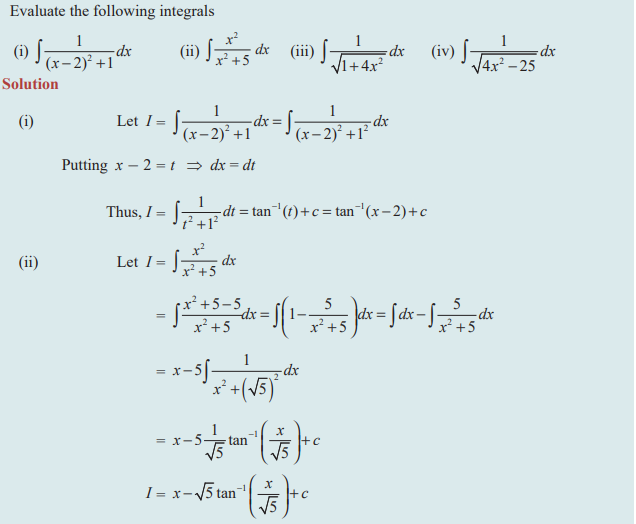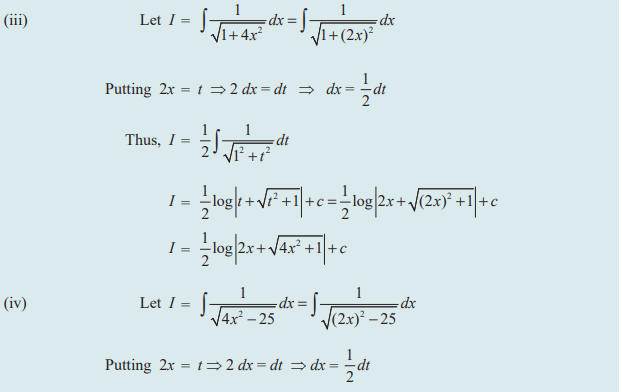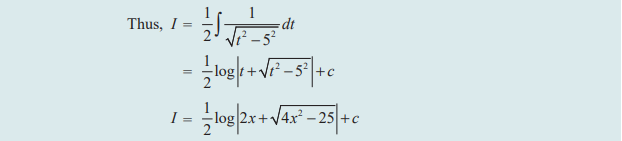INTEGRAL CALCULUS
Ø An integral assigns
numbers to functions in a way that can describe displacement, area, volume, and
other concepts that arise by combining infinitesimal data.
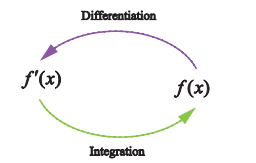
Ø Integration is one
of the two main operations of calculus, with its inverse operation,
differentiation, being the other.
Ø Calculus
deals principally with two geometric problems.
(i) The problem of finding SLOPE of the tangent line to the
curve, is studied by the limiting process known as differentiation and
(ii)
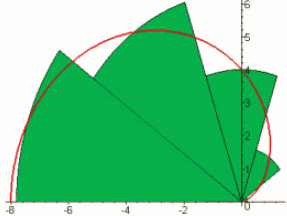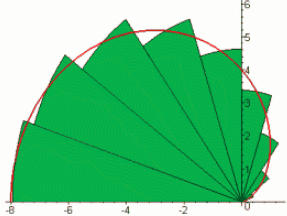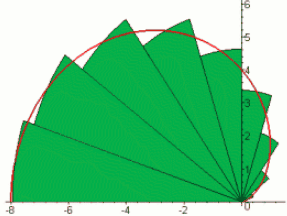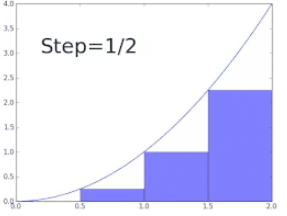
Problem of finding the AREA of a region under a curve is studied by another
limiting process called Integration.
Newton-Leibnitz
Integral:
Ø Integral
calculus is mainly divided into indefinite integrals and definite integrals.
