Skeletal System
·
Skeletal system consists of a framework of bones and a few
cartilages. This system has a significant role in movement shown by the body.
·
Bone and cartilage are specialised
connective tissues.
·
Bones has a very hard matrix due to calcium salts in it and
the cartilages has slightly pliable matrix due to chondroitin salts.
·
In human beings, this system is made up of 206 bones and a
few cartilages. It is grouped into two principal divisions –
a) The axial
b) The appendicular
skeleton
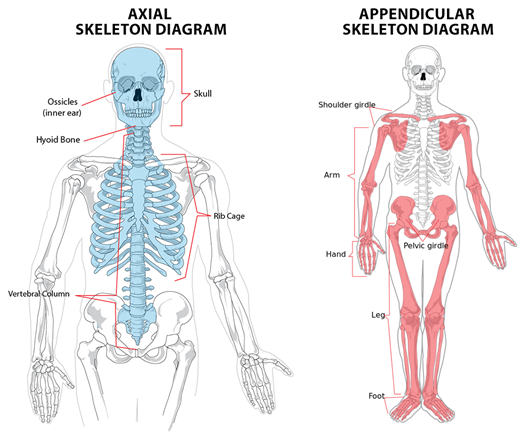
Axial Skeleton:
Axial skeleton comprises 80 bones
distributed along the main axis of the body.
·
The skull
·
Vertebral column
·
Sternum
·
Ribs constitute axial skeleton
The Skull:
·
The skull is composed of two sets of bones – cranial and
facial, that totals to 22 bones. Cranial bones are 8 in number. They form the
hard protective outer covering, cranium for the brain.
·
The facial region is made up of 14 skeletal elements which
form the front part of the skull. A single U-shaped bone called hyoid is
present at the base of the buccal cavity and it is also included in the skull.
·
Each middle ear contains three tiny bones – Malleus, Incus
and Stapes, collectively called ear Ossicles.
·
The skull region articulates with the superior region of the
vertebral column with the help of two occipital condyles (dicondylic
skull).
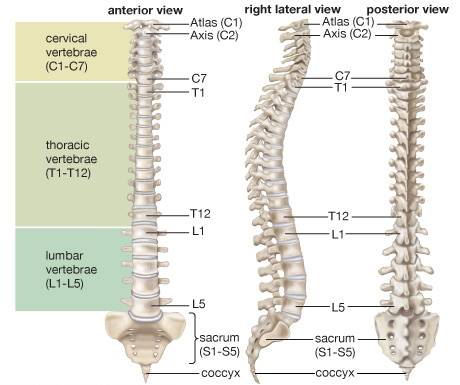
Vertebral
Column:
·
Our vertebral column is formed by 26 serially
arranged units called vertebrae and is dorsally placed. It extends from the
base of the skull and constitutes the main framework of the trunk.
·
Each vertebra has a central hollow portion (neural canal)
through which the spinal cord passes.
·
First vertebra is the atlas and it articulates with the
occipital condyles. The vertebral column is differentiated into
o Cervical (7),
o Thoracic (12),
o Lumbar (5),
o Sacral (1-fused) and
o Coccygeal (1-fused)
regions starting from the skull.
·
The number of cervical vertebrae are seven in almost all
mammals including human beings.
·
The vertebral column protects the spinal cord, supports the
head and serves as the point of attachment for the ribs and musculature of the
back.
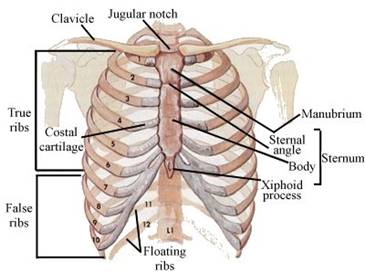
Sternum
and Ribs:
·
Sternum is a flat bone on the ventral midline of thorax.
·
There are 12 pairs of ribs. Each rib is a thin flat
bone connected dorsally to the vertebral column and ventrally to the sternum.
It has two articulation surfaces on its dorsal end and is hence called bicephalic.
True
Ribs:
First seven pairs of
ribs are called true ribs. Dorsally, they are attached to the thoracic
vertebrae and ventrally connected to the sternum with the help of hyaline
cartilage.
