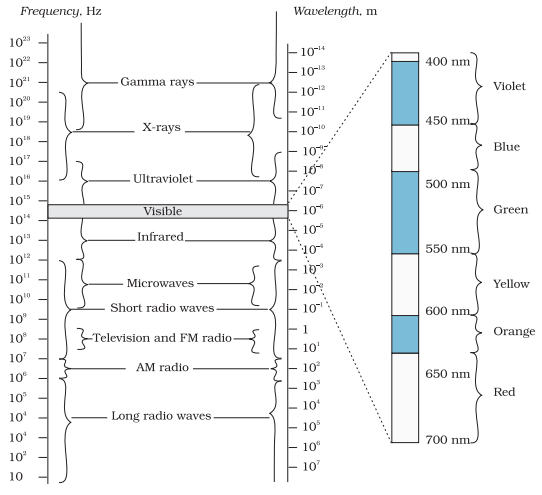
Electromagnetic Spectrum
The
orderly distribution of electromagnetic waves according to their wavelength or
frequency is called the electromagnetic spectrum.
Electromagnetic
spectrum covers a wide range of wavelengths (or) frequencies. The whole
electromagnetic spectrum has been classified into different parts and sub
parts, in order of increasing wavelength and type of excitation. All
electromagnetic waves travel with the velocity of light. The physical
properties of electromagnetic waves are determined by their wavelength and not
by their method of excitation
Uses of electromagnetic spectrum
The following
are some of the uses of electromagnetic waves:
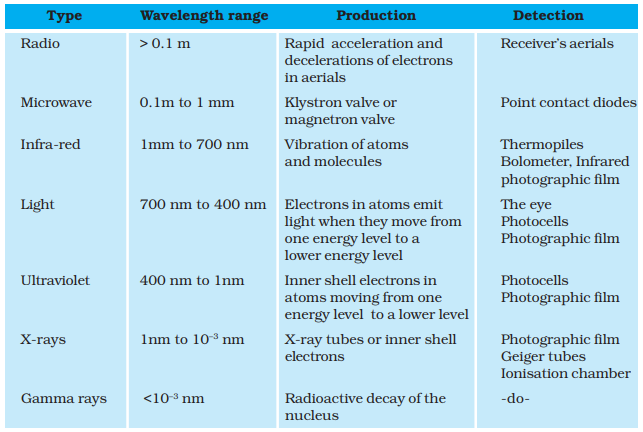
Radio waves
Ø Radio
waves are produced by the accelerated motion of charges in conducting wires.
Ø These
waves are used in radio and television communication systems.
Ø AM band
is from 530 kHz to 1710 kHz.
Ø Higher
frequencies upto 54 MHz are used for short waves
bands.
Ø Television
waves range from 54 MHz to 890 MHz.
Ø FM band
is from 88 MHz to 108 MHz.
Ø Cellular
phones use radio waves in ultra high frequency (UHF)
band.
Microwaves
Ø Microwaves
(short-wavelength radio waves), with frequencies in the gigahertz (GHz) range,
are produced by special vacuum tubes (called klystrons, magnetrons and Gunn
diodes).
Ø Due to
their short wavelengths, they are used in radar communication system.
Ø Microwave
ovens are an interesting domestic application of these waves.
Infra-red waves
Ø Infrared
waves are produced by hot bodies and molecules. This band lies adjacent to the
low-frequency or long-wave length end of the visible spectrum.
Ø Infrared
waves are sometimes referred to as heat waves.
Ø Infrared
lamps are used in physiotherapy.
Ø Infrared
photographs are used in weather forecasting.
Ø As
infrared radiations are not absorbed by air, thick fog, mist etc, they are used to take photograph of long distance
objects.
Ø Infra-red
absorption spectrum is used to study the molecular structure.
Visible light
Ø It is the
most familiar form of electromagnetic waves. It is the part of the spectrum
that is detected by the human eye.
Ø Visible
light emitted or reflected from objects around us provides information about
the world.
Ø The
wavelength range of visible light is 4000 Å to 8000 Å.
Ultra−violet radiations
Ø The sun
is an important source of ultraviolet light.
Ø They are
used to destroy the bacteria and for sterilizing surgical instruments.
Ø These
radiations are used in detection of forged documents, finger prints in forensic
laboratories.
Ø They are
used to preserve the food items.
Ø They help
to find the structure of atoms.
X-rays
Ø Beyond
the UV region of the electromagnetic spectrum lies the X-ray region.
Ø It covers
wavelengths from about 10–8 m (10 nm) down to 10–13 m
(10–4 nm).
Ø X-rays
are used as a diagnostic tool in medicine.
Ø It is
used to study the crystal structure in solids.
γ−rays
Ø They lie
in the upper frequency range of the electromagnetic spectrum and have
wavelengths of from about 10–10m to less than 10–14m.
Ø Study of
γ rays gives useful information about the nuclear structure and it is used
for treatment of cancer.