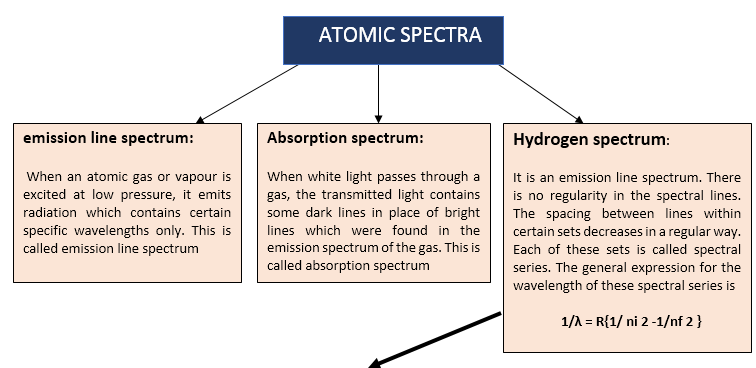
Bohr Atomic Model
Bohr
adopted Rutherford model of the atom & added some arbitrary conditions.
These conditions are known as his postulates:
(i) The electron in
a stable orbit does not radiate energy, i.e.,
![]()
(ii) A stable orbit is that in which the
angular momentum of the electron about nucleus is an integral (n) multiple of
![]() i.e. m
i.e. m![]() ;
;
where n = 1, 2, 3,………….(![]() )
)
(iii) The electron can absorb or radiate
energy only if the electron jumps from a lower to a higher orbit or falls from
a higher to a lower orbit.
(iv) The energy
emitted or absorbed is a light photon of frequency ![]() and of energy
and of energy
E = h![]()
For hydrogen atom : (Z =
atomic number = 1)
(i) ![]() = angular momentum in the nth orbit =
= angular momentum in the nth orbit = ![]() .
.
(ii) ![]() = radius of nth circular orbit = (0.529 A°)
= radius of nth circular orbit = (0.529 A°)![]() ; (1A° =
; (1A° = ![]() m).
m).
(iii) ![]() = Energy
of the electron in the nth orbit =
= Energy
of the electron in the nth orbit = ![]() eV
eV
Binding Energy = -![]() eV
eV
(iv) ![]() = Energy emitted when an electron jumps from n2
orbit to n1 orbit (
= Energy emitted when an electron jumps from n2
orbit to n1 orbit (![]() >
>![]() ).
).
![]()
(v) For hydrogen like atom/species of atomic
number Z:
![]()
![]()
![]()
Bohr's explanation of Spectral of Hydrogen Atom
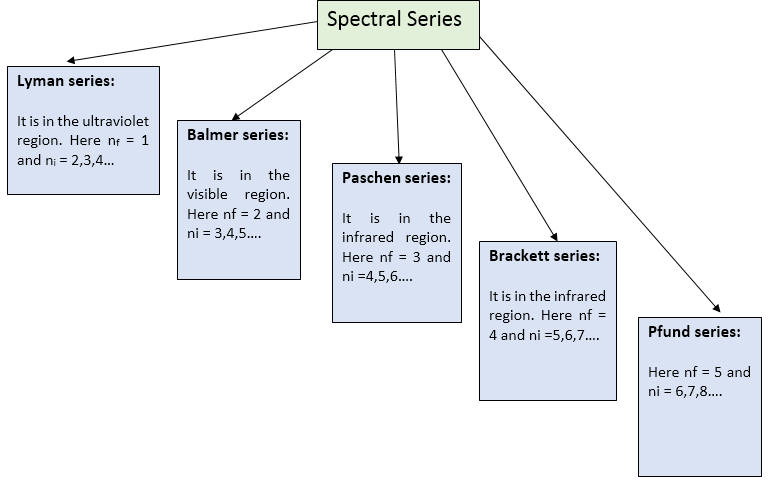
(i) Lyman Series:
Bohr postulated
that Lyman series of obtained when an electron jumps to the first orbit (n1 = 1) from any outer orbit
(n2 = 2, 3, 4 ........)
![]()
where n2: 2, 3, 4............ This
series lies in the ultra violet region of the spectrum and agree well with the
values of s observed experimentally by Lyman.
(ii) Balmer Series:
According
to Bohr, Balmer series is obtained when an electron
jumps to the second orbit (n1
= 2) from any outer orbit (n2
= 3, 4, 5 .......) Wave number of these spectral lines is
![]()
where n2 = 3, 4, 5......... This
series lie in the visible part of the spectrum.
(iii) Paschan Series:
According
to Bohr Paschen series is obtained when an electron
jumps to the 3rd orbit (n1
= 3) from any out of orbit (n2
= 4, 5, 6......) Bohr calculated the wave number of spectral lines of Paschen series from the relation.
![]()
where n2 = 4, 5, 6 ........ This
series lies in the infrared region of the spectrum.
(iv) Paschan Series:
According
to Bohr, Brackett series is obtained when an electron jumps to the 4th orbit (n1= 4) from any out orbit (n2 = 5, 6, 7 ..........).
This series lie in far infrared region.
![]()
where n2 = 5, 6, 7……….
(v) Pfund Series:
According
to Bohr, Pfund series is obtained when an electron
jumps to the 5th orbit (n1
= 5) from any outer orbit (n2
= 6, 7, 8........). This series lies in far infrared region.
![]()
where n2 = 6, 7, 8 .............
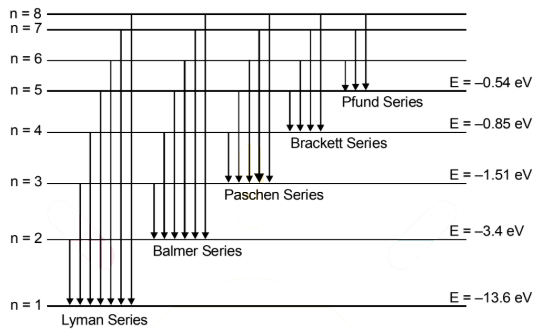
Energy Level Diagram:
A diagram
which represents the total energies of electron in different stationary orbits
of an atom are called the energy level diagram and are represented by parallel
horizontal lines. Total energy in the nth orbit of hydrogen atom is given by
E = ![]()
On substituting the values, we get
E = ![]() eV
eV
Substituting n = 1, 2, 3,............, we get the energies of electrons in
various stationary orbits as:
E1 = ![]() = -13.6eV
= -13.6eV
E2 = ![]() = -3.4eV
= -3.4eV
E3 = ![]() = -1.51.6eV
= -1.51.6eV
E4 = ![]() = -0.85eV
= -0.85eV
E5 = ![]() = -0.54eV
= -0.54eV
E6 = ![]() = -0.37eV
= -0.37eV
E7 = ![]() = -0.28eV
= -0.28eV
Clearly, as n increases, En
becomes less negative until at n = ∝,
En = 0
Limitations of Bohr's Theory:
Ø This
theory is applicable only to simplest atom like hydrogen, with Z = 1. The theory
fails in case atoms of other elements for which Z > 1
Ø The
theory does not explain why orbits of electrons are taken as circular, while
elliptical orbits are also possible.
Ø Bohr's theory
does not explain the fine structure of spectral lines even in hydrogen atom.
Ø Bohr's
theory does not say anything about the relative intensities of spectral lines.
Ø Bohr's
theory does not take into account the wave properties of electrons.
