ACIDS
AND BASES
Acids are chemical substances which are characterized by a
sour taste in an aqueous medium. They have the tendency to turn blue litmus
red. On the other hand, bases are chemical substances which are characterized
by a bitter taste and are slippery to the touch.
Some of the bases are soluble in water while others are
not. Water soluble bases are known as alkalis. They have the tendency to turn
red litmus blue. Acids and bases react with a wide range of chemical compounds
to form salts. Some of the chemical reactions of acids and bases are:
Reactions of acids and bases with metals:
When a metal reacts with an acid, it generally displaces
hydrogen from the acids. This leads to the evolution of hydrogen gas. The
metals combine with remaining part of acids to form a salt.
For example:
reaction of sulphuric acid with zinc.
H2SO4 + Zn → ZnSO4 + H2
Alkalis (bases that are soluble in water) react with the
metal to produce salt and hydrogen gas. For example:
reaction of zinc with sodium hydroxide.
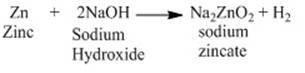
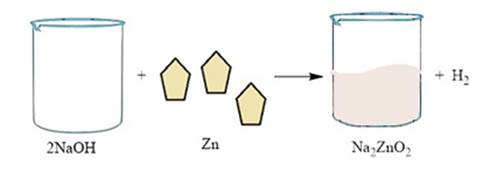
2 NaOH + Zn → Na2ZnO2 + H2
The reaction of metal carbonates/ metal bicarbonates with acids:
Metal carbonates/metal bicarbonates react with acids to
produce salt, carbon dioxide and water.
For example
the
reaction of sodium carbonate/sodium bicarbonate with hydrochloric acid.
Na2CO3 + HCl (aq) → 2NaCl (aq) + H2O(l) + CO2
The reaction of metal oxide with acids:
Metal oxides react with acids to produce salt and water.
For example reaction of copper oxide and dilute hydrochloric acid.
CuO + 2HCl → CuCl2 + H2
The reaction of non-metal oxide with bases:
Non-metal oxides react with bases to produce salt and water.
For example the reaction of carbon dioxide and lime water (calcium hydroxide)
CO2 + Ca (OH)2 → CaCO3 + H2O
The reaction between acids and bases:
Acids react with bases to produce salt and water. The
reaction between acids and bases to give salts is known as neutralization reactions.
For example
the
reaction of sodium hydroxide with hydrochloric acid.
NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H2O
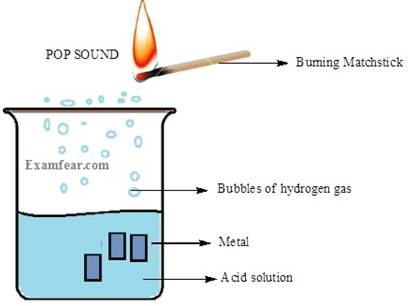
Reaction of metals with acids:
Metals react with acids and displaces hydrogen from
the acids to produce hydrogen gas and metal salt. If a matchstick is brought
near the mouth of the tube containing the product of the reaction then we hear
a pop sound. It is this hydrogen gas that burns with a pop sound.
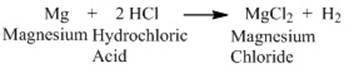
For instance, Magnesium reacts with
dilute hydrochloric acid to form magnesium chloride and hydrogen.
o Electrochemical series is the development of a
series of metals that are arranged as per their reactivity in a sequence from
highest to lowest. Copper does not react with hydrochloric acid because it is
below hydrogen in the electrochemical series due to which it does not react
liberate hydrogen but reacts with sulphuric acid.
Reaction of metals with bases:
Metals react with base to give metal salt and hydrogen
gas.
Metal like zinc reacts with sodium hydroxide to
produce hydrogen gas. For instance, zinc reacts with sodium hydroxide to give
sodium zincate.
Another
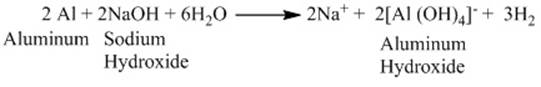
example
when aluminium reacts with sodium hydroxide
Reaction of metal carbonates and metal hydrogen
carbonates with acid:
Metal carbonates are formed by reaction of metal
salt with CO2 or with a carbonate of a more reactive metal.
Metal Hydrogen carbonates are formed by reaction of
metal salt with HCO3 or with a hydrogen carbonates of a more
reactive metal.
