Nutrition
In Plants
1. Nutrition
1.1 Why is food essential?
The food contains several components such as carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals. These are called nutrients.
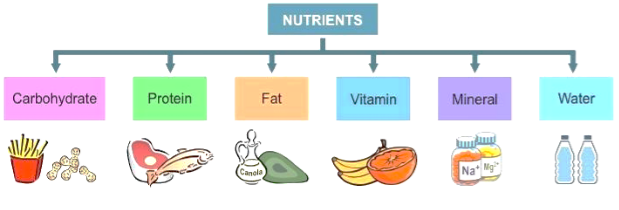
Nutrients
are essential as they enable living organisms to build their bodies, to grow,
to repair damaged parts of their bodies and provide the energy to carry out
life processes.
1. Nutrition
1.1 Why is food essential?
The food contains several components
such as carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals. These are called
nutrients

Nutrition is the mode of taking food by an organism and its utilization by the body.
1.2 How is food produced?
Plants can make their own food,
whereas animals including humans cannot and thus depend on plants and other
animals for their food.
Animals are directly or indirectly
dependent on plants for their food as animals get food either from plants or
other animal-eating plants.
1.3 Different mode of nutrition
Nutrition is the mode of taking food
by an organism and its utilization by the body.
A. The mode of nutrition in which organisms make food themselves from a simple substance is called autotrophic (auto = self; trophs = nourishment). Most plants are autotrophs.

B. The mode of nutrition in which
organisms don't make their own food and depend on others is called
heterotrophic (hetero = other; trophos = nourishment). Animals are
heterotrophs.

2. Photosynthesis: The
process of producing food in plants
2.1 What is photosynthesis?
Plants use water, minerals, carbon
dioxide from their surroundings to make their food in the presence of sunlight
and chlorophyll-containing pigment, this process is called photosynthesis.
Photo means light, and synthesis means preparation of food.
2.2 Where is food produced in plants?
The synthesis of food takes place in
the leaves. Therefore, it is called the food factory.
2.3 How does the raw material reaches the leaf?
A. Water and minerals from the soil
are absorbed by the roots and transported to the leaves.
B. Carbon dioxide from air is taken
through tiny pores, called stomata, present on the surface of the leaves.
C. The green pigment, called
chlorophyll, on the leaves helps in capturing the energy of the sunlight to
prepare food.
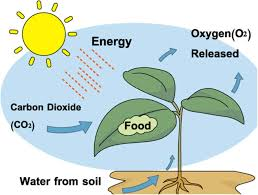
What is produced as a result of
photosynthesis?
As a result of photosynthesis, oxygen and carbohydrates is formed in the plants.
![]()
Carbon dioxide + Water (in presence of sunlight and
chlorophyll) gives Carbohydrates + Oxygen
2.4 Synthesis of other nutrients in plants:
A. Starch: Carbohydrates convert into starch.
B. Proteins and Fats: With the help of nitrogen, plants can synthesise components of food other than carbohydrates such as proteins and fats.
Where does the plant gets the nitrogen from?
Nitrogen is present in abundance in gaseous form in the air.
However, plants cannot absorb nitrogen in this form. Soil has certain bacteria that
convert gaseous nitrogen into a usable form and release it into the soil. These
soluble forms are absorbed by the plants along with water.
2.5 Can photosynthesis occur without sunlight?

Solar
energy is used to prepare food, therefore, photosynthesis is not possible in
the absence of sunlight. Thus, the sun is the ultimate source of energy for all
living organisms.
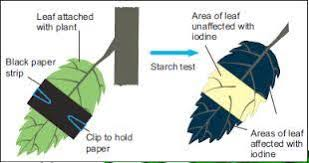
Experiment to show sunlight is essential
for photosynthesis
To verify our reasoning, we can perform an iodine test (an iodine test is used to confirm the presence of starch) on a part of leaf covered with a black paper to block sunlight (say, for 3-4- days). The iodine test fails proving that a plant away from sunlight has not made any food.
2.6 Can photosynthesis occur without chlorophyll?
Besides leaves, green parts of the plant — in green stems
and green branches. The desert plants have scale- or spine-like leaves to
reduce the loss of water by transpiration.
These plants have green stems which carry out photosynthesis.

The
leaves other than green also have chlorophyll. The large amount of red, brown
and other pigments mask the green color Photosynthesis takes place in these
leaves also.

