Fibre to Fabric
Fibres:
Are the materials which are
available in the form of thin, continuous and flexible strands spun into yarn
and made into fabrics.
Yarn:
Yarn is defined as
a long, twisted and continuous strand composed of interlocked fibres or
filaments which are used in knitting and weaving to form cloth.
Fabrics
Are defined as a
cloth material made by knitting or weaving or of threads together.
Types of Fibres:
The fibres of some fabrics such as
cotton, jute, silk and wool are obtained from plants and animals. These are
called natural fibres. Cotton and jute are examples of fibres obtained from
plants. Wool and silk fibres are obtained from animals. Wool is obtained from
the fleece of sheep or goat. It is also obtained from the hair of rabbits, yak
and camels. Silk fibre is drawn from the cocoon of silkworm.
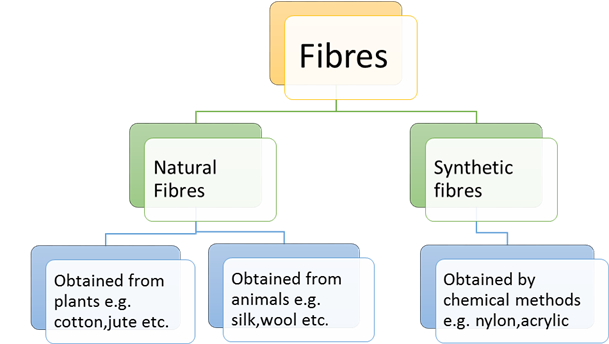
In
the last hundred years or so, fibres are also made from chemical substances,
which are not obtained from plant or animal sources. These are called synthetic
fibres. Some examples of synthetic fibres are polyester, nylon and acrylic.
Some Plant Fibres:
Cotton
Ø
Cotton is used for making wicks for diyas, filling
mattresses, quilts or pillows.
Ø Cotton
plants are usually grown at places having black soil and warm climate.
Ø Some cotton producing Indian states are Punjab, Gujarat,
Madhya Pradesh, Karnataka, Maharashtra etc.
Ø The
fruits of the cotton plant (cotton bolls) are about the size of a lemon.
Ø After
maturing, the bolls burst open and the seeds covered with cotton fibres can be
seen.
Ø From
these bolls, cotton is usually picked by hand. Fibres are then separated from
the seeds by combing. This process is called ginning of cotton.
Ø Ginning
was traditionally done by hand (shown in adjoining figure). These days,
machines are also used for ginning.
Ø


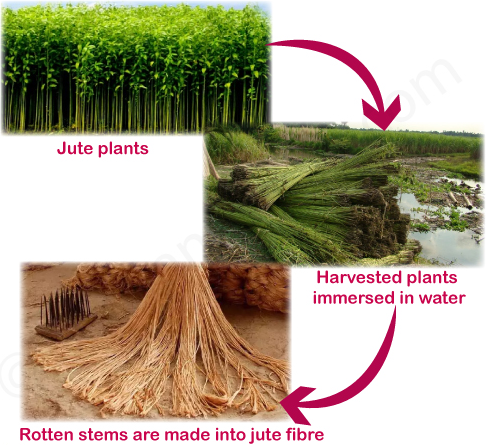
Jute:
Ø Jute is used for making bags, ropes,
mats etc.
Ø Jute
fibre is obtained from the stem of the jute plant (see figure below).

Ø It
is cultivated during the rainy season.
Ø In
India, Jute Is Mainly Grown In West Bengal, Bihar And Assam.
Ø The
Jute Plant Is Normally Harvested When It Is At Flowering Stage.
Ø The
Stems Of The Harvested Plants Are Immersed In Water For A Few Days.
Ø The
Stems Rot And Fibres Are Separated By Hand.
Ø To Make Fabrics,
All These Fibres Are First Converted Into Yarns.
Spinning
Cotton Yarn
Ø The process of making yarn from fibres is called spinning.
Ø In this process, fibres from a mass of cotton wool are drawn
out and twisted. This brings the fibres together to form a yarn.
Ø A simple device used for spinning is a hand spindle, also
called talky (adjoining figure).
Ø Another hand operated device used for spinning is charkha
(Fig. below).

Ø Use of charkha was popularized by Mahatma Gandhi as part of
the Independence movement. He encouraged people to wear clothes made of
homespun yarn termed as khadi and shun imported cloth made in the mills of
Britain.
Ø To popularize and promote khadi, the Government of India
constituted a body called Khadi and Village Industries Commission in 1956.
Ø Spinning of yarn on a large scale is done with the help of
spinning machines.
Ø After spinning, yarns are used for making fabrics.
Yarn into Fabric:
The two main processes by which fabrics are
made from yarns are weaving and knitting.
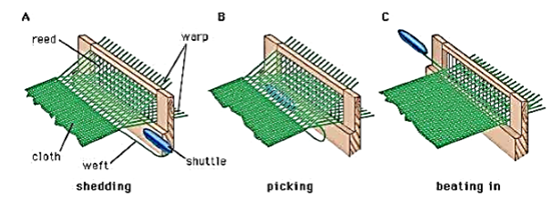
Weaving:
The process of arranging two sets of yarns together to
make a fabric is called weaving. Weaving of fabric is done on looms (Fig.
below). The looms are either hand operated or power operated which interlaces
two sets of yarn at right angles to each other.
Knitting:
In knitting, a single yarn is used to make a piece
of fabric. Socks and many other clothing items are made of knitted fabrics.
Knitting is done by hand and also on machines.

History of Clothing Material
Ø In
ancient times people used the bark and big leaves of trees or animal skins and
furs to cover themselves.
Ø After
people began to settle in agricultural communities, they learnt to weave twigs
and grass into mats and baskets. Vines, animal fleece or hair were twisted
together into long strands. These were woven into fabrics.
Ø The
early Indians wore fabrics made out of cotton that grew in the regions near the
river Ganga.
Ø Flax is
also a plant that gives natural fibres.
Ø In
ancient Egypt, cotton as well as flax were cultivated near the river Nile and
were used for making fabrics.
Ø In
those days, stitching was not known. People simply draped the fabrics around
different parts of their body. Many different ways of draping fabrics were
used.
Ø With
the invention of the sewing needle, people started stitching fabrics to make
clothes. Stitched clothes have gone through many variations since this
invention.
