Understanding Elementary
Shapes
Line and Angles:
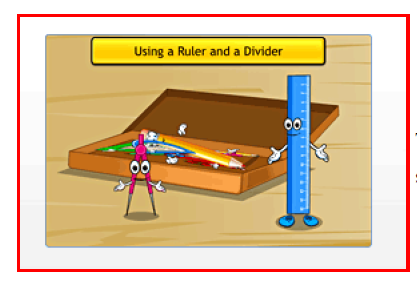
The distance between the endpoints of a line segment is the length
of the line segment.
Length of a
line segment:
The distance between the endpoints of a line segment is the
length of the line segment. The length of a line segment can be measured
accurately using a ruler and a divider.
Complete angle:
An angle of
measure 360° is
called a complete angle.
One quadrant = ¼ (Complete angle) = 1/4 x 360°90° = Two quadrants = 1/2
(Complete angle) = 1/2 x 360° = 180°
Three quadrants = 3/4 (Complete angle) = 3/4 x 360° = 270°
Right angle:
An angle that measures 90° is called a right
angle. A right angle makes a quarter revolutions.
Straight angle:
An angle that measures 180° is called a straight angle. A
straight angle makes a half revolution.
Acute angle:
An angle that measures less than 90° is called an acute
angle.
Obtuse angle:
An angle that measures more than 90° and
less than 180° is called an obtuse angle.
Reflex angle:
An angle that measures more than 180° is
called a reflex angle.
Intersecting lines:
Two lines that meet each other at a single point are
called intersecting lines.
Perpendicular lines:
Two lines that intersect each other at right angles are said
to be perpendicular to each other.
Bisector of a line segment:
A bisector of a line segment is a line that divides the
line segment into two equal parts.
Perpendicular bisector of a
line segment:
The perpendicular line that divides a line segment into
two equal parts is called the perpendicular bisector of the line segment.
Two Dimensional Figures
The closed figure formed by joining three line segments
end-to-end is called a triangle. Each line segment forms a side of the
triangle.
Scalene Triangle:
A triangle is called a scalene triangle if all the three
sides are of unequal length.
Isosceles Triangles:
A triangle is called an isosceles triangle if two of its
sides are of equal length.
Equilateral Triangle:
A triangle is said to be an equilateral triangle if the
lengths of all of its sides are equal.
Acute-Angled Triangle:
If all the angles of a triangle are less than 90°, then
the triangle is called an acute-angled triangle.
Right-Angled triangle:
If one of the angles in a triangle is a right
angle, then the triangle is called a right-angled triangle.
Obtuse-Angled Triangle:
If one of the angles in a triangle is an obtuse angle,
then the triangle is called an obtuse-angled triangle.
Parallelogram:
A parallelogram is a four-sided figure in which the opposite
sides are parallel to each other and are of equal length. In a parallelogram,
the diagonals need not be equal in length.
Rectangle:
A rectangle is a type of parallelogram that has opposite
sides equal in length and parallel to each other. Its diagonals are equal in
length. A rectangle has four
right angles.
Square:
A square is a type of parallelogram in which all the four
sides are equal in length. Its diagonals are equal in length. A square has four
right angles.
Rhombus:
In a rhombus, all the sides are equal in length, and the opposite sides are
parallel to each other. Its diagonals are not equal in length. Also, the
opposite angles are equal to each other.
Trapezium:
A trapezium has one pair of sides parallel to each other.
The other two sides are not parallel to each other.
Polygon:
A polygon is a closed figure with three or more than three
sides.
Three Dimensional Shapes

Solid figures have three dimensions - length, breadth and
height.
Eg: A ball, a brick, an ice
cream cone and a can.
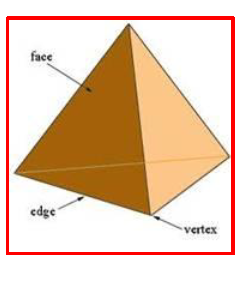
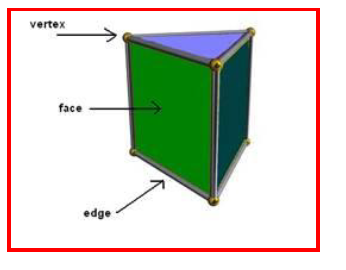
Face
The flat surface of a solid shape is called a face.
Edge
An edge is a line segment two faces of a solid shape meet.
Vertex
A vertex of a solid shape is a point where three or more
edges meet. A cuboid has 6
faces, 12 edges and 8 vertices. Prisms and pyramids are named after their
bases. The base of a prism can be of any polygonal shape.
There are 5
faces, 9 edges and 6 vertices in a
Triangular prism
There are 4 faces, 6 edges and 4 vertices in
a triangular pyramid.