Selection and Repetition
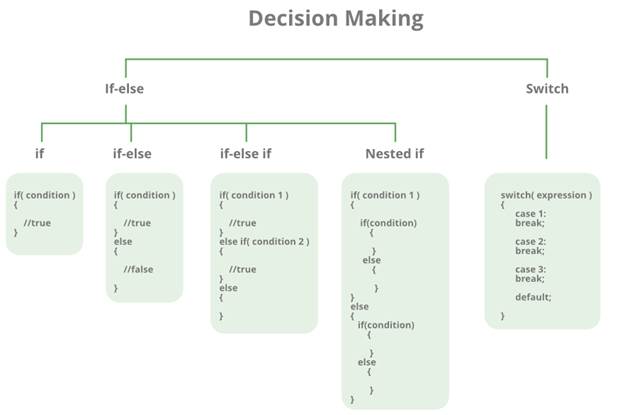
1) Conditional Statements/ Decision
Making Statements
In
the C programming language, the program execution flow is line by line from top
to bottom. That means the c program is executed line by line from the main
method. But this type of execution flow may not be suitable for all the program
solutions. Sometimes, we make some decisions or we may skip the execution of
one or more lines of code. Consider a situation, where we write a program to
check whether a student has passed or failed in a particular subject. Here, we
need to check whether the marks are greater than the pass marks or not. If
marks are greater, then we decide that the student has passed otherwise failed.
To solve such kind of problems in c we use the statements called decision
making statements.
Decision-making statements are the statements that are
used to verify a given condition and decide whether a block of statements gets
executed or not based on the condition result.
In
the c programming language, there are two decision-making statements they are
as follows.
1.
if statement
2.
switch statement
if statement in c
In
c, if statement is used to make decisions based on a condition. The if statement verifies the given condition and decides
whether a block of statements are executed or not based on the condition
result. In c, if statement is classified into four types as follows...
1.
Simple if statement
2.
if-else statement
3.
Nested if statement
4.
if-else-if statement (if-else ladder)
Simple if statement
Simple
if statement is used to verify the given condition and executes the block of
statements based on the condition result. The simple if statement evaluates
specified condition. If it is TRUE, it executes the next statement or block of
statements. If the condition is FALSE, it skips the execution of the next
statement or block of statements. The general syntax and execution flow of the
simple if statement is as follows.
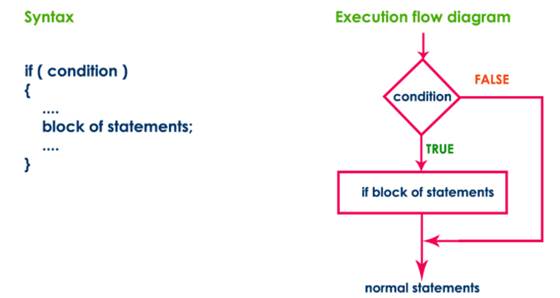
Simple
if statement is used when we have only one option that is executed or skipped
based on a condition.
if-else statement
The
if-else statement is used to verify the given condition and executes only one
out of the two blocks of statements based on the condition result. The if-else
statement evaluates the specified condition. If it is TRUE, it executes a block
of statements (True block). If the condition is FALSE, it executes another
block of statements (False block). The general syntax and execution flow of the
if-else statement is as follows.
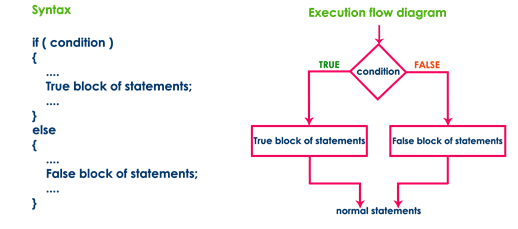
The
if-else statement is used when we have two options and only one option has to
be executed based on a condition result (TRUE or FALSE).
Nested if statement
Writing a if statement inside another if statement is called
nested if statement. The general syntax of the nested if statement is as
follows...
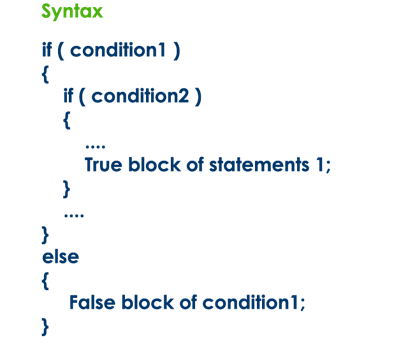
The nested if statement can
be defined using any combination of simple if & if-else statements.
if-else-if statement (if-else
ladder)
Writing a if statement inside else of an if statement is
called if-else-if statement. The general syntax of the if-else-if statement is
as follows...
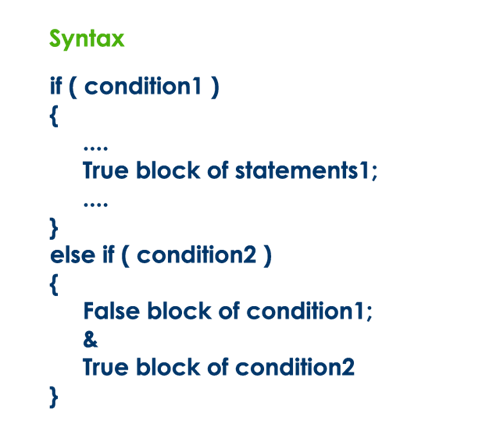
The if-else-if statement
can be defined using any combination of simple if & if-else statements.
MOST IMPORTANT POINTS TO BE
REMEMBERED
When we use a conditional
control statement like if statement, the condition might be an expression
evaluated to a numerical value, a variable or a direct numerical value. If
the expression value or direct value is zero the condition becomes FALSE
otherwise becomes TRUE.
To understand more consider
the following statements.
- if(10) - is TRUE
- if(x) - is FALSE if x
value is zero otherwise TRUE
- if(a+b) - is FALSE if a+b value is zero
otherwise TRUE
- if(a = 99) - is TRUE
because a value is non-zero
- if(10, 5, 0) - is FALSE
because it considers last value
- if(0) - is FALSE
- if(a=10, b=15, c=0) - is FALSE because last value is zero
'switch' statement in C
Consider
a situation in which we have many options out of which we need to select only
one option that is to be executed. Such kind of problems can be solved
using nested if statement. But as the number of options
increases, the complexity of the program also gets increased. This type of
problem can be solved very easily using a switch statement.
Using the switch statement, one can select only one option from more number of
options very easily. In the switch statement, we provide a value that is to be
compared with a value associated with each option. Whenever the given value
matches the value associated with an option, the execution starts from that
option. In the switch statement, every option is defined as a case.
The
switch statement has the following syntax and execution flow diagram.
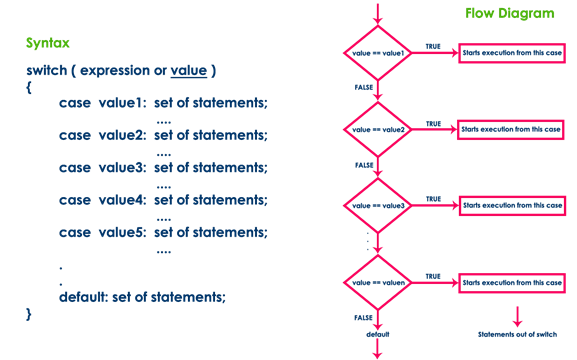
The
switch statement contains one or more cases and each case has a value
associated with it. At first switch statement compares the first case value
with the switchValue, if it gets matched the
execution starts from the first case. If it doesn't match the switch statement
compares the second case value with the switchValue
and if it is matched the execution starts from the second case. This process
continues until it finds a match. If no case value matches with the switchValue specified in the switch statement, then a special
case called default is executed.
When
a case value matches with the switchValue, the
execution starts from that particular case. This execution flow continues with
the next case statements also. To avoid this, we use the "break"
statement at the end of each case. That means the break statement
is used to terminate the switch statement. However, it is optional.
MOST IMPORTANT POINTS
TO BE REMEMBERED
When we use switch
statement, we must follow the following...
- Both switch and case are keywords
so they must be used only in lower case letters.
- The data type of case value and the value specified in the switch
statement must be the same.
- switch and case values must be either integer or character but not float
or string.
- A switch statement can contain any number of cases.
- The keyword case and its value must be superated with a white space.
- The case values need not be defined in sequence, they can be in any
order.
- The default case is optional and it can be defined
anywhere inside the switch statement.
- The switch value might be direct, a variable or an expression.
2) Conditional looping statements
Consider
a situation in which we execute a single statement or block of statements
repeatedly for the required number of times. Such kind of problems can be solved
using looping statements in C. For example, assume a situation
where we print a message 100 times. If we want to perform that task without
using looping statements, we have to either write 100 printf
statements or we have to write the same message 100 times in a single printf statement. Both are complex methods. The same task
can be performed very easily using looping statements.
The looping statements are used to execute a single
statement or block of statements repeatedly until the given condition is FALSE.
C
language provides three looping statements...
- while
statement
- do-while
statement
- for
statement
while Statement
The
while statement is used to execute a single statement or block of statements
repeatedly as long as the given condition is TRUE. The while statement is also
known as Entry control looping statement. The while statement has
the following syntax...
