Phylum – Arthropoda
and Phylum – Mollusca
Phylum – Arthropoda:
·
This is the largest
phylum of Animalia which includes insects.
·
Over two-thirds of
all named species on earth are arthropods.
·
They have
organ-system level of organisation.
·
They are bilaterally
symmetrical, triploblastic, segmented and coelomate animals.
·
The body of
arthropods is covered by chitinous exoskeleton.
·
The body consists of
head, thorax and abdomen. They have jointed appendages (arthros-joint,
poda-appendages).
·
Respiratory organs
are gills, book gills, book lungs or tracheal system.
·
Circulatory system is
of open type. Sensory organs like antennae, eyes (compound and simple), statocysts or balance organs are present.
·
They are mostly
dioecious. Fertilisation is usually internal. They are mostly oviparous.
Development may be direct or indirect.
·
Examples:
Economically important insects – Apis (Honey bee), Bombyx (Silkworm), Laccifer (Lac
insect) Vectors – Anopheles, Culex and Aedes (Mosquitoes) Gregarious pest – Locusta
(Locust) Living fossil – Limulus (King crab).
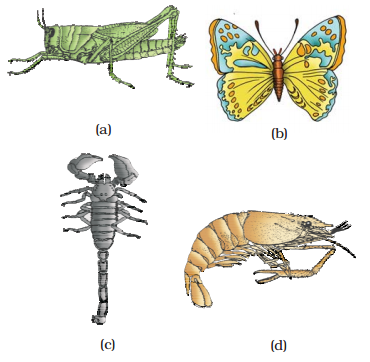
Examples of Arthropoda : (a) Locust (b) Butterfly (c) Scorpion (d) Prawn
Phylum – Mollusca:
·
This is the second
largest animal phylum.
·
Molluscs are
terrestrial or aquatic (marine or fresh water) having an organ-system level of
organisation.
·
They are bilaterally
symmetrical, triploblastic and coelomate animals.
·
Body is covered by a
calcareous shell and is unsegmented with a distinct head, muscular foot and
visceral hump.
·
A soft and spongy
layer of skin forms a mantle over the visceral hump.
·
The space between the
hump and the mantle is called the mantle cavity in which feather like gills are
present.
·
They have respiratory
and excretory functions.
·
The anterior head
region has sensory tentacles.
·
The mouth contains a
file-like rasping organ for feeding, called radula.
·
They are usually
dioecious and oviparous with indirect development.
·
Examples: Pila (Apple
snail), Pinctada (Pearl oyster), Sepia (Cuttlefish), Loligo (Squid), Octopus (Devil fish), Aplysia
(Seahare), Dentalium (Tusk
shell) and Chaetopleura (Chiton).
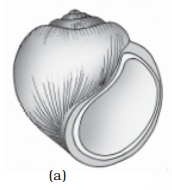

Examples of Mollusca : (a) Pila (b) Octopus