Wastewater Story
What is Water Pollution ?
Define water
pollutants and name the major water pollutants.
When
the water present on earth in the oceans, seas, rivers, lakes, ponds and under
the ground gets contaminated, it is termed as water pollution. The
contamination of water results in a change in its physical, biological and
chemical properties and hence makes it unsafe for drinking or usage of other
purposes. The substances that cause water pollution are called Water
Pollutants. The pollution of water can lead to serious effects such as
diseases, an effect on the ecosystem of a region, and loss of aquatic life.
Major Water Pollutants
·
Sewage: a massive amount of
wastewater or sewage is dumped into water bodies such as rivers and seas which
pollutes their freshwater and makes it inappropriate for any kind of
consumption due to the rise of several bacteria and other microorganisms. It
not only affects the aquatic life of the water body but also leads to severe
diseases like cholera, diarrhoea and typhoid.
·
Industrial Chemical Wastes: Harmful chemicals such as
lead and mercury are often dumped by industries into the water bodies directly
which contaminate their water.
·
Agricultural Effluents: Fertilizers, pesticides,
insecticides and farm wastes are often washed off by the rain to the water
bodies and contaminate the water.
·
Oil Spills: Oil spills often occur due
to accidents and leakages of oil in the sea which leads to loss of aquatic
life.
·
Thermal Wastes: Thermal industries often
spill warm water in the water bodies which decreases its oxygen content. It
also leads to a rise in temperature of water which is not suitable for aquatic
animals.
·
Suspended Solids: They come from soil
erosion, untreated sewage and mining. These suspended pollutants block the
sunlight from reaching the aquatic plants and animals.
What is wastewater?
The water
that has been used and is not fit for usage again is called Wastewater.
It is dirty water from the laundry, toilets, sinks and drains.
|
Organism |
Diseases |
Remarks |
|
Ascaris sp. |
Nematode
worms |
Danger
to man from polluted water and dried sludge used as a fertilizer. |
|
Bacillus anthracis |
Anthrax |
Found
in waste water spores are resistant to treatment. |
|
Virus |
Poliomyelitus hepatitis |
Waste
water treatment plants |
|
Shigella sp. |
Bacillary
dysentery |
Polluted
water |
|
Vibrio cholarae |
Cholera |
Polluted
water |
|
E. coil |
Diarrhoea |
Polluted
water |
Water - Our Lifeline
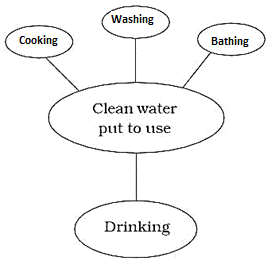
Figure 1:
Usage of clean water
·
We all need clean water however, not all can access
the same.
·
Hence, it is necessary not only to preserve water
but clean the used water before dumping it into the seas or any other water
body.
·
This is why the United Nations proclaimed the
period between 2005 and 2015 as the International decade for action on
‘water for life’.
What do you mean by cleaning of water?
It is a
process in which the pollutants from the water are removed before the water
reaches a water body or before it is used again. This process is also
called Sewage Treatment.
What is sewage?
·
Wastewater from houses, offices, Industries,
hospitals and other sources is called Sewage.
·
Rainwater that flows into the drains during heavy
rainfalls is also sewage because it contains pollutants that it washes off from
the roads.
·
Any liquid waste can be called sewage.
·
Sewage water contains impurities mixed into it as
well as some suspended pollutants.
·
These impurities present in the sewage are
called Contaminants as they contaminate the water.