There
are some plants which do not have chlorophyll. They cannot synthesise their
food. Thus, they follow heterotrophic mode of nutrition.
3. Alternate mode of nutrition in plants:
There are some plants which do not
have chlorophyll. They cannot synthesise
their food. Thus, they follow alternate mode of nutrition.
3.1 Parasitic mode of nutrition

This is a plant called Cuscuta
(Amarbel). It does not have chlorophyll. It takes readymade food from the plant
on which it is climbing. The plant on which it climbs is called a host. Since
it deprives the host of valuable nutrients, it is called a parasite.
3.2 Insectivorous plants
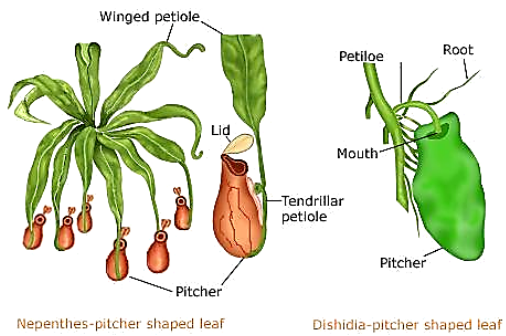
Adaptation:
The pitcher-like structure is the modified part of the leaf. The apex of the leaf forms a lid which can open and close the mouth of the pitcher. Inside the pitcher there are hairs which are directed downwards.
Process:
When an insect lands in the pitcher,
the lid closes and the trapped insect gets entangled into the hair. The insect
is digested by the digestive juices secreted in the pitcher. Such insect-eating
plants are called insectivorous plants.
3.3 Saprotrophic mode of nutrition
Have you seen fluffy umbrella-like patches growing on bread? These organisms are called fungi. Fungi also grow on pickles, leather, clothes and other articles that are left in hot and humid weather for long time.

Why fungi growth increases in rainy season?
This happens because the fungal spores are generally present
in the air. When they land on wet and warm things they germinate and grow.
They have a different mode of nutrition. They secrete digestive juices on the dead and decaying matter and convert it into a solution. Then they absorb the nutrients from it. This mode of nutrition is called saprotrophic nutrition. Plants which use saprotrophic mode of nutrition are called saprotrophs.
3.4 Symbiotic Relationship in Plants
Some organisms live together and
share shelter and nutrients. This is called symbiotic relationship.
Examples of Symbiotic relationship:
1. Certain fungi live in the roots of trees. The tree provides nutrients to the fungus and, in return, receives help from it to take up water and nutrients from the soil.

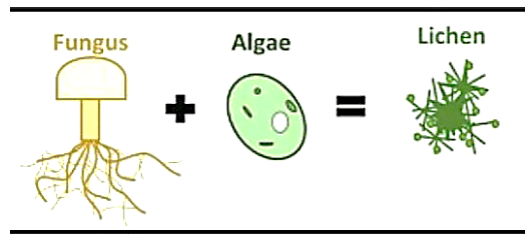
2. Lichen: Symbiotic relationship
between fungus and algae. Have you seen green patches on ponds? These are
algae. They have chlorophyll.

In
organisms called lichens, a chlorophyll-containing partner, which is an alga,
and a fungus live together. The fungus provides shelter, water and minerals to
the alga and, in return, the alga provides food which it prepares by
photosynthesis.
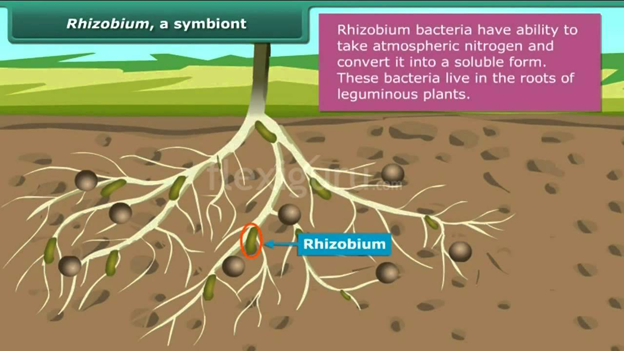
3. Rhizobium and Legume
The bacterium called Rhizobium can
take atmospheric nitrogen and convert it into a soluble form. But Rhizobium
cannot make its own food. So it lives in the roots of gram, peas, moong, beans
and other legumes and provides them with nitrogen. Most of the pulses (deals)
are obtained from leguminous plants. In return, the plants provide food and
shelter to the bacteria. They have a symbiotic relationship.
Why does farmers not need to put fertilizers on legumes?
The farmers do not need to add nitrogen fertiliser to the
soil in which leguminous plants are grown because the Rhizobium bacteria is
sufficient providing the necessary nitrogen.
4. Replenishing the soil with
nutrients
4.1 Why are fertilisers added to soil after harvest?
Since plants absorb mineral
nutrients from the soil, hence their amounts in the soil keep on declining.
Fertilisers and manures contain plant nutrients such as nitrogen, potassium,
phosphorous, etc. These nutrients need to be added from time to time to enrich
the soil.
