DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS - LIMITS AND CONTINUITY
Ø Calculus
is about rates of change. Rates of change occur in all the sciences.
Ø Calculus
is the mathematics of ratio of change of quantities.
Ø It is
also the mathematics of tangent lines, slopes, areas, volumes, arc lengths,
centroids, curvatures and a variety of other concepts that have enabled
scientists, engineers and economists to model real-life situations.
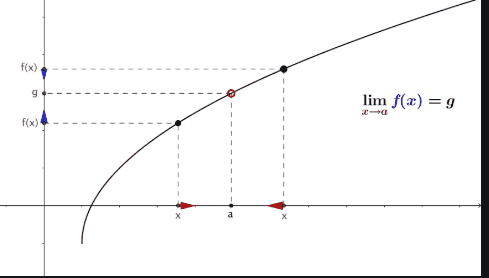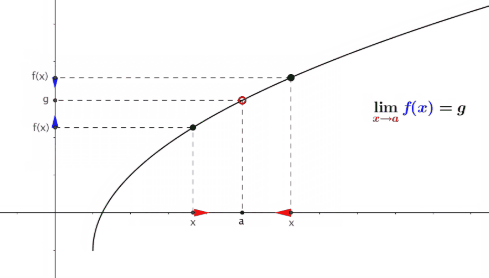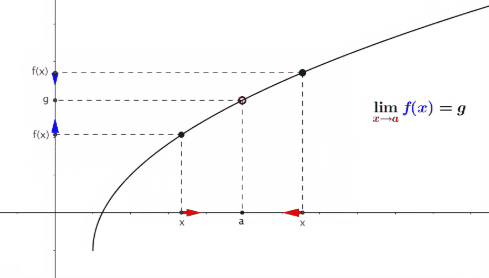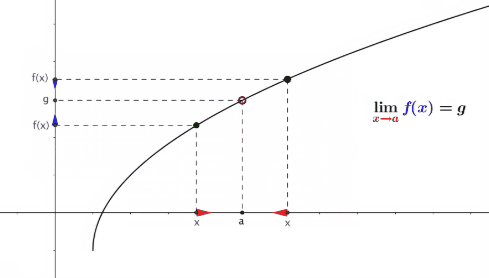
Limits:
Ø A
limit is the value that a function "approaches" as the input
"approaches" some value.
Ø Limits
are essential to calculus and are used to define continuity, derivatives, and
integrals.

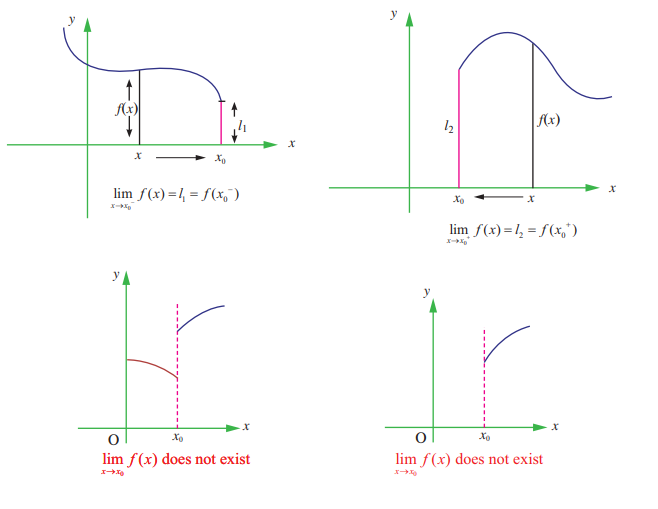
One sided limits:
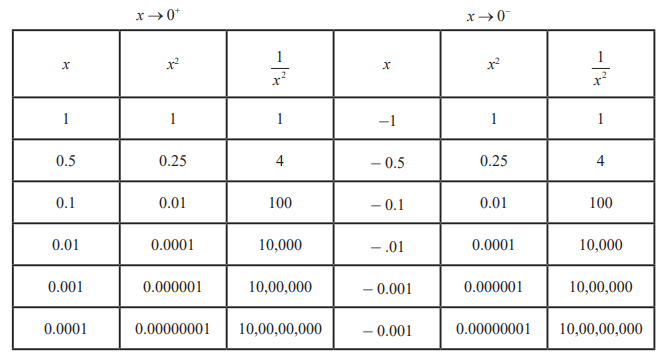
Infinite limits and
limits at infinity:
Continuity:
Ø One of the chief features in the behaviour of
functions is the property known as continuity.
Ø It reflects mathematically the general trait
of many phenomena observed by us in nature.
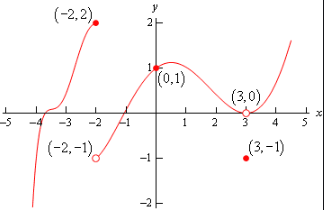
PROBLEMS
Question 1:
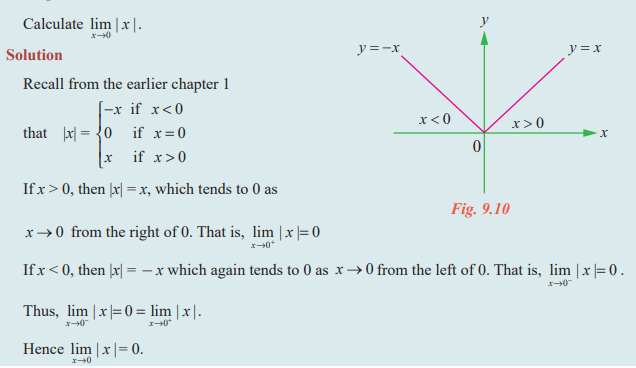
Question 2:
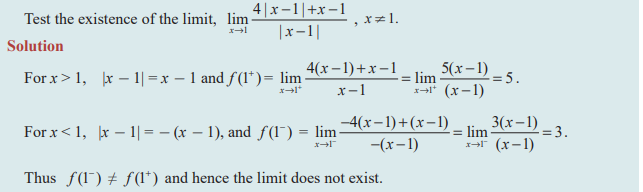
Question 3:
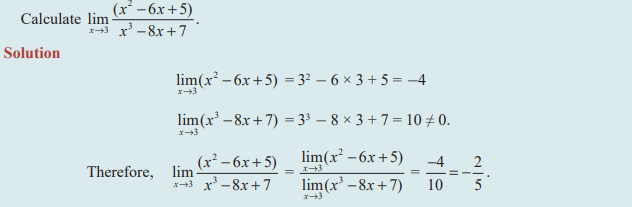
Question 4:
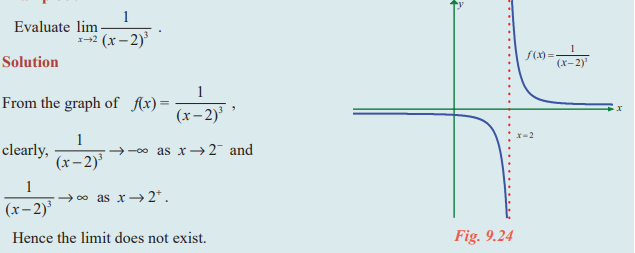
Question 5:
Question 6:
SUMMARY