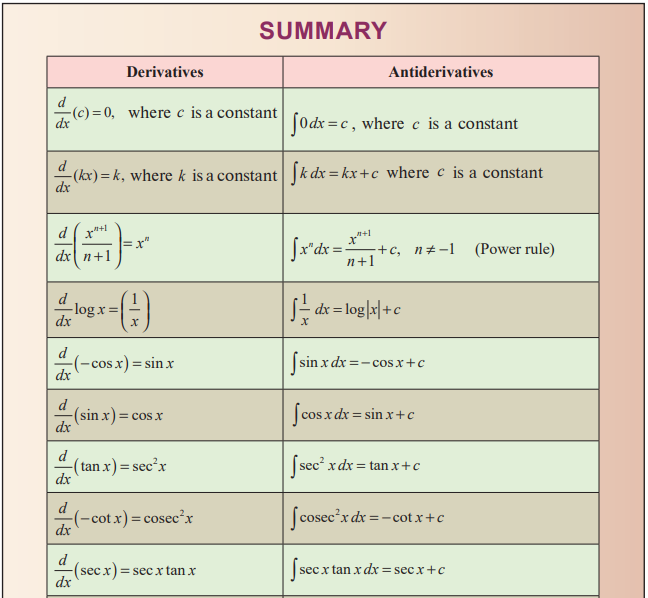
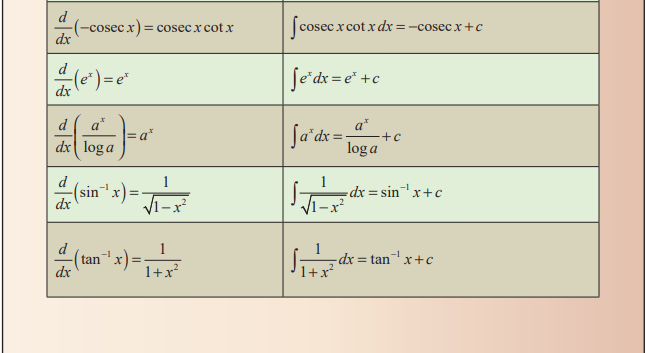
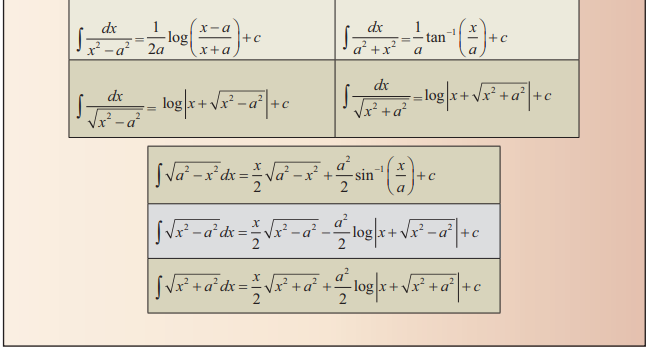
Basic
Rules of Integration:
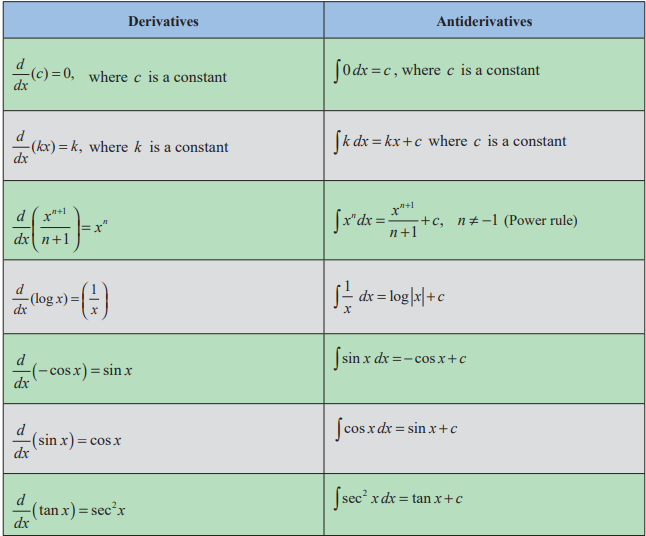
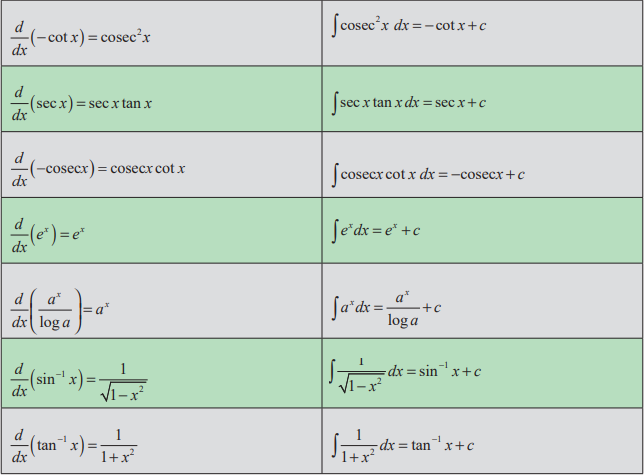
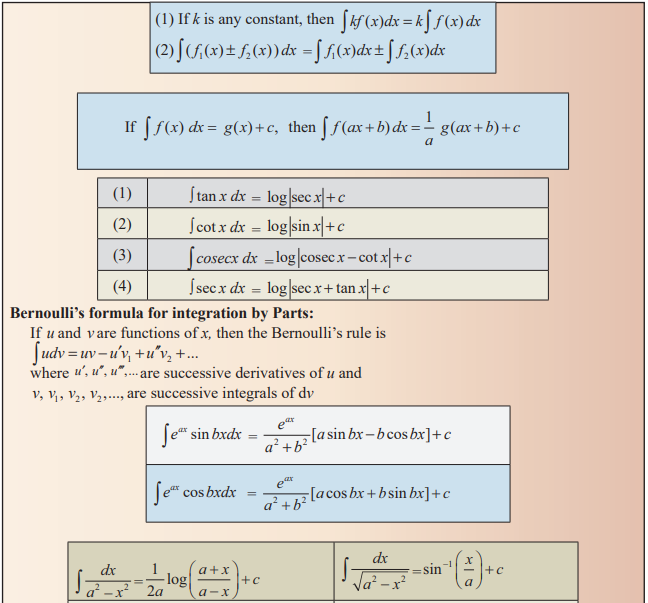
Methods
