Nomenclature
and Isomerism
All six hydrogen atoms in benzene are equivalent; so it forms one and only one type of monosubstituted product.
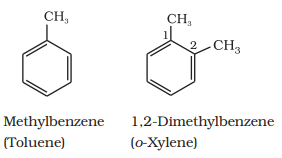
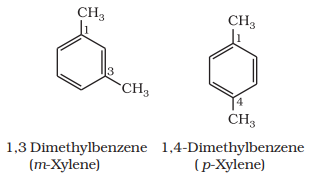
When two hydrogen atoms in benzene are replaced by two similar or different monovalent atoms or groups, three different position isomers are possible. The 1, 2 or 1, 6 is known as the ortho (o–), the 1, 3 or 1, 5 as meta (m–) and the 1, 4 as para (p–) disubstituted compounds.
A few examples of derivatives of benzene are: