going to
actual compilation.
2.
The next line int main() is the main function where program execution begins.
3.
The next line /*...*/ will be ignored by the
compiler and it has been put to add additional comments in the program. So such
lines are called comments in the program.
4.
The next line printf(...) is another
function available in C which causes the message "Hello, World!" to
be displayed on the screen.
5.
The next line return 0; terminates main() function and returns the value 0.
3) Tokens in C
A C program consists of various tokens and a token is either a
keyword, an identifier, a constant, a string literal, or a symbol. For example,
the following C statement consists of five tokens:
![]()
The individual tokens are:

Semicolons ;
In C program, the semicolon is a statement terminator. That
is, each individual statement must be ended with a semicolon. It indicates the
end of one logical entity.
Comments
Comments are like helping text in your C program and they are
ignored by the compiler. They start with /* and terminates with the characters
*/. You cannot have comments within comments and they do not occur within a
string or character literals.
Identifiers
A C identifier is a name used to identify a variable,
function, or any other user-defined item. An identifier starts with a letter A
to Z or a to z or an underscore _ followed by zero or
more letters, underscores, and digits (0 to 9).
C does not allow punctuation characters such as @, $, and %
within identifiers. C is a case sensitive programming language. Thus, Manpower
and manpower are two different identifiers in C.
Keywords
The following list shows the reserved words in C. These
reserved words may not be used as constant or variable or any other identifier
names. Below is the list of keywords in C.

3) Data-types in C
In the C programming language, data types refer to an
extensive system used for declaring variables or functions of different types.
The type of a variable determines how much space it occupies in storage and how
the bit pattern stored is interpreted.
The types in C can be classified as follows:
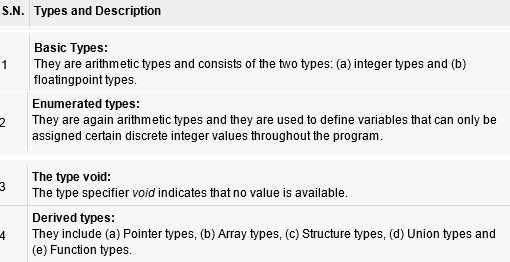
The array types and structure types are referred to
collectively as the aggregate types. The type of a function specifies the type
of the function's return value.
4)
Valid Numerical Values in C
Decimal Integer constant (base 10)
It consists of any combinations of digits taken from the set 0 through 9, preceded
by an optional – or + sign.
The first digit must be other than 0.
Embedded spaces, commas, and non-digit characters are
not permitted between digits.
Valid: 0
32767
-9999 -23
Invalid:
12,245
- Illegal character (,)
10 20
30 - Illegal character (blank
space)
Octal Integer Constant (base 8)
It consists of any combinations of digits taken from
the set 0 through 7.
If a constant contains two or more digits, the first
digit must be 0.
In programming, octal numbers are used.
Valid:
037
0 0435
Invalid:
0786
- Illegal digit 8
123
- Does not begin
with zero
01.2
- Illegal character
(.)
Hexadecimal integer constant
It consists of any combinations of digits taken from the set 0 through 7 and
also a through f (either uppercase or lowercase).
The letters a through f (or
A through F) represent the decimal quantities 10 through 15 respectively.
This constant must begin with either 0x or 0X.
In programming, hexadecimal numbers are used.
Valid Hexadecimal
Integer
Constant:
0x 0X1
0x7F
Invalid Hexadecimal Integer
Constant:
0xefg -
Illegal character g
123 -
Does not begin with 0x
5)
Rules for Constructing Variable Names
1. A
Variable name consists of any combination of alphabets, digits and underscores.
Avoid creating long variable name as it adds to your typing effort.
2. The
first character of the variable name must either be alphabet or underscore. It
should not start with the digit.
3. No
commas and blanks are allowed in the variable name.
4. No
special symbols other than underscore are allowed in the variable name.
5. No
C keywords are allowed