Management of Natural Resources
Anything
in the environment which can be used is called a natural resource.
Natural
Resources includes total natural environment that support human life and
contribute to the production of necessities and comforts to mankind. So natural
resources are the coihponents of atmosphere,
hydrosphere and lithosphere.
Types of
Natural Resources:
On the
basis of abundance and availability, the natural resources are of two types
·
Inexhaustible.
·
Exhaustible.
(a)
Inexhaustible:
These are
in plenty and cannot be exhausted by man’s consumption. For example; air, sand,
clay etc. It gets affected by the over-population of mankind.
(b) Exhaustible:
These are
limited and can get exhausted over a period of time, i.e., coal, petroleum etc.
Management
of Natural Resources:
A system
of controlling the use of natural resources in such a way, as to avoid their
wastage and to use them in the most effective way is called management of
natural resources.
Why do we
Need to Manage Our Natural Resources: We need to manage our natural resources
because of the following reasons :
·
The resources of the earth are
limited. Because of the rapid increase in human population,
the demand for resources is increasing day-by-day. The proper management can
ensure that the natural resources are used judiciously, so that they fulfill the needs of present generation and also last for
the generations to come. –
·
The proper management of
natural resources takes into consideration long-term perspective (or view) and
prevents their exploitation to hilt for short-term gains.
·
The proper management can
ensure equitable distribution of natural resources so that all the people can
benefit from the development of these resources.
·
The proper management will take
into consideration the damage caused to the environment during the ‘extraction’
or ‘use’ of the natural resources and find ways and means to minimise this
damage.
Conservation
of Wildlife:
It is very
important to conserve wild-life to maintain the ecological balance in nature
and to preserve the gene pool. Some of the measures (or steps) to be taken for
the conservation of wildlife are given below:
·
Laws should be made to impose a
total ban on the poaching (killing) or capturing of any animal or bird
belonging to an endangered species.
·
The natural habitats of wild
animals and birds should be preserved by establishing National Parks and Sanctuaries
throughout the country.
·
The Government Department
connected with the conservation of wildlife should conduct a periodic survey in
all the forests, National parks and Sanctuaries to have knowledge of the
population of all species of wild animals and birds.
·
Special attention should be
paid to the conservation of endangered species of wild animals and birds to
prevent their extinction altogether.
·
The unauthorized felling
(cutting) of forest trees for timber trade and fuel-wood should be curbed
(stopped) immediately.
Forest and
wild life conservation:
Forests
are biodiversity hot spots. Biodiversity of an area is the number of species of
different life forms like bacteria, fungi, powering plants insects, birds, etc.
Hotspot means an area full of biological diversity.
Loss of diversity may lead to a loss of ecological stability/ecological
imbalance.
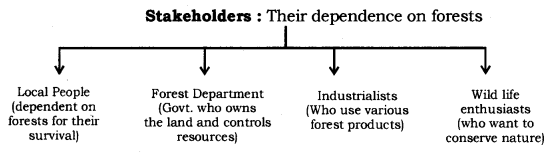
Stake holders:
A person
having interest or concern for something is called as a stakeholder.
Sustainable
Management:
Management
of forest resources wisely to make it available for future generations.
To consider the conservation of forests, we need to look at the stakeholders
who are :
·
The people who live in or
around forests are dependent on forest products for various aspects of their
life.
·
The Forest Department of the
Government which owns the land and controls the resources from forests.
·
The industrialists—from those
who use ‘tendu’ leaves to make bidis to the ones with
papermills who use various forest produce.
·
The wild life and nature
enthusiasts who want to conserve nature in its pristine form.
A major program called silviculture has been started
to replenish the forests by growing more trees and plants.
Conservation
of forests:
It is
carried out by the following methods
·
Afforestation: It
is growing of forests on unprotected barren lands. Van Mahotsava
is a tree plantation movement carried out twice a year (February and July) by
both government and voluntary agencies.
·
Reforestation: It
is developing forest cover in the area which has been damaged or cleared during
exploitation.
·
Separation of Commercial
Forestry: Useful plants required by
industry should be planted separately preferably on waste land. Growing
industry required plants is called production plantation.
·
Grazing: Grazing
should be regulated according to the availability of pasturage.
Deforestation: Removal, decreases or deterioration of forest cover of an area
is called deforestation.
Effects of Deforestation
·
Soil Erosion: Removal
of plant cover exposes the fertile soil to wind and water. The latter remove
the top soil and make the area infertile.
·
Desertification: Removal
of forest cover in the plains makes the area dry. In hot season, the soil
becomes loose. Air currents take away the fine soil particles leaving behind
sand.
·
Floods: In
rainy season many temporary rivulets are formed due to loss of absorption
capacity by unprotected soil. The rivulets produce floods in low land causing
loss to agriculture, property and life.
·
Destruction of wildlife: Deforestation
leads to destruction of natural habitats of wild animals and plants. Wildlife
is, therefore, destroyed.
·
Climatic Changes: In
the absence of forest cover, the summer becomes hotter while the winters become
extra cool. The frequency of rainfall decreases.
National
Award for Wildlife Conservation:
The Govt, of India, has recently instituted an ‘Amrita Devi Bishnoi National Award for wildlife conservation in the
memory of Amrita Devi, who in 1931 sacrificed her life along with 363 other for
the protection ‘Khejri Trees’ in Kherali
Village near Jodhpur in Rajasthan.
Chipko Andolan:
Movement
originated in Garhwal in early 1970’s that was the
result of a grassroot level effort to end the
alienation of people from their forest.
Thus, Chipko Movement (i.e., chipko
Andolan) is the tree hugging movement, in which the
villagers compel the axeman to stop tree felling by embracing and forming ring
(circle) around the marked trees. Example : Protection
of Sal Forest in West Bengal in 1972.