of Integration:
(1)
Integration by decomposition into sum or difference.
(2)
Integration by substitution.
(3)
Integration by parts
(4)
Integration by successive reduction.
PROBLEMS
Question 1 :
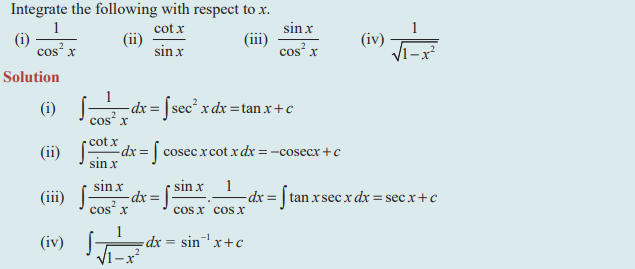
Question 2 :
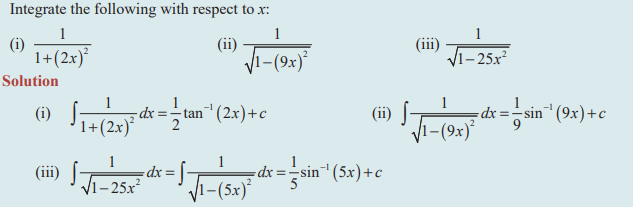
Question 3 :
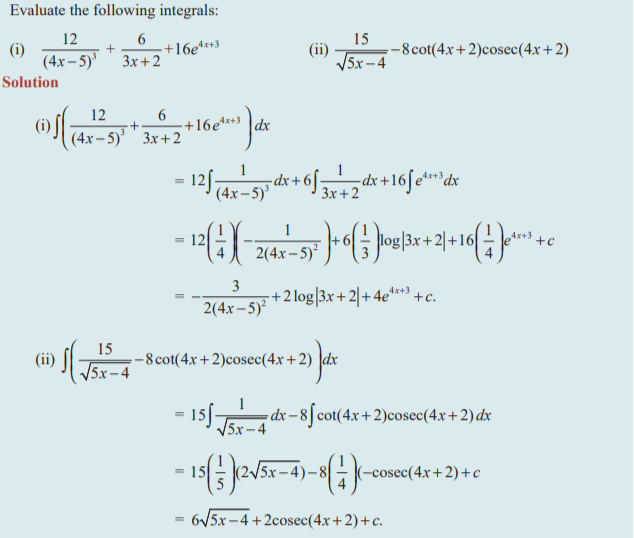
Question 4 :

Question 5 :
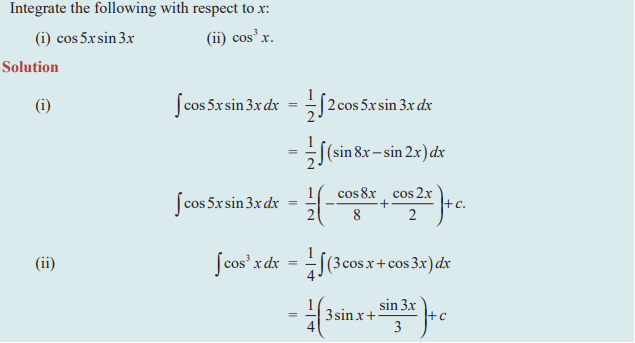
Question 6 :

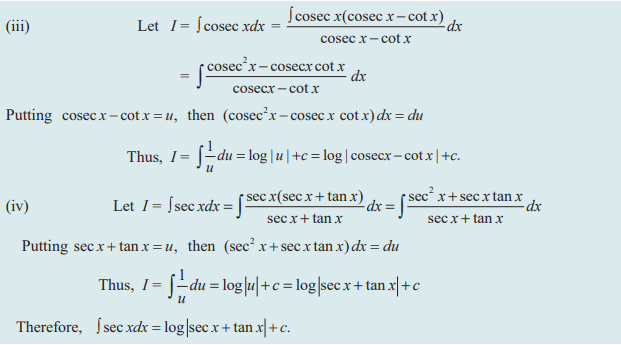
Question 7 :
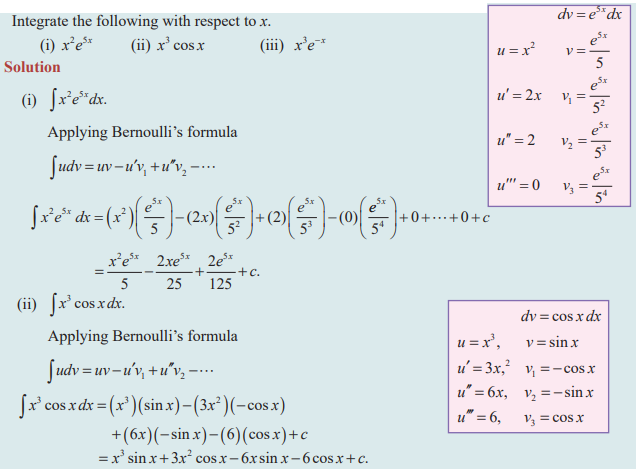
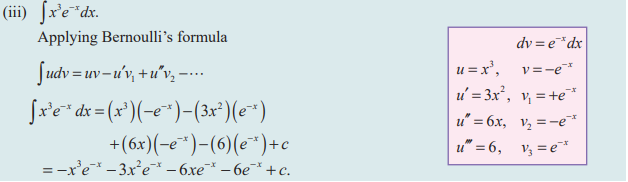
Question 8 :