Functions
Exercises Problems
1)
Find
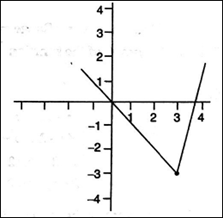
the domain and range of f(x) = |2x - 3| - 3
Solution:
Given, f(x) = |2x - 3| - 3.
The domain of the expression in all
real number except where the expression in undefined. In this case, there is
not real number that makes the expression undefined
Therefore,
Domain of f = (- ?, ?) = R
The absolute value of expression has
a ‘V’ shape. The range of a positive absolute value expression starts at its
vertex and extends to infinity.
Range of f = (- 3, ꚙ) or {y/y ≥ - 3}
2)
Draw
the graph of the Greatest Integer Function.
Solution:
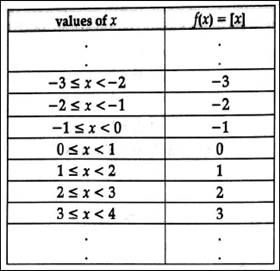 The greatest integer function is denoted
by y = [x]. For all real numbers, x, the greatest integer function returns the
largest integer less than or equal to x.
The greatest integer function is denoted
by y = [x]. For all real numbers, x, the greatest integer function returns the
largest integer less than or equal to x.
3)
Draw
the graph of constant function f: R → R; f(x) = 2Ɐ
x ϵ
R. Also, find its domain and range.
Solution:
Given,
f: R → R;
f(x) = 2Ɐ x ϵ R
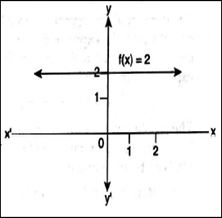
Domain
= R and range = {2}
4)
Find
the domain and range of the following
real function : f(x) = ![]()
Solution:
Given,
f(x) = ![]()
Domain:
We
know that f(x) is defined when x – 2 ≠ 0
i.e.,
x ≠
2
Therefore, The domain is all values
of x that makes the expression defined i.e.,
Domain of f = R – (2)
Range:
Let y = f(x)
Therefore
y = ![]()
Y(x
– 2) = x + 1
X(y
– 1) = 2y + 1
x = ![]()
Since, x is defined, when y – 1 ≠
0 i.e., y ≠
1
Therefore, Range of f = R – {1}.
5)
Find
the domain and range of the following
real function : f(x) = ![]()
Solution:
Given, f(x) = ![]()
Domain: Clearly, f(x) is defined for
all x ←
R except x = 1
Therefore, Domain of f = R – {1}
Range:
Now, f(x) = ![]() = 1, when x > 1
= 1, when x > 1
And f(x) = ![]() = - 1, when x < 1
= - 1, when x < 1
Therefore, Range of f = {-1, 1}
6)
Find
the domain and range of the following
real function : f(x) = ![]()
Solution.
Given, f(x) = ![]()
Domain: Clearly, f(x) is defined for
all x ϵ
R expect x = 3
Therefore, Domain of f = R – {3} = (- ꚙ, 3), ꓴ
(3, ꚙ)
Range:
Let y = f(x)
Therefore, y = ![]()
ð y = x + 3
It follows from the above relation
that y takes all real values except 6 when x takes values in the set R – {3}
Therefore, Range of f = R – {6}
7)
Find
the domain and range of the following
real function : f(x) = ![]()
Solution:
Given, f(x) = ![]()
Domain:
Clearly, f(x) is defined for all x ϵ R except x = 4
Therefore,
Domain of f = R – {4} = (- ꚙ, 4), U (4, ꚙ)
Range:
Let y
= f(x)
ð y = ![]()
ð y = ![]() = - 1
= - 1
ð Therefore, Range
of f = {- 1}
8)
Find
the domain and range of the following real
function : f(x) = 1 - |x - 3|
Solution:
Given, f(x) =
1 - |x - 3|
Domain: We observe that f(x) is
defined for all x ϵ R
Therefore, Domain of f = R
Range: Now,
0 ≤ |x
- 3| < ꚙ Ɐ x ϵ R
ð - ꚙ < - |x - 3| ≤ 0 Ɐ x ϵ R
ð - ꚙ < 1 - |Ɐ - 3| ≤ 1 Ɐ x ϵ R
ð - ꚙ < f(x) ≤ 1 Ɐ x ϵ R
Hence,
Range of f = (- ꚙ,
1)
9)
Determine
a quadratic function (f) is defined by f(x) = ax² + bx + c. If f(0) = 6, f(2) = 1, f(-3) = 6.
Solution:
Given,
f(x) = ax²
+ bx + c.
At x = 0,
f (0) = 6(given)
Therefore,
a x 0 + b x 0 + c = 6
Therefore,
c= 6 …. (i)
At
x = 2, f (2) = 1(given)
Therefore,
a (2)²
+ b (2) + c = 1
ð 4a
+ 2b + 6 = 1 (using(i))
ð 4a
+ 2b = - 5 (ii)
At x = - 3, f (-3) = 6
Therefore, a (-3)²
+ b (-3) + c = 6
ð 9a
– 3b + 6 = 6 (using(i))
ð 9a
– 3b = 0 ….(iii)
On solving eqs. (ii) And (iii), we
get
a = - ![]() and a = -
and a = - ![]()
Therefore, required quadratic
function (f) = ![]() x²
+
x²
+ ![]() x
+ 6
x
+ 6
10)
If
[x] denotes the greatest integer function. Find the solution set of
equation.[x]² - 5[x] + 6 = 0
Solution:
Given,
equation, [x]²
- 5[x] +6 = 0
[x]² - 3[x] – 2[x] + 6 = 0
[x]([x] – 3) – 2([x] – 3) = 0
([x] – 3) ([x] – 2) = 0
[x] = 2 or [x] = 3
2 ≤ x < 3 or 3 ≤
x < 4
Hence,
x ϵ
[2, 4]