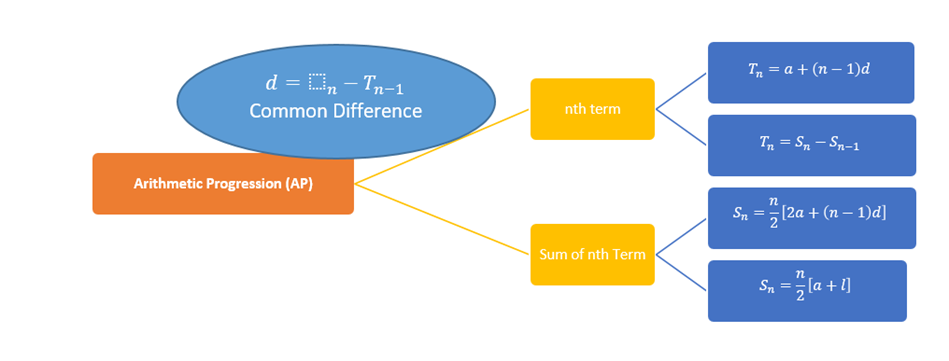
Arithmetic progression
Definition:
·
In nature, many things follow a
certain pattern or Sequence.

·
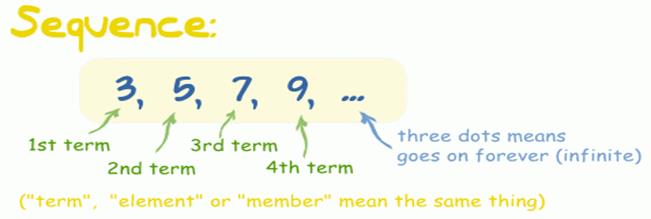
Sequence: A Sequence is a set of things (usually
numbers) that are in order.
·
Each number in
the sequence is called a term.
·
Some more common sequence example,

Arithmetic Progression (AP):
·
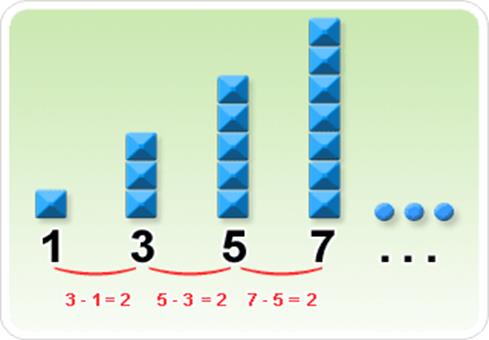
An Arithmetic Progression (AP)
or Arithmetic Sequence is a sequence of numbers such that the difference
between the consecutive terms is constant.
·
In General, we could write an
arithmetic sequence like this,
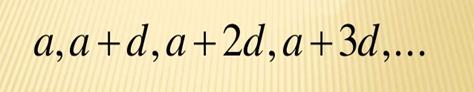
·
Initial
term/first term: In an
arithmetic progression, the first number in the series is called the first term
/initial term, here a is the first term.
·
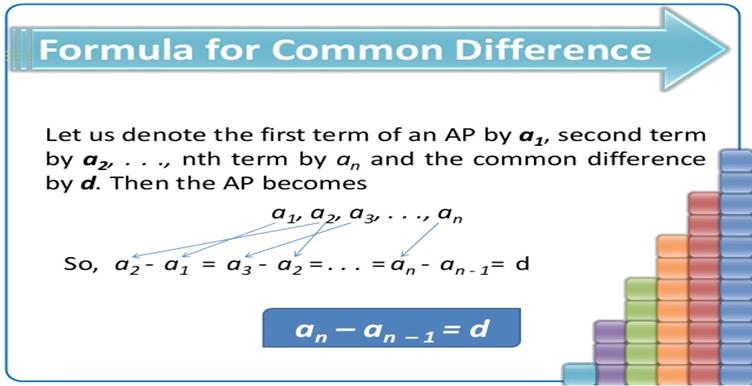
Common
difference: The
value by which consecutive terms increase or decrease is called the common difference.
Here d is the difference between the
terms.
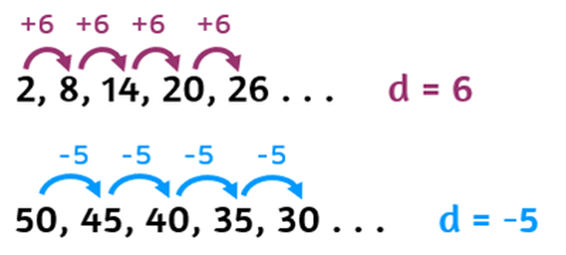
·
If the common difference is positive, then the members
(terms) will grow towards positive infinity.
·
If the common difference is negative, then the members
(terms) will grow towards negative infinity.

