Redox
Reactions and Electrode Processes
The experiment corresponding to
redox reaction can also be observed if zinc rod is dipped in copper sulphate
solution. The redox reaction takes place and during the reaction, zinc is
oxidised to zinc ions and copper ions are reduced to metallic copper due to
direct transfer of electrons from zinc to copper ions. During this reaction heat is also evolved.
Now we modify the experiment in such a manner that for the same redox reaction
transfer of electrons takes place indirectly. This necessitates the separation
of zinc metal from copper sulphate solution.
We take copper sulphate solution
in a beaker and put a copper strip or rod in it. We also take zinc sulphate
solution in another beaker and put a zinc rod or strip in it. Now reaction
takes place in wither of the beakers and at the interface of the metal and its
salt solution in each beaker both reduces and oxidised forms of the same
species are present. These represents the species in the reduction and
oxidation half reactions. A redox couple is defined as having together the
oxidised and reduced forms of a substance taking part in an oxidation or
reduction half reaction.
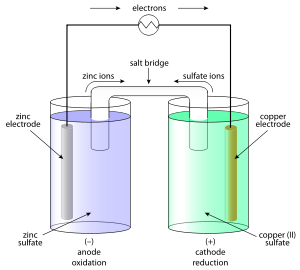
We can
connect solution in two beakers by a slat bridge (a U-tube containing a
solution of potassium chloride or ammonium nitrate usually solidified by
boiling with agar and later cooling to a jelly like substance). This provides
an electric contact between the two solutions without allowing them to mix with
each other. The zinc and copper rods are connected by a metallic wire with a
provision for an ammeter and a switch. The setup is known as Daniell Cell. When the switch is in the off position, no
reaction takes place in wither of the beakers and no current flows through the
metallic wire, as soon as the switch is in the on position, we make the
following observation:
1. The
transfer of electrons now does not take place directly from Zn to Cu2+
but through the metallic wire connecting the two rods as is apparent from the
arrow which indicates the flow of current.
2. The
electricity from solution in one beaker to solution in the other beaker flows
by the migration of ions through the salt bridge. We know that the flow of
current is possible only if there is a potential difference between the copper
and zinc rods known as electrodes here.
The
potential associated with each electrode is known as electrode potential. If
the concentration of each species taking part in the electrode reaction is
unity and further the reaction is carried out at 298K, then the potential of
each electrode is said to be the Standard
Electrode Potential.