Metal carbonates and Metal Hydrogen carbonates
reacts with acids and produces corresponding metal salt, carbon dioxide and
water.
Let us consider the reaction of sodium carbonate
with dilute HCl. The reaction proceeds in the following manner.
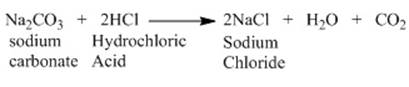
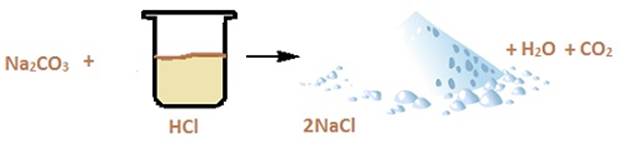
Secondly let
us consider the reaction of sodium hydrogen carbonate with dilute HCl. The
reaction proceeds as follows.
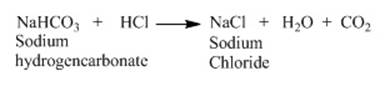
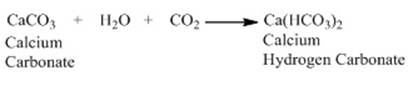
Both the reaction produces CO2 which
on passing through lime water makes lime water milky due to formation of
calcium carbonate.
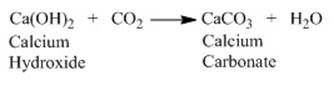
On passing
excess carbon dioxide following reaction occurs.
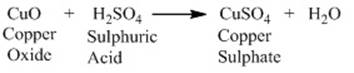
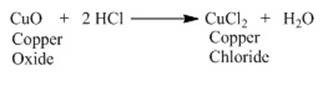
Reaction of metallic oxides with acids:
Metallic oxides react with acids to give salts and
water. Let us consider the reaction of copper oxide with dilute hydrochloric
acid.
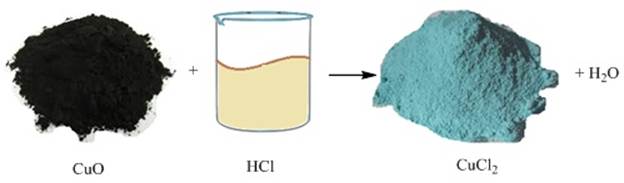
After the
reaction takes place the colour of the solution becomes blue-green due to the
formation of copper (II) chloride and the copper oxide dissolves. This proves
that metallic oxides are basic oxides.
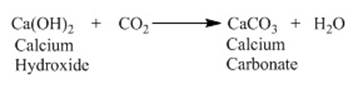
Reaction of non-metallic oxides with base:
Non-metallic oxides are formed by the reaction of
non-metals with oxygen. They react with base to give salts and water. Let us
consider the reaction of Calcium hydroxide (base) with carbon dioxide
(non-metallic oxide) to produce salt and water.
Reaction of acids and bases:
Acids and bases react with each other to nullify
the effect of each other. Let us consider a simple reaction. Take a sample of NaOH which is a base and add drops of dilute HCl.
The reaction
will be as follows:
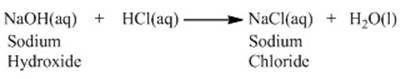
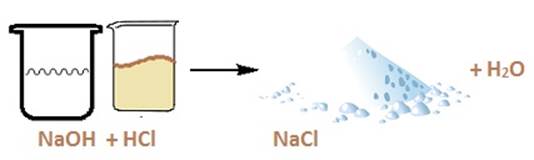
The reaction
between an acid and a base to give a salt and water is known as a
neutralisation reaction.
Therefore while suffering from acidity it is
prescribed to take antacid which are bitter in taste i.e. they are base. And on
entering the body they neutralise the acid and convert into salt and water.
What happens to acid and base in water?
Acids in water solution dissociates H+ ions.
Let us consider the reaction between water and hydrochloric acid (HCl).
HCl in presence of water produces H+ ion. This ion cannot exist
alone and hence combines with water molecules and forms H3O+.
The reaction is as follows:
![]()
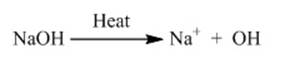
Base when dissolved in water produces OH- ion.
Let us consider the reaction between water and sodium hydroxide NaOH.
NaOH in presence of water produces OH- ion.