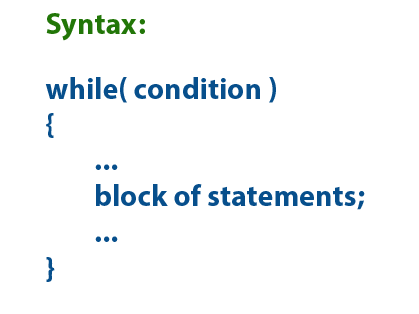
The
while statement has the following execution flow diagram...
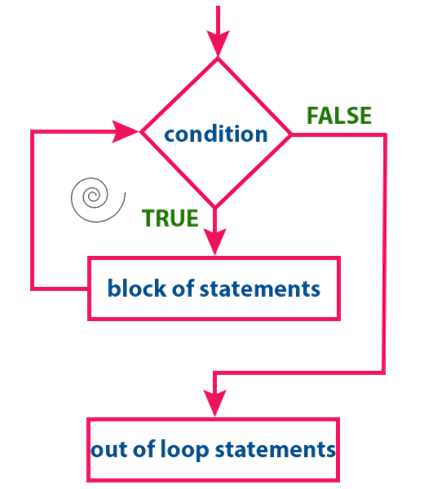
At first, the given
condition is evaluated. If the condition is TRUE, the single statement or block
of statements gets executed. Once the execution gets completed the condition is
evaluated again. If it is TRUE, again the same statements get executed. The
same process is repeated until the condition is evaluated to FALSE. Whenever
the condition is evaluated to FALSE, the execution control moves out of the
while block.
MOST IMPORTANT POINTS
TO BE REMEMBERED
When we use a while
statement, we must follow the following...
- while is a keyword so it must be used only in lower case letters.
- If the condition contains a variable, it must be assigned a value
before it is used.
- The value of the variable used in condition must be modified
according to the requirement inside the while block.
- In a while statement, the condition may be a direct integer value,
a variable or a condition.
- A while statement can be an empty statement.
'do-while' statement in
C
The do-while statement is
used to execute a single statement or block of statements repeatedly as long as
given the condition is TRUE. The do-while statement is also known as the Exit
control looping statement. The do-while statement has the following
syntax...

The do-while statement has
the following execution flow diagram...
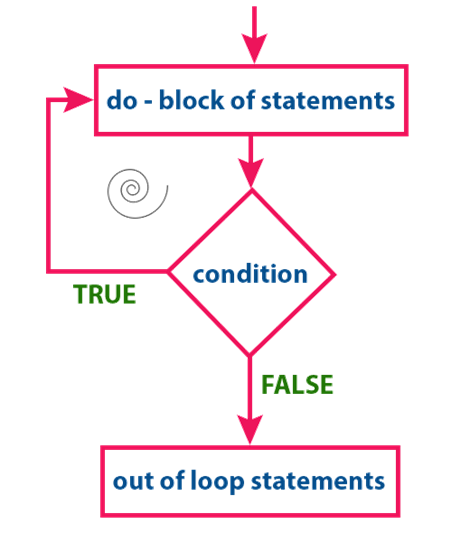
At first, the single
statement or block of statements which are defined in do block
are executed. After the execution of the do block, the given condition gets
evaluated. If the condition is evaluated to TRUE, the single statement or block
of statements of do block are executed again. Once the execution gets completed
again the condition is evaluated. If it is TRUE, again the same statements are
executed. The same process is repeated until the condition is evaluated to
FALSE. Whenever the condition is evaluated to FALSE, the execution control moves
out of the while block.
MOST IMPORTANT POINTS
TO BE REMEMBERED
When we use the do-while
statement, we must follow the following...
- Both do and while are keywords so
they must be used only in lower case letters.
- If the condition contains a variable, it must be assigned a value
before it is used.
- The value of the variable used in the condition must be modified
according to the requirement inside the do block.
- In a do-while statement, the condition may be a direct integer
value, a variable or a condition.
- A do-while statement can be an empty statement.
- In do-while, the block of statements is executed at least once.
'for' statement in C
The
for statement is used to
execute a single statement or a block of statements repeatedly as long as the
given condition is TRUE. The for statement has the
following syntax and execution flow diagram...
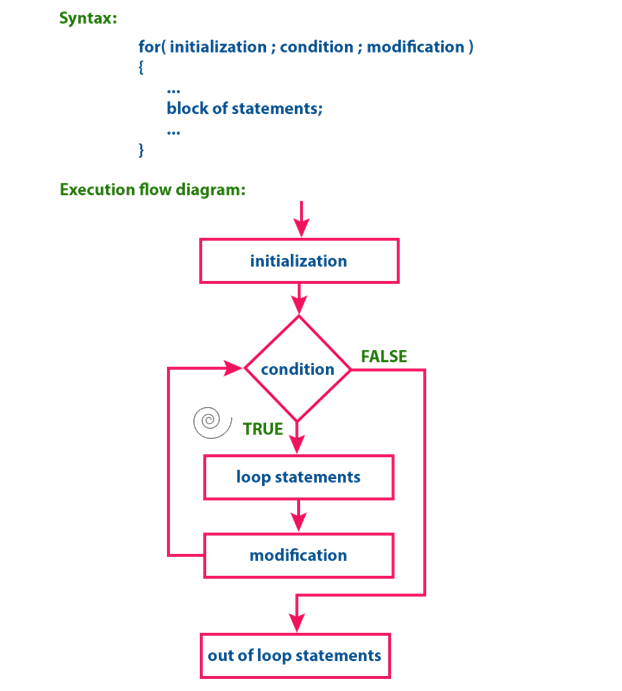
At
first, the for statement executes initialization followed
by condition evaluation. If the condition is evaluated to
TRUE, the single statement or block of statements of for statement are
executed. Once the execution gets completed, the modification statement
is executed and again the condition is evaluated. If it is TRUE, again the same
statements are executed. The same process is repeated until the condition is
evaluated to FALSE. Whenever the condition is evaluated to FALSE, the execution
control moves out of the for block.
MOST IMPORTANT POINTS
TO BE REMEMBERED
When we use for statement,
we must follow the following...
- for is a keyword so it must be used only in lower case letters.
- Every for statement must be provided with
initialization, condition, and modification (They can be empty but must be
separated with ";")
Ex: for ( ; ; ) or for ( ; condition ; modification ) or for ( ; condition ; ) - In for statement, the condition may be a direct integer value, a
variable or a condition.
- The for statement can be an empty statement.
3)
Unconditional control statement:
In c, there
are control statements that do not need any condition to control the program
execution flow. These control statements are called as unconditional
control statements. C programming language provides the following
unconditional control statements...
- break
- continue
- goto
The above three statements
do not need any condition to control the program execution flow.
break statement
In C, the break
statement is used to perform the following two things...
1.
break statement is
used to terminate the switch case statement
2.
break statement is also used to terminate looping
statements like while, do-while and for.
When a break statement
is encountered inside the switch case statement, the execution control moves
out of the switch statement directly.
When the break statement
is encountered inside the looping statement, the execution control moves out of
the looping statements. The break statement execution is as
shown in the following figure.
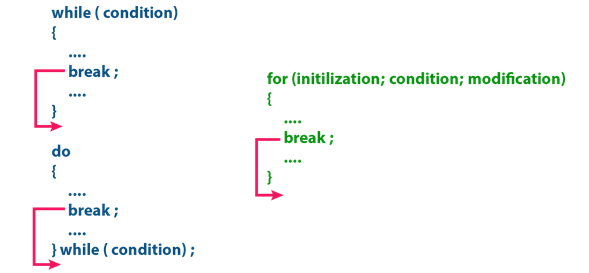
For example, consider the
following example program...
continue statement
The continue statement
is used to move the program execution control to the beginning of the looping statement.
When the continue statement is encountered in a looping
statement, the execution control skips the rest of the statements in the
looping block and directly jumps to the beginning of the loop. The continue statement
can be used with looping statements like while, do-while and for.
When we use continue statement
with while and do-while statements the
execution control directly jumps to the condition. When we use continue statement
with for statement the execution control directly jumps to the
modification portion (increment/decrement/any modification) of the for loop. The continue statement
execution is as shown in the following figure.
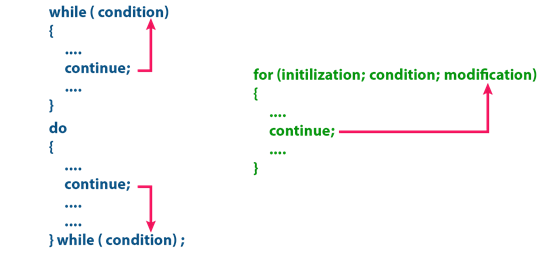
goto statement
The goto statement is used to jump from one line to
another line in the program. Using goto statement
we can jump from top to bottom or bottom to top. To jump from one line to
another line, the goto statement requires a label.
Label is a name given to the instruction or line in the program. When we use
a goto statement in the program, the
execution control directly jumps to the line with the specified label.
MOST IMPORTANT POINTS
TO BE REMEMBERED
When we use break, continue
and goto statements, we must follow the following...
- The break is a keyword so it must be used only in
lower case letters.
- The break statement can not
be used with if statement.
- The break statement can be used only in switch
case and looping statements.
- The break statement can be used with if statement,
only if that if statement is written inside the switch
case or looping statements.
- The continue is a keyword so it must be used only in
lower case letters.
- The continue statement is used only within looping
statements.
- The continue statement can be used with if statement,
only if that if statement is written inside the looping statements.
- The goto is a keyword so
it must be used only in lower case letters.
- The goto statement must
require a label.
- The goto statement can
be used with any statement like if, switch, while, do-while, and for, etc.