Figure 2:
Sewage is a mixture of impurities
Water freshens up - An
Eventful Journey
·
Sewers - Large and small pipes that are installed in
buildings to carry sewage water are sewers.
·
Sewerage - A network or transport system consisting
of sewers is called Sewerage.
·
It carries sewage water from the point where it is
produced to the point where it is disposed (treatment plant).
·
It consists of manholes that are located at every
50 to 60 metres.
·
The manholes are installed at a point where two or
more sewers intersect or change their directions.
·
Every locality has as a system that allows removal
of waste from the houses and industries.
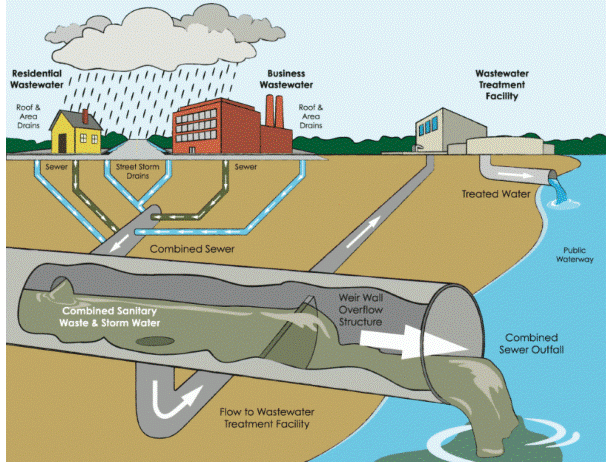
Figure 3:
Sewerage
Wastewater Treatment
Plant (WWTP)
Wastewater
includes biological, physical and chemical matter and hence involves
biological, physical and chemical processes of removal of the contaminants.
The physical and biological process of
treatment of water:
1. Separation of Large Objects from Sewage Water
The
wastewater is first passed through bar screens which remove
big objects from the water like plastic bottles, napkins, rags, cans and
sticks.

Figure 4:
Bar Screens
2. Separation of Sand and Dirt
The
wastewater is then sent to a grit and sand removal tank. The speed
of the water is decreased at this step. This allows the sand, dirt and pebbles
to settle down.

Figure 5:
Sand and Girt Removal Tank
3. Removal of Solids
·
Now the water cycles in a tank called Clarifier which
is sloped in the centre. This lets the solids like faeces
to settle at the bottom. This is called Sludge.
·
The sludge is then separated from the water with
the help of a Scrapper.
·
Substances like oil and grease are removed with the
help of a Skimmer as they float above the water. In this step
clarified water is obtained.
·
The sludge so obtained is passed into a tank
where anaerobic bacteria can decompose it and produce biogas.
The biogas is then used as a fuel.

4. Suspended Sludge Removal
·
The clarified water also needs to be cleaned
further. Hence, it is moved to an aerator that pumps air into
it.
·
This allows aerobic bacteria to grow in this water.
·
The aerobic bacteria consume
organic waste, soaps, food waste and other elements that remain in the
clarified water.
·
This water is allowed to settle for several hours
and then these waste materials settle down in the tank. This is called Activated
Sludge.
·
The water is removed from the top of this sludge
with the help of machines or sand drying beds. The sludge is then dried and can
be used as manure.

Figure 6:
Aerator
This
treated water contains fewer amounts of impurities and suspended matter. This
water is safe to dump into a water body or under the ground. Hence, it is then
discharged into a sea, river or underground. Nature further cleans it up.
Chemical Treatment of Wastewater:
·
Sometimes harmful chemicals can be present in the
water even after treating them physically and biologically.
·
These chemicals are therefore removed by using
disinfectants such as chlorine and Ozone.
·
Often chlorine gas or ozone gas is introduced in
this water which purifies it chemically.
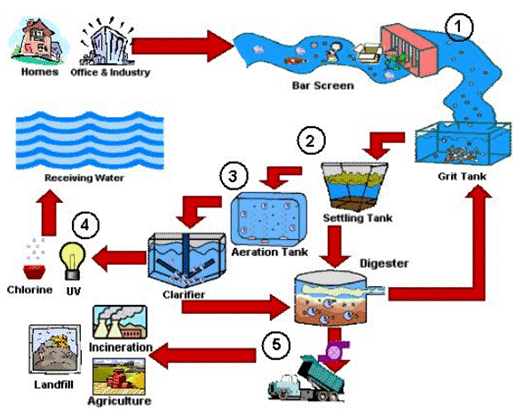
Figure 7:
WWTP
Eucalyptus Plant and Cleaning of Water
Eucalyptus
plants can absorb the water at a faster rate and then they release pure water vapour. In this way, they act as a natural water purifier.
Hence, it is advised to plant Eucalyptus trees along the sewage ponds.

