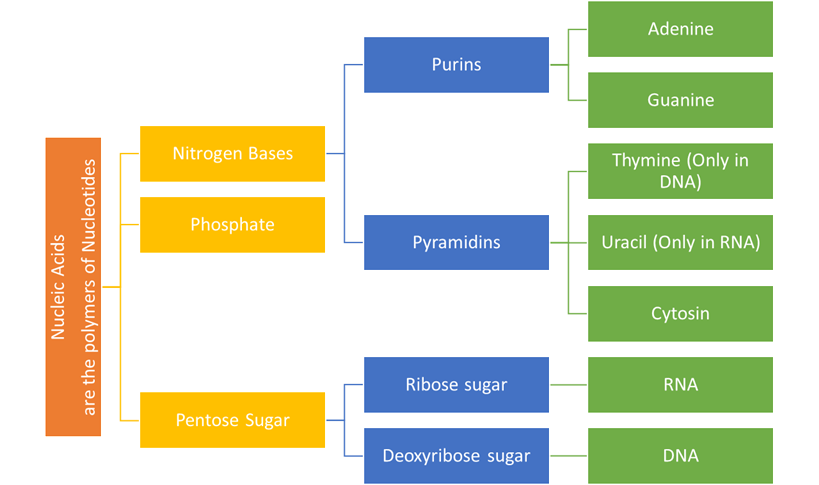
Nucleic Acids
It can be said that nucleic
acid is one of the most important biopolymers. They are present in all
organisms. Think of them as the mother chip of your body. This is where your genetic
information is encoded and recorded. The function of nucleic acid is to express
this information outside the cell to the future generation. So it felicitates
the transfer of genetic information from one generation to the next and so
onwards.
Now nucleic acids are big
and complex molecules. They have a linear binding between nucleotides. They are
double-stranded and have highly complex sequencing.
Types of Nucleic Acids
Now there are two main
types of nucleic acids, namely Deoxyribonucleic Acid and Ribonucleic Acid. And
although the name sounds complicated you will be surprised to know you are
already aware of them both. They are nothing but DNA and RNA. Let us study
these both in a little more detail.
Deoxyribonucleic
Acid
Better known as DNA this is
the first type of nucleic acid. You are probably aware of DNA and know that
every humans DNA is unique to themselves. But how does this happen and what
exactly is DNA.
There are approximately 200
types of cells in our bodies like white blood cells, neurons (brain cells),
cardiac muscle cells etc. Their chemical compositions within their cells
differ. The cells get their instructions from this biopolymer that
is Deoxyribonucleic Acid.
This information is the DNA
code. This code forms due to the sequencing of the nucleotides in the polymer
chain. The DNA has very long chains of nucleotides in their molecules and hence
there are billions upon billions of sequences possible. This is the reason all
of our DNA sequences are unique only to us.
Only 0.01% of our DNA
coding is special and different for every human. This is what makes every
individual unique.
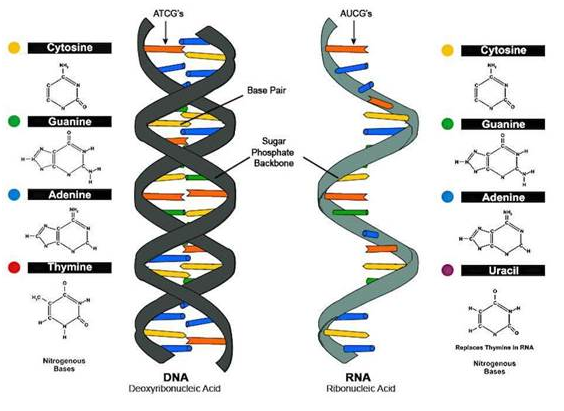
Structure of the DNA
DNA is a double helix formed by
twisting of two polynucleotide chains around each other. Watson and Crick
proposed the DNA structure using X-ray diffraction studies. The two strands are
antiparallel to each other. The bases are stacked inside the helix. The two
helices are bonded together via hydrogen bond. Adenine forms two hydrogen bonds
with thymine and cytosine forms three hydrogen bonds with guanine.
DNA is negatively charged due to the presence
of phosphate groups. This negative charge is stabilized by basic proteins known
as histone proteins.
Ribonucleic
Acid
RNA is our second type of
nucleic acid. Although it does not get as much importance as
DNA, Ribonucleic Acid is absolutely essential for our survival. RNA is
actually the blueprint of our DNAs. While the DNA is always inside the nucleus
of our cells, the RNA travels outside the nucleus to perform its functions.
RNA exists as single stranded structure. In RNA, thymine is replaced by
uracil.
There are actually three types
of Ribonucleic Acids, namely:
·
Ribosomal
RNA: Is
the main part of the ribosome, which is where the protein maker of our bodies.
·
Messenger
RNA: This
RNA carries the message outside from the nucleus. It carries the information
about what type of protein cells are to be manufactured.
·
Transfer
RNA: It
brings the amino acid to the ribosome for protein production.