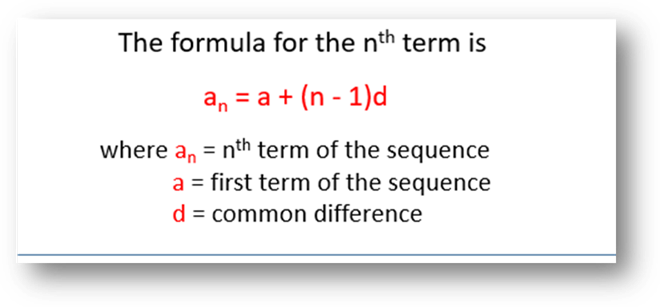
nth Term of an AP:
·
The formula for finding the
n-th term of an AP is,
·
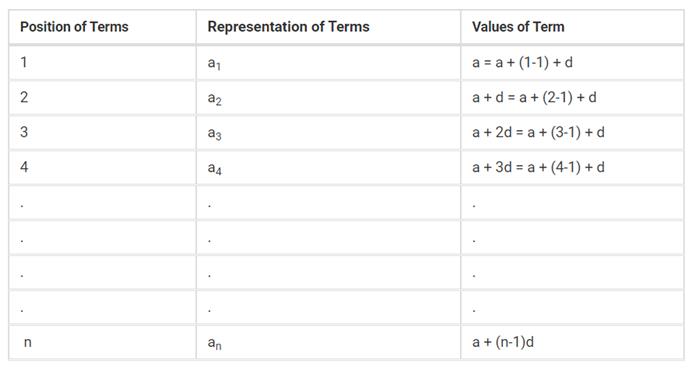
Consider an AP to be: a1, a2, a3,
……………., an,
·
Example on finding nth term,

Arithmetic Progression Sum
Formula:
·
For an AP, the sum
of the first n terms can be calculated if the first term and the total terms
are known or when first and last terms are given, The formula for the
arithmetic progression sum is,

· Proof:
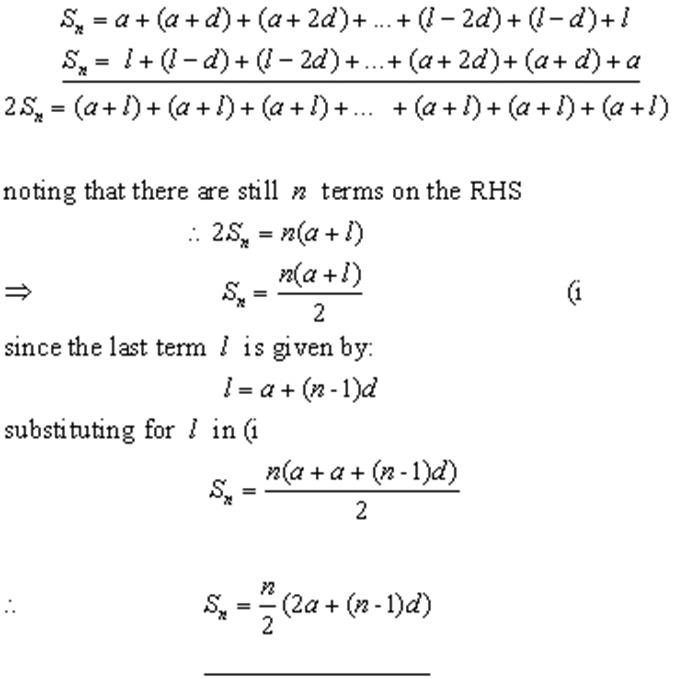
· Special Formula I:
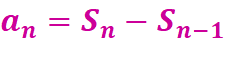
Proof:

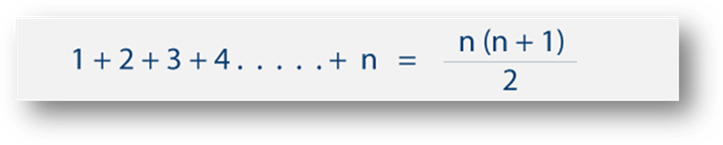
· Special Formulas: Sum of first n natural
numbers,
·
Example on Sum of AP,

Summary: