Algebra
There
are so many branches of mathematics-
·
The study of numbers is called Arithmetic.
·
The study of shapes is called Geometry.
·
The study to use the letters and symbols in
mathematics is called Algebra.
Algebra
Algebra
is a part of mathematics in which the letter and symbols are used to represent
numbers in equations. It helps us to study about unknown quantities.
Matchstick Patterns
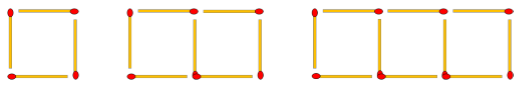
No. of
matchsticks used to make 1st square = 4
No. of
matchsticks used to make 2nd square = 7
No. of
matchsticks used to make 3rd square = 10
So,
the pattern that we observe here is 3n + 1
With
this pattern, we can easily find the number of matchsticks required in any
number of squares.
Example
How
many matchsticks will be used in the 50th figure?
Solution
3n + 1
3 × 50
+ 1
= 151
matchsticks
The Idea of a Variable
Variable
refers to the unknown quantities that can change or vary and are represented
using the lowercase letter of the English alphabets.
One
such example of the same is the rule that we used in the matchstick pattern
3n + 1
Here
the value of n is unknown and it can vary from time to time.
More Examples of Variables
·
We can use any letter as a variable, but only
lowercase English alphabets.
·
Numbers cannot be used for the variable as they
have a fixed value.
·
They can also help in solving some other problems.
Example:
1
Karan
wanted to buy story books from a bookstall. She wanted to buy 3 books for
herself, 2 for her brother and 4 for 2 of her friends. Each book cost Rs.15.how
much money she should pay to the shopkeeper?
Solution:
Cost
of 1 book = Rs.15
We
need to find the cost of 9 books.
|
No. of notebooks |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
. |
a |
..... |
|
Total cost |
15 |
30 |
45 |
60 |
. |
15 a |
. |
In the
current situation, a (its a variable) stands for 9
Therefore,
Cost
of 9 books = 15 × 9
=
135
Therefore
Karan needs to pay Rs.135 to the shopkeeper of the bookstall.
The
variable and constant not only multiply with each other but also can be added
or subtracted, based on the situation.
Example:
2
Manu
has 2 erasers more than Tanu. Form an expression for
the statement.
Solution
1
Erasers
that Tanu have can be represented using a variable
(x)
Erasers
that Manu have = erasers that Tanu have + 2
Erasers
with Manu = x + 2
Solution
2
Erasers
that Manu have can be represented using a variable (y)
Erasers
that Tanu has = erasers that Manu have - 2
Erasers
with Tanu = y - 2
Use of Variables in Common Rules (Geometry)
1. Perimeter of Square
The
perimeter of a square = Sum of all sides
= 4 ×
side
= 4s
Thus,
p = 4s
Here s is variable, so the perimeter changes as the value
of side change.
2. Perimeter of Rectangle
Perimeter
of rectangle = 2(length + breadth)
= 2 (l
+ b) or 2l + 2b
Thus,
p + 2 × (l + b) or 2l + 2b
Where,
l and b are variable and the value of perimeter changes with the change in l
and b.
Use of Variables in Common Rules (Arithmetic)
1. Commutativity of Addition
5 + 4
= 9
4 + 5
= 9
Thus,
5 + 4 = 4 + 5
This
is the commutative property of addition of the numbers, in
which the result remains the same even if we interchanged the numbers.
a + b
= b + a
Here, a and b are different variables.
Example
a = 16
and b = 20
According
to commutative property
16 +
20 = 20 + 16
36 =
36
2. Commutativity of Multiplication
8 × 2
= 16
2 × 8
= 16
Thus,
8 × 2 = 2 × 8
This
is the commutative property of multiplication, in which the result remains the
same even if we interchange the numbers.
a × b = b × a
Here, a and b are different variables.
Example
18 ×12
= 216, 12 ×18 = 216
Thus,
18 × 12 = 12 × 18
3. Distributivity of Numbers
6 × 32
It is
a complex sum but there is an easy way to solve it. It is known as the distributivity of multiplication over the
addition of numbers.
6 ×
(30 + 2)
= 180
+ 12
= 192
Thus,
6 × 32 = 192
A × (b
+ c) = a × b + a × c
Here,
a, b and c are different variables.
4. Associativity of Addition
This
property states that the result of the numbers added will remain same
regardless of their grouping.
(a +
b) + c = a + (b + c)
Example
(4 +
2) + 7 = 4 + (2 + 7)
6 + 7
= 4 + 9
13 =
13
Expressions
Arithmetic
expressions may use numbers and all operations like addition, subtraction,
multiplication and division
Example
2 + (9
3), (4 × 6) 8 etc
(4 ×
6) 8 = 24 8
= 16
Expressions
with variable
We can
make expressions using variables like
2m, 5
+ t etc
..
An
expression containing variable/s cannot be analyzed
until its value is given.
Example
Find
3x 12 if x = 6
Solution
(3 ×
6) 12
= 18
12
= 5
Thus,
3x
12 = 5
Formation of Expressions
|
Statement |
Expression |
|
y subtracted from 12 |
12 - y |
|
x multiplied by 6 |
6x |
|
t Multiplied by 4,
and then subtract 5 from the product. |
4t -
5 |
Practical use of Expressions
Example
3 boys
go to the theatre. The cost of the ticket and popcorn is $33 and $15
respectively. What is the cost per person?
Solution
Lets
say,
x =
cost of ticket per person
y =
cost of popcorn/person
Total
cost of the movie (ticket + popcorn) per person = x + y
Total
cost of ticket + popcorn for 3 boys = 3(x + y)
= 3
(33 + 15)
= 3
(48)
= 144
Hence
the total cost of movie ticket and popcorn for 3 boys is $144.
Equation
If we
use the equal sign between two expressions then they form an equation.
An
equation satisfies only for a particular value of the variable.
The
equal sign says that the LHS is equal to the RHS and the value of a variable
which makes them equal is the only solution of that equation.
Example
3 + 2x
= 13
5m 7
= 3
p/6 = 18
If there
is the greater then or less than sign instead of the equal sign then that
statement is not an equation.
Some examples
which are not an equation
23 +
6x > 8
6f 3
< 24
The Solution of an Equation
The
value of the variable which satisfies the equation is the solution to that
equation. To check whether the particular value is the solution or not, we have
to check that the LHS must be equal to the RHS with that value of the variable.
Trial and Error Method
To
find the solution of the equation, we use the trial and error method.
Example
Find
the value of x in the equation 25 x = 15.
Solution
Here
we have to check for some values which we feel can be the solution by putting
the value of the variable x and check for LHS = RHS.
Lets
take x = 5
25 5
= 15
20
≠ 15
So x =
5 is not the solution of that equation.
Lets
take x = 10
25
10 = 15
15 =
15
LHS =
RHS
Hence,
x = 10 is the solution of that equation.