Separation of Substances
1 a. A pure substance contains one kind of particles.
Eg:
distilled water.
b.
An impure substance contains more than one kind of particle.
Eg:
tap water.
Most of the substances found in
nature are impure.
2. Separation of impure
substances is often done because of the following reasons:
a. To separate harmful
substances from useful substances
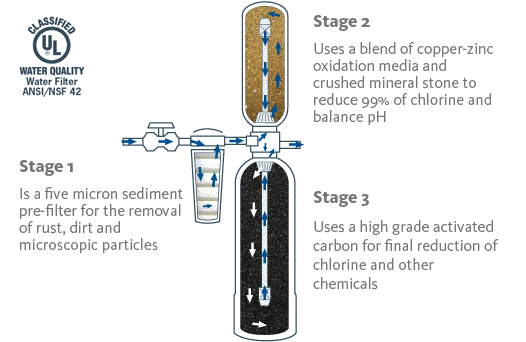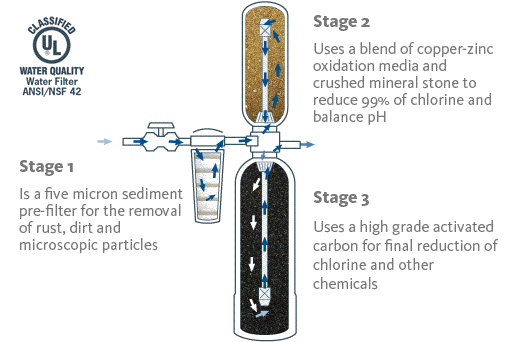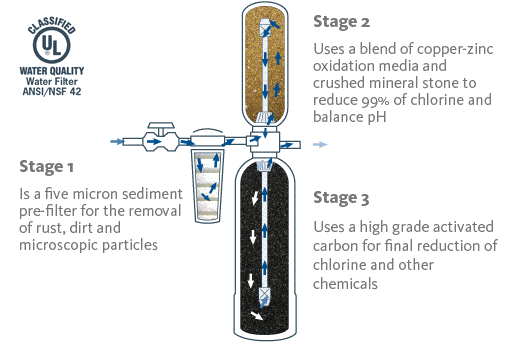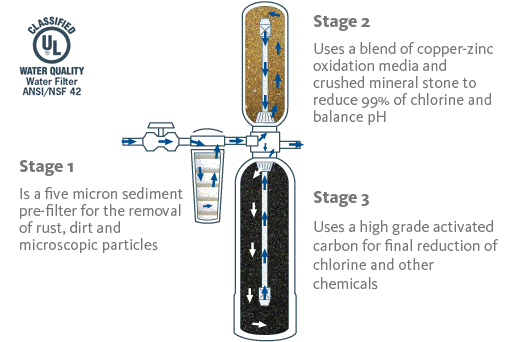
Eg: Dirt or germs are separated
from drinking water before consuming it.
b. To separate non-useful
substances from useful substances
Eg: Separating husk from
grain

c. To separate different
but useful things
Eg: Separating notebooks
from pencils.
3. The method of
separation used depends on various factors:
a. Size of components
b. Use of components
c. Quantity of component
4 a. Handpicking Method:
As the name suggests we separate various
components by using our hands.

b. The method of handpicking can be used for
separating slightly larger sized impurities found in less quantity like the
pieces of dirt, stone, and husk from wheat, rice or pulses.
5 a.
Threshing:
Beating something to that the loose part gets
separated
b. Grain is separated from stalks etc. using
threshing. In this process, the stalks are beaten to free the grain seeds.
Sometimes, threshing is done with the help of bullocks. Machines are also used
to thresh large quantities of grain.

6 a.
Winnowing:
To separate lighter component from heavier
component by blowing or using air/ wind
b. Husk is
separated from seeds using winnowing. The husk particles are carried away by
the wind. The seeds of grain get separated and form a heap near the platform
for winnowing. The separated husk is used for many purposes such as fodder for
cattle.

7 a. Sieving:
In
this method a wired gauge (called sieve) is used which permits the finer
component to pass through and collects the bigger impurities.

b. Common
uses of sieving include separating impurities from flour; and separating
pebbles and stones from sand

8 a.
Sedimentation:
Settling
of heavier component when water is added.
b. Rice
or pulses are usually washed before cooking. When you add water to these, the impurities
like dust particles get separated. These impurities go into water.
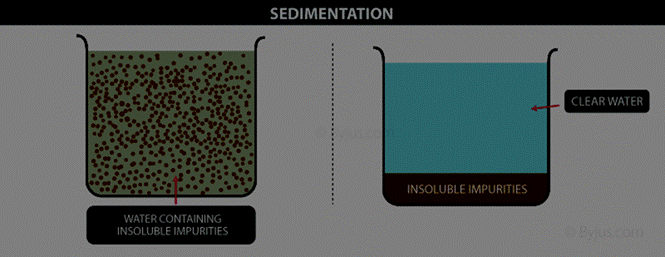
8 c. When
the water (along with the dust) is removed, the process is called decantation.
The component that forms the top layer can then be separated by decantation.
d.
Oil
and water from their mixture can be separated by sedimentation and decantation.
e.

9 a.
Filtration:
This
method is similar to sieving, however, a more porous substance (eg: filter
paper, linen cloth) is used).

b. Common
uses include the process of preparing cottage cheese (paneer).
10 a.
Evaporation:
The
process of conversion of water into its vapours is called evaporation.
b. Common
salt is separated from sea water using this method.

Process:
When sea water is allowed to stand in shallow pits,
water gets heated by sunlight and slowly turns into water vapour, through
evaporation. In a few days, the water evaporates completely leaving behind the
solid salts.
11 a. Condensation:
The
process of conversion of water vapour into its liquid form by cooling the
vapours is called condensation.
b. The dew formed in winters is due to
condensation.

12 a. often more than 1 method is used to separate a mixture.
b. Separating salt and sand.
First add water to the mixture,
this will allow salt to dissolve in water while the sand will remain
undissolved.
Next sand could be separated by
using a filter paper.
To separate salt from water, we
can use evaporation.
13 a. Many liquids (especially
water) dissolves a number of substances in it. However, a given quantity of the
liquid has an upper limit to the amount of substance which is dissoluble.
b.
A saturated solution is one in which no
more of that substance can be dissolved.
c. Saturation limit of
a substance can be increased by heating the mixture, i.e., if a solution of
water and sugar is saturated, we will be able to add more sugar to the solution
if we start heating it.