Speed of Wave Motion
A wave is
a disturbance in a medium, in fact wave motion is not the motion of
the medium but rather motion of the disturbance itself. To understand wave motion
we have to know about the 3 basic properties of waves, let us visualize this
better with the following diagram.
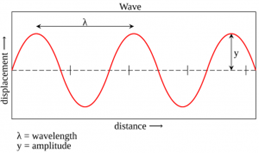
Amplitude:
The
amplitude y for the wave is given by the distance from the centre line to the
tip of the crest or the tip of a trough, the amplitude of the wave tells about
the energy of the wave, amplitude is measured in meters (m).
Wavelength:
Wavelength
is denoted by the symbol λ, it’s the Greek letter ‘Lambda’, well
wavelength is the distance between two consecutive crest or
trough. Wavelength is also measured in meters (m).
Frequency:
It
is denoted by f and is the number of waves passing through a point in one
second; it is measured in hertz (Hz). Waves we find in day to day life
like radio waves, microwaves have very high frequency so we
make use of multiple of hertz like kilo-hertz, mega-hertz.
1
mega-hertz = 1000 kilo-hertz = 1000000 hertz
Speed
of a wave is how far a wave travels in one second, it is calculated in meters
per second. The speed of light is around 3 x 108 m/s whereas the speed of sound is just 380m/s,
because they are two different types of waves,
Speed of waves on string depends
upon tension and mass density of the string and is given by
v=√Tμ