Chemical Properties
Arenes are characterised
by electrophilic substitution reactions. However, under special conditions they
can also undergo addition and oxidation reactions.
Mechanism of electrophilic substitution
The common electrophilic substitution
reactions of arenes are nitration, halogenation, sulphonation, Friedel Craft’s
alkylation and acylation reactions in which attacking reagent is an
electrophile (E+)
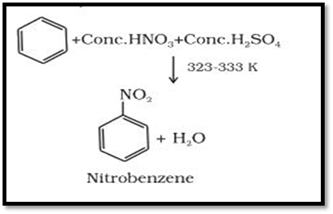
Nitration
A nitro group is introduced
into benzene ring when benzene is heated with a mixture of concentrated nitric
acid and concentrated sulphuric acid (nitrating
mixture).
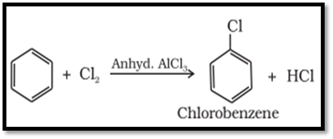
Halogenation
Arenes react with halogens in the presence of a
Lewis acid like anhydrous FeCl3, FeBr3 or AlCl3
to yield haloarenes.
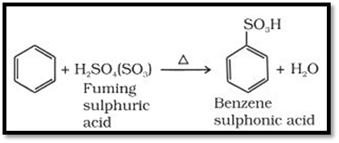
Sulphonation
The replacement of a
hydrogen atom by a sulphonic acid group in a ring is
called sulphonation. It is carried out by heating benzene
with fuming sulphuric acid (oleum).
|
Reaction |
Product |
|
Nitration |
nitro group is introduced
into benzene ring |
|
Halogenation |
Haloarenes |
|
Sulphonation |
replacement of a
hydrogen atom by a sulphonic acid group
in a ring |