False
Ribs:
The 8th, 9th
and 10th pairs of ribs do not articulate directly with the sternum
but join the seventh rib with the help of hyaline cartilage. These are called vertebrochondral (false) ribs.
Floating
Ribs:
Last 2 pairs (11th
and 12th) of ribs are not connected ventrally and are therefore,
called floating ribs. Thoracic vertebrae, ribs and sternum together form the
rib cage.
Appendicular Skeleton:
The bones of the
limbs along with their girdles constitute the appendicular skeleton.
Each limb is made of 30 bones.
Upper Limb:
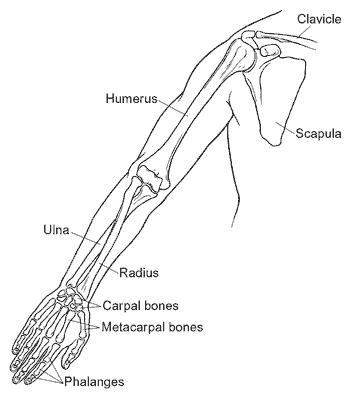
The bones of the hand
(fore limb) are humerus, radius and ulna, carpals
(wrist bones – 8 in number), metacarpals (palm bones – 5 in number) and
phalanges (digits – 14 in number).
Lower
Limb:
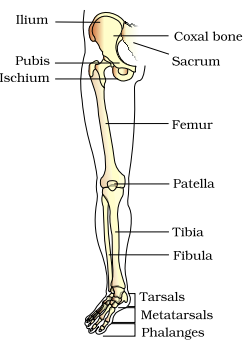
Femur (thigh bone –
the longest bone), tibia and fibula, tarsals (ankle bones – 7 in number),
metatarsals (5 in number) and phalanges (digits – 14 in number) are the bones
of the legs (hind limb). A cup shaped bone called patella cover the knee
ventrally (knee cap).
Pectoral
and Pelvic Girdle:
Pectoral and Pelvic girdle bones
help in the articulation of the upper and the lower limbs respectively with the
axial skeleton. Each girdle is formed of two halves.
Pectoral
Girdle:
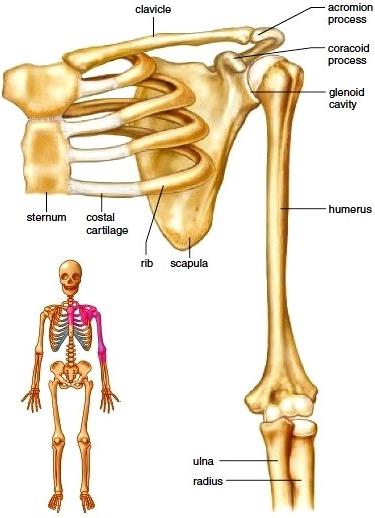
Each half of pectoral
girdle consists of a clavicle and a scapula.
Scapula is a large
triangular flat bone situated in the dorsal part of the thorax between the
second and the seventh ribs. The dorsal, flat, triangular body of scapula has a
slightly elevated ridge called the spine which projects as a flat, expanded
process called the acromion. The clavicle articulates with this. Below the
acromion is a depression called the glenoid cavity which articulates with the head
of the humerus to form the shoulder joint. Each
clavicle is a long slender bone with two curvatures. This bone is commonly
called the collar bone.
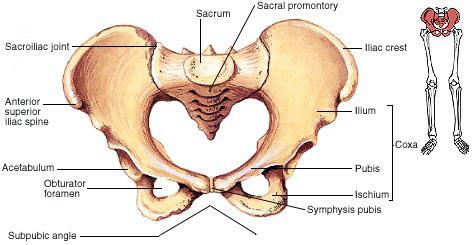
Pelvic Girdle:
Pelvic girdle consists
of two coxal bones. Each coxal
bone is formed by the fusion of three bones – ilium, ischium and pubis. At the
point of fusion of the above bones is a cavity called acetabulum to which the
thigh bone articulates. The two halves of the pelvic girdle meet ventrally to
form the pubic symphysis containing fibrous cartilage.