Menstrual Cycle
The menstrual
cycle refers to the maturation and release of an egg as well as the
preparation of the uterus to receive and nurture the fertilized egg
(embryo). The hormones released during the menstrual cycle control
the sequence of events that lead to pregnancy.
Ø Menstrual cycle is the reproductive cycle in all primates and
begins at puberty (menarche).
Ø In human females, menstruation occurs once in 28 to 29 days. The
cycle of events starting from one menstruation till the next one is called the menstrual
cycle.
Ø During the middle of the menstrual cycle, one ovum is released
(ovulation).
Ø The cycle starts with the menstrual flow (3 to 5 days),
caused due to the breakdown of the endometrium of the uterus. Blood vessels in
liquid state are discharged, but this occurs only when the ovum is not fertilised.
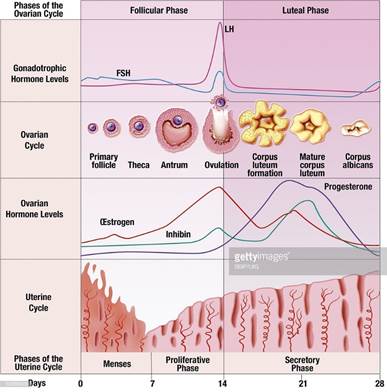
Ø It is followed by the follicular phase.In this phase, the primary
follicles mature into the Graffian follicles. This
causes the regeneration of the endometrium.
Ø These changes are brought about by ovarian and pituitary hormones.
In this phase, the release of gonadotropins (LH and FSH) increases. This causes
follicular growth and the growing follicles produce oestrogen.
Ø The LH and FSH are at their peak in the middle of the cycle (14th
day), and cause the rupture of the Graffian follicles
to release ovum. This phase is called the ovulatory phase.
Ø The remains of the Graffian follicles
get converted into the corpus luteum, which secretes progesterone for the
maintenance of the endometrium.
Ø In the absence of fertilisation, the
corpus luteum degenerates, thereby causing the
disintegration of the endometrium and the start of a new cycle.
Ø In humans, the menstrual cycle ceases to operate at the age of 50
years. This phase is known as the menopause.