Re-use is better than recycling as it saves energy.
Water as a
Resource
·
Water is a basic necessity for
all terrestrial forms of life. Regions of water scarcity are closely
related to the regions of acute poverty.
·
Failure to sustain water
availability has resulted in loss of vegetation cover, diversion for high water
demanding crops and pollution from industries and, urban wastes and less rain.
·
Irrigation methods like dams,
tanks should be used in various part of India.
Advantages of Dams
·
Water from a dam is used for
irrigation in fields through a network of canals. Dams ensure round the year
water supply to the crop fields and help raise agricultural production.
·
Water from a dam is supplied to
the people in towns and cities through pipelines after suitable treatment. In
this way, construction of dams ensures continuous water supply in the region.
·
The falling water (or flowing
water) from the dam is used for generating electricity. The water rushing down
the dam turns turbines which run electric generators.
Disadvantages of Dams
·
Social Problems: Due
to the construction of high-rise dams, a large number of human settlements (or
villages) are submerged in the water of large reservoir formed by the dam and
many people are rendered homeless. This creates a social problem.
·
Environmental Problems: The
construction of high-rise dams on the rivers contributes to deforestation and
loss of biodiversity. This is because a vast variety of flora and fauna (plants
and animals) get submerged in the water of large reservoir formed by the dam
and disturb the ecological balance.
·
Economic Problems: Some
people say that the construction of high-rise dams involves the spending of a
huge amount of public money without the generation of proportionate benefits.
Forests:
Forests
are important renewable natural resources dominated mainly by trees forming a
sort of canopy, they are essential for the ecological balance of all
ecosystems. They maintain the biological ecosystem.
Water
Harvesting:
Aim is to
develop primary resources of land and water and to produce secondary resources
of plants and animals for use in a manner which will not cause ecological
imbalance.
Various ancient methods of water harvesting
|
Methods |
State |
|
Khadin, tanks, nadis |
Rajasthan |
|
Banderas, tals |
Maharashtra |
|
Bundhis |
Madhya Pradesh and U.P. |
|
Pyhes and Pynes |
Bihar |
|
Kulhs |
Himachal Pradesh |
|
Ponds |
Jammu Region |
|
Eris (tanks) |
Tamilnadu |
Baylis – Old
method of water harvesting in Delhi and nearby region.
These techniques are local specific to ensure the mismanagement and
over-exploitation of these resources.
Advantages of Water Harvesting
System
·
Water does not evaporate.
·
Recharge wells and moisture for
vegetation.
·
Does not provide breeding
grounds for mosquitoes.
·
Ground water is protected from
contamination by human and animal waste.
Pollution
of Water:
The
pollution of water is caused by the dumping of untreated sewage and industrial
wastes into it.
The contamination of river water can be usually found from two factors :
·
the presence of coliform
bacteria in river water, and
·
measurement of pH of
river water.
Gangs
Action Plan (GAP):
Muticrore project
came in 1985 to improve the quality of Ganga. Ganga Action Plan (GAP) was
formulated to reduce the pollution load of river Ganga by more than 75%. The
water quality has been tested from time-to-time by checking coliform (a group
of harmless bacteria in human intestine) number/100 ml.
Accordingly, a survey was conducted and data was collected for total coliform
(a group of bacteria found in human intestine) between 1993-1994 which was as
below:
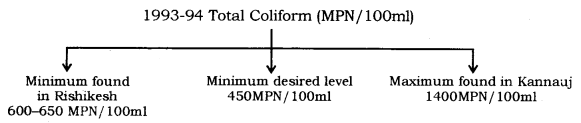
MPN – Most Probable Number.
Advantages of Water Stored in
the Ground
·
The water stored in the ground
does not evaporate.
·
The water stored in the ground
spreads out to recharge wells and provides moisture for crops over a wide area.
·
The water stored in the ground
does not promote the breeding of mosquitoes (unlike stagnant water collected in
ponds or artificial lakes).
·
The water stored in the ground
is protected from contamination by human and animal waste.
Coal and
Petroleum Conservation:
Coal and
petroleum are fossil fuels found in earth’s
crust. They are non-renewable and exhaustible resources.
1. Coal: Coal is combustible fossilized
rock derived from a large accumulation of plant remains that is gradually
compressed. Coal is used for cooking, heating, in industry and thermal power
plants.
2. Petroleum: Petroleum
is another fossil fuel that occurs in the form of liquid oil. It has been
formed in the past (about 10 to 20 crore years old) from plant and animal
remains and occur in the form of mineral oil in sedimentaiy
rocks. Petroleum is mainly used as fuel for transport, agricultural operations,
generators and some industries.
Methods of Conservation of
Fossil Fuels
·
Burning of coal causes air
pollution. Thus direct use of coal for the purpose or burning should be
avoided. Coal may be converted into liquid fuel and compressed natural gas
(CNG) through coal gasification.
·
Techniques should be developed
to recover maximum fossil fuel that lies in deep mines and wells. Wastage
during extraction and transportation should be avoided.
·
Both oil wells and coal mines
are prone to catch fire. Therefore, these should be well protected from fire to
avoid wastage pollution and loss of life and property.
·
Over-consumption of oil in
automobiles should be checked. We must save oil for future use because only a
few years are left for its depletion.
·
Alternative sources of energy,
such as hydroelectric, nuclear, solar, wind power and biogas plants should be
encouraged.
Steps for Conservation of Energy Resources
· Save electricity, water, etc. by not using when not required.
· Use energy efficient electrical appliances to save electricity.
· Use pressure cooker for cooking food.
· Use solar cookers.
· Encourage the use of biogas as domestic fuel.
· Fuel efficient motor vehicle should be designed to reduce consumption of petrol and diesel.