Laws of Reflection and Refraction
Laws of refraction:
(i) The incident wave front AB, the refracted
wave front CD and the refracting surface XY all lie in the same plane.
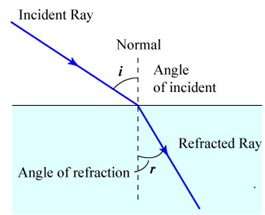
(ii) Angle of incidence
i = ∠PAN =![]() − ∠ NAB = ∠BAC
− ∠ NAB = ∠BAC
Angle of
refraction
r = ∠N1AD = ![]() − ∠ DAC =
∠ACD
− ∠ DAC =
∠ACD
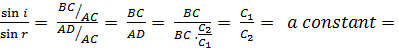 1μ2
1μ2
1μ2 is called the refractive index of second medium with respect to first
medium. This is Snell’s law of refraction.
If 1μ2 > 1, the first medium is rarer and the second medium is denser.
Then ![]() . This means that
the velocity of light in rarer medium is greater than that in a denser medium.
. This means that
the velocity of light in rarer medium is greater than that in a denser medium.
Refractive index of a medium μm is given by
![]()
Since only wavelength changes on refraction,
![]()
![]()
where ![]() and
and ![]() are the wavelengths in medium and
air respectively.
are the wavelengths in medium and
air respectively.
Laws of
reflection:
(i) The incident wavefront AB, the reflected wavefront
CD and the reflecting surface XY all lie in the same plane.
(ii) Angle of incidence
i = ∠ PAN =
![]() − ∠ NAB =
∠BAC
− ∠ NAB =
∠BAC
Angle of
reflection
r = ∠ NAD = ![]() − ∠ DAC =
∠DCA
− ∠ DAC =
∠DCA
For right angled triangle
∠B
= ∠ D = ![]()
BC = AD and AC is common
∴ The two triangles are congruent
∠
BAC = ∠DCA
i.e. i = r
Thus the angle of incidence is equal to angle of
reflection.