Figure 8:
Eucalyptus Plant
Why should we adopt better housekeeping
practices and become an active citizen?
·
We should try to reduce the waste that produced in
our households so that there is not much pressure on WWTP. It is often
difficult to clean tons of wastewater.
·
The sewage water can cause several problems such as
harmful diseases, unhygienic and unsanitary conditions in the locality.
·
Hence, we can be more considerate about producing a
limited amount of waste and we can accomplish this by adopting better
housekeeping practices.
·
Also, we can become an active citizen by making
sure that there are no open drains or sewers in our locality. If we find any we
should immediately report the same to the municipality.
What better housekeeping practices we can
adopt?
A good
way to minimise the sewage water is to check what is
going in our drains. If we dispose of our waste properly we may be able to
reduce the sewage. Here are some housekeeping practices that we should adopt:
·
We should through all the oil and fats in dustbin
rather than throwing them of the dream. Oil and fats harden and block the
drains. Moreover, it is difficult to separate them from the water.
·
We should not throw chemicals in the drains like
insecticides, pesticides or medicines. They can kill the microbes in the water
that help in its purification.
·
We should not throw things in the drain that can
block them like tea leaves, food remains, cotton, soft toys etc. We should
always through them in the dustbin.
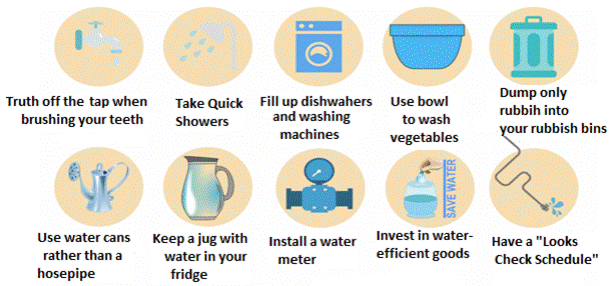
Figure 9:
Treating Water at home
Sanitation and Disease
·
Sanitation refers to the health conditions of
people related to the disposal of sewage, human excreta and provision of clean
drinking water.
·
Poor sanitation and polluted drinking water can
lead to many diseases.
·
Hence, a sanitation system aims to provide a clean
environment for us so that we can stay away from diseases.
·
Improper sanitation can give rise to different
diseases that arise from contaminated water such as typhoid, dysentery,
hepatitis, polio, cholera and meningitis.
·
The human excreta is a health hazard and can lead
to soil and water pollution. It can pollute the surface water and groundwater.
Hence people should never defecate in open areas.
Alternative Arrangement for Sewage Disposal
·
As an alternative for sewage disposal on-site
sewage is being used nowadays, for example, septic tanks, compost pit
toilets and chemical toilets.
·
The onsite sewage treatments use natural procedures
to treat and dispose of the wastewater or sewage.
·
This system is suitable in places where there is no
central wastewater collection system.
o
Septic Tanks – A septic tank is often
installed under the ground in houses or buildings such as hospitals. It allows
decomposition of sewage from home through the action of anaerobic bacteria.
o
Chemical Toilets – A chemical toilet has a
separate compartment that treats human waste with chemicals and decreases their
odour.
o
Composting Toilets – A composting toilet
treats human waste with biological processes. The aerobic bacteria are present
in a storage tank that act upon the waste and turn it into compost.
Many
organizations have also installed on-site hygienic waste disposal technology in
which the human excreta directly flows into a biogas plant and is then used as
an energy resource.
Sanitation at Public Places
·
There are numerous places in our country which are
very busy such as airports, railway stations and bus depots.
·
Many times large gatherings such as fairs and
festivals are also organized where a large number of people visits.
·
This results in the generation of large amounts of
waste and if the waste is not treated properly it can lead to several diseases
and even an epidemic.
·
Hence we should all become aware and contribute to
maintaining sanitation not only in our homes but also at public places.
·
If we adopt certain practices at public places we
can help in maintaining their sanitation, for instance:
o
We should not throw garbage in public places and
always use the dustbins.
o
We should not spit around in a public place.