![]()
Therefore the
neutralisation stands out as follows:
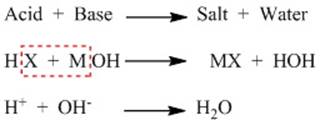
Cautions while adding acid to water:
![]() Reaction of
acid or base with water leads to the decrease in the concentration of ions (H3O+/OH–)
per unit volume. This process is known as dilution.
Reaction of
acid or base with water leads to the decrease in the concentration of ions (H3O+/OH–)
per unit volume. This process is known as dilution.
![]() The procedure of dissolving acid or base in water
is highly exothermic reaction.
The procedure of dissolving acid or base in water
is highly exothermic reaction.
![]() The acid needs to be added slowly to water with
constant stirring.
The acid needs to be added slowly to water with
constant stirring.
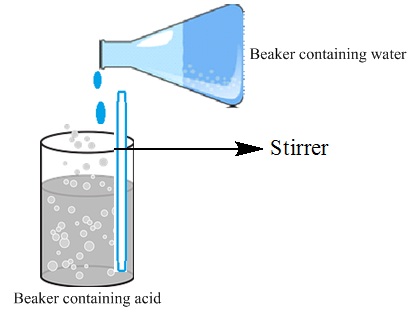
Fig. Adding water to concentrated acid
![]() Adding water to concentrated acid generates
tremendous heat causing the mixture to splash out and can even cause burns.
Adding water to concentrated acid generates
tremendous heat causing the mixture to splash out and can even cause burns.
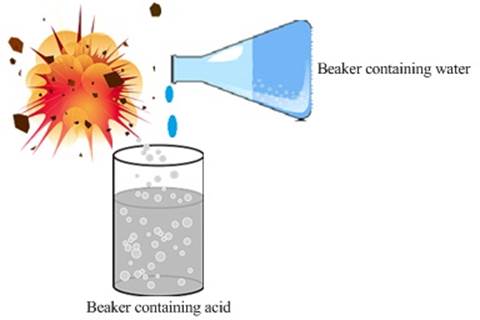
![]() The beaker
used for the reaction may also break due to the generation of excessive
indigenous heating
The beaker
used for the reaction may also break due to the generation of excessive
indigenous heating
Acid and bases conduct electricity:
Acids and Bases exhibit their conducting property
only if they are in aqueous solution in which they could completely ionize in
water. An acid in water solution dissociates H+ ions. Let us
consider the reaction between water and hydrochloric acid (HCl).
HCl in presence of water produces H+ ion.
This ion cannot exist alone and hence combines with water molecules and forms H3O+.
The reaction is as follows:
![]()
Base when dissolved in water produces OH- ion.
Let us consider the reaction between water and sodium hydroxide NaOH.
NaOH in presence of water produces OH- ion.
The H+ and OH- ions
contain a free electron that carries the electric charge and thereby conducts
electricity.
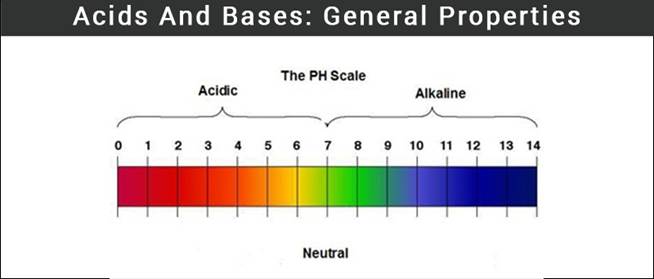
pH scale:
Ø A scale developed to measure the concentration of
hydrogen ion in a solution is known as pH scale where p in pH implies ‘potenz’ in German.
Ø pH scale ranges from 0 (highly acidic) – 14 (highly
alkaline).
Ø The pH of a neutral solution is 7.
Ø Acidic solution is represented by a value less than
7 on the pH scale.
Ø Whereas basic solution is represented by a value
greater than 7 on the pH scale.
Ø An increase in OH– ions
concentration in the solution results in increase in the strength of alkali
hence the value of pH increases.
Ø Acids giving rise to more H+ ions
are strong acids whereas those giving rise to less H+ ions are termed as weak
acids.
Ø Similarly bases giving rise to more OH- ions
are strong bases whereas those giving rise to less OH- ions are termed as weak
bases.
Ø Salts of a strong acid and a strong base are
neutral with pH value of 7.
Ø Salts of strong acid and weak base are acidic with
pH value less than 7.
Ø Salts of a strong base and weak acid are basic in
nature, with pH value more than 7.
