Chlorine
Occurrence
Common salt, NaCl
is the major source of chlorine. It is also present in sea water and as rock
salt.
Preparation of Chlorine
a.
By
heating manganese dioxide with concentrated hydrochloric acid.
MnO2 + 4HCl → MnCl2 +
Cl2 + 2H2O
However, a
mixture of common salt and concentrated H2SO4 is
used in place of HCl (Weldon’s Process).
4NaCl + MnO2 + 4H2SO4 →
MnCl2 + 4NaHSO4 + 2H2O + Cl2
b.
By the
action of HCl on potassium permanganate.
2KMnO4 + 16HCl → 2KCl +
2MnCl2 + 8H2O + 5Cl2
|
Oxo acid |
Name |
|
H3PO2 |
Hypophosphorus acid |
|
H3PO3 |
Phosphorus acid |
|
H4P2O6 |
Hypophosphoric acid |
|
H3PO4 |
Orthophosphoric acid |
|
H4P2O7 |
Pyrophosphoric acid |
|
HPO3 |
Metaphosphoric acid |
Manufacture of chlorine
a.
Deacon’s process:
By oxidation of hydrogen chloride gas by atmospheric oxygen in the presence of CuCl2(catalyst) at 723 K.
4HCl + O2 ![]() 2Cl2 + 2H2O
2Cl2 + 2H2O
b.
Electrolytic process:
Chlorine is obtained by the electrolysis of brine (concentrated NaCl solution). Chlorine is liberated at anode. It is also
obtained as a by–product in many chemical industries.
2NaCl + 2H2O ↔ 2NaOH + Cl2 +
H2
Physical properties of chlorine
It is yellowish green gas, collected by upward displacement of (it is
heavier than) air, poisonous in nature, soluble in water. It’s
aqueous solution is known as chlorine water. Boiling point is 239K.
Chemical properties of chlorine
- Chlorine reacts with a number of metals
and non-metals to form chlorides.
2Al + 3Cl2 → 2AlCl3
P4 + 6Cl2 →
4PCl3
2Na + Cl2 → 2NaCl
S8 + 4Cl2 →
4S2Cl2
2Fe + 3Cl2 → 2FeCl3
- It has great affinity for hydrogen,
H2 + Cl2 →
2HCl
H2S + Cl2 →
2HCl + S
C10H16 + 8Cl2 →
16HCl + 10C
- Action of water
Cl2 + H2O → HOCl + HCl
HOCL → HCl +
[O] (Nascent Oxygen)
- The bleaching action of chlorine is due
to oxidation and is permanent.
Cl2 + H2O →
2HCl + [O]
Coloured matter + [O] → colourless
matter
With dry
slaked lime it gives bleaching powder.
2Ca(OH)2 + 2Cl2 →
Ca(OCl)2 +
CaCl2 + 2H2O
The
composition of bleaching powder is Ca(OCl)2.CaCl2.Ca(OH)2.2H2O.
- It oxidises ferrous to ferric and
sulphite to sulphate. Chlorine oxidises sulphur dioxide to sulphur
trioxide and iodine to iodate. In the presence of water they form
sulphuric acid and iodic acid respectively.
2FeSO4 + H2SO4 +
Cl2 → Fe2(SO4)3 +
2HCl
Na2SO3 + Cl2 +
H2O → Na2SO4 + 2HCl
SO2 + 2H2O + Cl2 →
H2SO4 + 2HCl
I2 + 6H2O + 5Cl2 →
2HIO3 + 10HCl
- With cold and dilute alkalies
chlorine produces a mixture of chloride and hypochlorite but with hot and
concentrated alkalies it gives chloride and
chlorate.
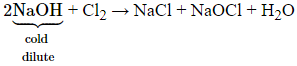

- Chlorine reacts with hydrocarbons and
gives substitution products with saturated hydrocarbons and addition
products with unsaturated hydrocarbons. For example,
CH4 + Cl2 ![]() CH3Cl
+ HCl
CH3Cl
+ HCl
C2H4 + Cl2 ![]() C2H4Cl2
C2H4Cl2
Uses of chlorine
Ø Chlorine is used for bleaching wood pulp
(required for the manufacture of paper and rayon), bleaching cotton and
textiles.
Ø It is used in the extraction of gold and
platinum.
Ø It is used in the manufacture of dyes, drugs
and organic compounds such as CCl4, CHCl3, DDT,
refrigerants, etc.
Ø It is used in sterilising drinking water.
Ø Chlorine is used in preparation of poisonous
gases such as phosgene (COCl2), tear gas (CCl3NO2),
mustard gas (ClCH2CH2SCH2CH2Cl).