Amniocentesis
Amniocentesis also called as Amniotic Fluid Test (AFT) is a medical
procedure in which amniotic fluid is taken out from the uterus of pregnant
woman to determine genetic arrangement and sex of the fetus.
Amniotic fluid contains fetal cells and wastes
from the fetus and a fluid is used for prenatal
diagrams of dmomosomal abnormalities, genetic
disorder, sickle cell, anemia and Cystic fibrosis.
Amniocentesis is performed between 14-16 weeks of pregnancy. The term
amniocentesis refers to the process in which the fluid is tested between weeks
11 to 13. These are four purposes of amniocentesis:
1. To enable timely medical
treatment of children before or after birth.
2. To give the parents the
chance to abort the fetus if there is any
abnormalities.
3. If prepares the parents
psychologically, economically, socially and medically for a baby with health
problems.
4. It helps in diagnosis of
uterine infection.
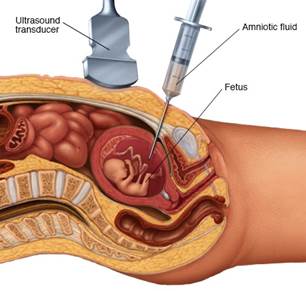
Procedure
Before the start of the procedure a local anesthetic
is given to the mother in order to relieve the pain felt during insertion of
surgical needle. The surgical needle is inserted with the guidance of
ultrasound, which is connected with monitor in order to see position of needle
inside the needle about 10-20 ml amniotic fluid is taken out and poured into
Petri dish. The cells from the amniotic fluid are separated and then turned and
stained. The cells are then examined under the microscope and chromosomal
edition of the fetus is detected.
Women over the age of 35 have an increased change of carrying a baby
with genetic abnormalities. Therefore such women are recommended for
amniocentesis. If there is a family history of chromosomal problems in the
offspring, amniocentesis is also recommended in such cases.