Ø 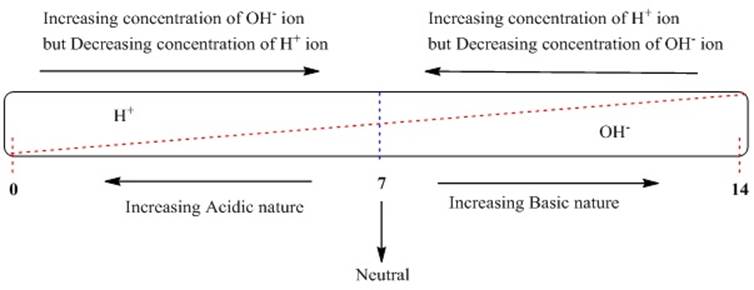
pH scale in our day to day life:
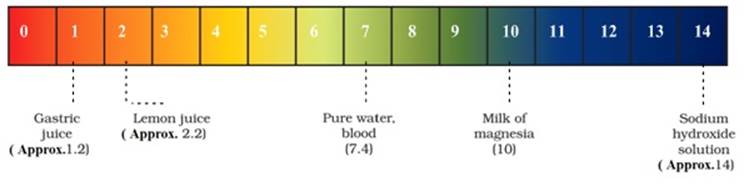
![]() Our body
works within the pH range of 7.0 to 7.8. The pH of saliva ranges from 6.5-7.5.
Our body
works within the pH range of 7.0 to 7.8. The pH of saliva ranges from 6.5-7.5.
![]() When pH of
rain water is less than 5.6, it is called acid rain that lowers the pH of the
river water and makes it difficult for marine creatures to survive.
When pH of
rain water is less than 5.6, it is called acid rain that lowers the pH of the
river water and makes it difficult for marine creatures to survive.
![]() The pH of
surface water is 6-8.5 and that of ground water is nearly 6.5-8.5
The pH of
surface water is 6-8.5 and that of ground water is nearly 6.5-8.5
![]() Plants
require a specific pH range for their healthy growth.
Plants
require a specific pH range for their healthy growth.
![]() pH
of tomato juice ranges from 4.1 to 4.6 whereas the pH of carrot juice is 6.4.
pH
of tomato juice ranges from 4.1 to 4.6 whereas the pH of carrot juice is 6.4.
![]() Our stomach
produces hydrochloric acid during digestion of food causing no harm. But during
indigestion an excess amount of acid is produced causing pain and irritation.
Our stomach
produces hydrochloric acid during digestion of food causing no harm. But during
indigestion an excess amount of acid is produced causing pain and irritation.
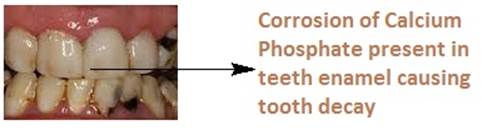
![]() Bacteria
present in the mouth generates acids by decomposing the remaining sugar and
food particles in the mouth that lowers the pH to 5.5 and corrodes calcium
phosphate present in our teeth enamel.
Bacteria
present in the mouth generates acids by decomposing the remaining sugar and
food particles in the mouth that lowers the pH to 5.5 and corrodes calcium
phosphate present in our teeth enamel.
Ant sting injects formic acid and
nettle stings and injects methanoic acid causing pain
and irritation. Use of a mild base like baking soda on the stung area can
provide relief to some extent due to neutralization reaction between acid and
base.

Chemicals from salt:
·
Salts formed
by the blend of hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide solution is called
sodium chloride.

Fig. Sprinkling common salt (sodium chloride) on salad
- The salt we commonly consume. It is neutral.
- This neutral common salt acts as a preliminary raw material for
extracting several other materials of daily use, like sodium hydroxide,
baking soda, washing soda, bleaching powder etc.
Sodium hydroxide:
o Passing electricity through brine solution (an
aqueous solution of sodium chloride), it decomposes to give chlorine and sodium
hydroxide.
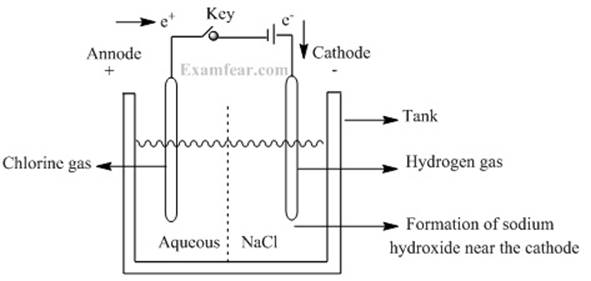
o The
process is termed as the choler-alkali process. The term chlor
for chlorine and alkali for sodium hydroxide.
o Chlorine gas is given off at the anode,
o Hydrogen gas is given off at the cathode.
o Sodium hydroxide solution is formed near the
cathode.
