Energy Flow
Ø Sun is the sole source of energy for all ecosystems on the earth.
Ø Plants and other photosynthetic organisms utilize less than 50% of the solar radiation known as the photosynthetically active radiation (PAR).
Ø In an ecosystem, plants are called producers and all animals depend upon the plants directly or indirectly for their food. Hence, they are known as consumers or heterotrophs.
Ø The consumers can be further divided into -
o Primary consumers (herbivores)
o Secondary consumers (primary carnivores)
o Tertiary consumers (secondary carnivores)
Herbivores
Obviously the primary consumers will be herbivores. Some common herbivores are insects, birds and mammals in terrestrial ecosystem and molluscs in aquatic ecosystem
Primary carnivores
The consumers that feed on these herbivores are carnivores, or more correctly primary carnivores (though secondary consumers).
Secondary carnivores
Those animals that depend on the primary carnivores for food are labelled secondary carnivores.
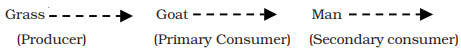
A simple grazing food chain (GFC)
Food chain
The energy flow among the various constituent animals is known as the food chain.
Food web
The interconnection of the various food chains is called the food web.
Trophic level
Every organism occupies a specific level in their food chain known as the trophic level.
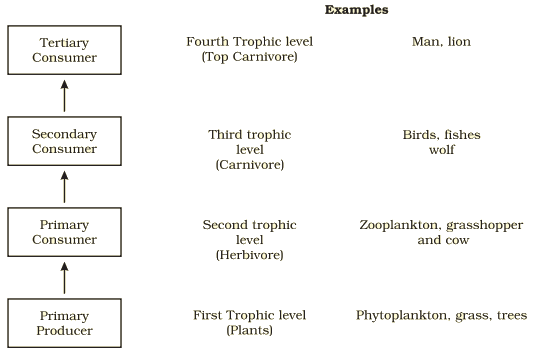
Trophic levels in an ecosystem
Standing crop
Each trophic level contains a certain amount of living material at a certain time known as the standing crop.
The number of trophic levels in a food chain is restricted since the energy transfer follows the 10 percent law i.e., only 10% of the energy is transferred from a lower trophic level to a higher one.
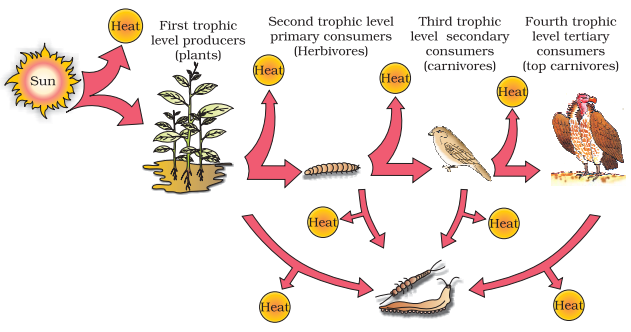
Energy flow through different trophic
levels