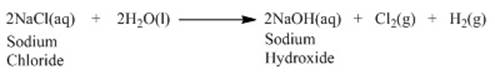
o The reaction that takes place is as follows:
Bleaching powder :
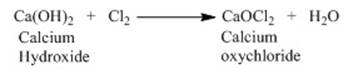
o
Chlorine
produced on passing electricity through brine solution undergoes reaction with
dry slaked lime [Ca (OH)2] to produce
Bleaching powder.
o The reaction is as follows:
o It is used for several purposes:
o As a bleaching agent for bleaching cotton and linen
in the textile industry,
o To bleach wood pulp in paper manufacturing
industry.
o To bleach washed clothes in laundry.
o As an oxidising agent in many chemical industries.
o To disinfect drinking water and make it germfree.

Fig. Bleaching
Powder
Baking soda:
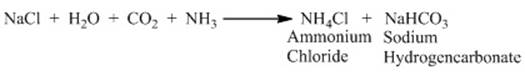
o Chlorine produced on passing electricity through
brine solution undergoes reaction with ammonia produces baking soda.
o
The chemical
name of baking soda is sodium hydrogencarbonate (NaHCO3).
o It is a mild non-corrosive basic salt.
o The following reaction takes place.
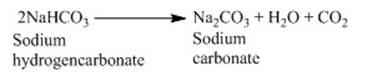
o On heating the reaction that takes place is as
follows:
o It is used for following purposes:
o Baking soda (sodium hydrogencarbonate)
undergoes reaction with mild edible acid such as tartaric acid to manufacture
baking powder. This baking powder on heating undergoes following reaction.
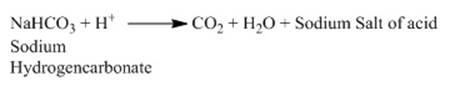
o This carbon-dioxide produced makes bread or cake
rise thereby making them soft and spongy.
o Being alkaline it is also an active ingredient in
antacids that acts by neutralising the excess acid produced in the stomach.
o It is also used in soda-acid fire extinguishers.

Fig. Baking Soda
Washing soda
o This is another chemical derivative of sodium
chloride. The heating of baking soda produces sodium carbonate.
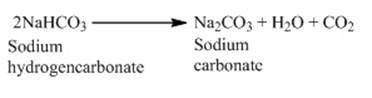
o This sodium carbonate undergoes recrystallization
to give off washing soda.
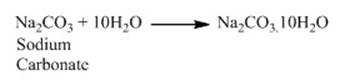
o It is also a basic salt.
o It is used for following purposes:
o It is used in glass, soap and paper manufacturing
industries.
o It is also used in the manufacture of sodium
compounds like borax.
o It is also used as a cleaning agent for domestic
purposes.
o It also plays a pivotal role in removing permanent
hardness of water.

Fig. Washing Soda
Water of crystallisation
o The fixed number of water molecules present in one
formula unit of a salt is called water of crystallisation.
o
For
instance, there are five molecules of water in one formula unit of copper
sulphate and hence the chemical formula for hydrated copper sulphate is CuSO4.
5H2

Fig. Copper sulphate crystal
o
Gypsum has
two molecules of water as water of crystallisation and hence the chemical
formula for hydrated gypsum stands out to be CaSO4.2H2
o
This gypsum
on getting heated loses water molecules and becomes calcium sulphate
hemihydrate (CaSO4.1/2 H2O). This is known as plaster of
Paris.
o Uses of Plaster of Paris are as follows:
o Plaster for supporting fractured bones in their
appropriate position.
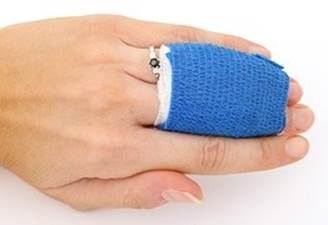
o When mixed with water, it again changes to gypsum
giving a hard solid mass. The reaction is as follows:
![]()
o It is also used for making toys, materials for
decoration and for making smooth surfaces

Fig. Statue
made of plaster of Paris