Coal and petroleum

![]() In
our daily life, we use both natural and man -made materials.
In
our daily life, we use both natural and man -made materials.
![]() There
are two types of resources,
natural and manmade.
There
are two types of resources,
natural and manmade.

![]() Natural materials or resources are obtained directly from
nature (plants or animals or earth).
Natural materials or resources are obtained directly from
nature (plants or animals or earth).
Example: Wood, clay,
fibres, leather, minerals, metals, natural rubber, etc.

![]() Synthetic materials or resources are made by
man from natural resources to improve our daily life.
Synthetic materials or resources are made by
man from natural resources to improve our daily life.
Example:
Paper, plastics, polymers,
synthetic fibres like nylon, polyester, and materials like concrete, glass,
etc.

Renewable and non -
renewable resources
![]() Natural
resources can be classified into two types, exhaustible and non- exhaustible.
Natural
resources can be classified into two types, exhaustible and non- exhaustible.
|
Exhaustible resources |
Inexhaustible resources |
|
Ø Exhaustible
resources or non- renewable
resources are present in nature only in limited amounts. They can be
exhausted by human activities, and once they are exhausted, it takes a very
long time by nature to replenish them. Ø Examples
of exhaustible resources are coal, petroleum, natural gas, etc.
|
Ø Inexhaustible resources or renewable resources are those which are present in nature in
unlimited quantity. They can be replenished by nature again and again. Ø
Examples
of inexhaustible resources are water, wind, soil, sunlight, air, etc.
|

![]() Even though water is a renewable resource,
mismanagement of water decreases its availability at a certain place. So, it
can be treated as a non-renewable resource.
Even though water is a renewable resource,
mismanagement of water decreases its availability at a certain place. So, it
can be treated as a non-renewable resource.

![]() Over
exploitation of non-renewable resources leads to decrease in their availability
for future generations. So, they should be used sustainably.
Over
exploitation of non-renewable resources leads to decrease in their availability
for future generations. So, they should be used sustainably.
Fossil fuels
![]() The
fuels derived from dead and decaying remains of plants and animals (fossils)
are called fossil fuels.
The
fuels derived from dead and decaying remains of plants and animals (fossils)
are called fossil fuels.
![]() Coal,
petroleum, and natural gas are common examples of fossil fuels.
Coal,
petroleum, and natural gas are common examples of fossil fuels.

Coal

![]() Coal is a black, solid rock like
substance that can be burned as a fuel.
Coal is a black, solid rock like
substance that can be burned as a fuel.
![]() It is used to cook food, to produce
steam in thermal power plants, and as a fuel in many industrial processes.
It is used to cook food, to produce
steam in thermal power plants, and as a fuel in many industrial processes.
![]() It is also used in paper manufacture,
alumina refineries, and chemical & pharmaceutical industries.
It is also used in paper manufacture,
alumina refineries, and chemical & pharmaceutical industries.
![]() Several chemical products can be
obtained from coal products and by-products.
Several chemical products can be
obtained from coal products and by-products.
![]() Earlier, it was used in railway engines
to produce steam.
Earlier, it was used in railway engines
to produce steam.
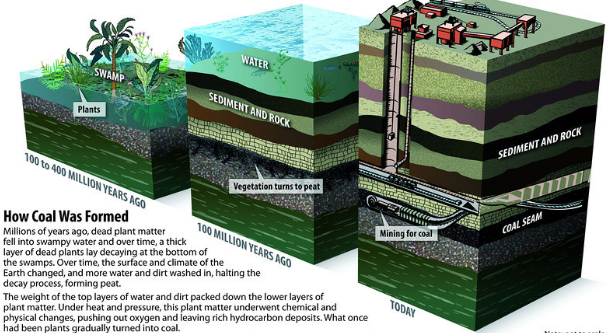
![]() The process of coal mining is shown
below
The process of coal mining is shown
below


![]() About
300 million years ago, due to natural processes like flooding, dense forests
got buried under the soil.
About
300 million years ago, due to natural processes like flooding, dense forests
got buried under the soil.
![]() As
more soil got deposited upon them, they sank deeper and deeper into the earth.
As
more soil got deposited upon them, they sank deeper and deeper into the earth.
![]() There,
due to high temperature and pressure, they got compressed and were converted
into coal.
There,
due to high temperature and pressure, they got compressed and were converted
into coal.
![]() As
coal contains mainly carbon, the slow process of conversion of dead vegetation
into coal is called
carbonisation.
As
coal contains mainly carbon, the slow process of conversion of dead vegetation
into coal is called
carbonisation.
![]() When
burnt in air, coal gives carbon dioxide gas.
When
burnt in air, coal gives carbon dioxide gas.
![]() There
are four types of coal; Lignite, sub- bituminous, bituminous, and anthracite.
There
are four types of coal; Lignite, sub- bituminous, bituminous, and anthracite.

![]() Coal
is used to produce industrially useful products like coke, coal tar, and coal
gas.
Coal
is used to produce industrially useful products like coke, coal tar, and coal
gas.
Coke

![]() Coke
is a tough, porous, black substance with high carbon content and few
impurities.
Coke
is a tough, porous, black substance with high carbon content and few
impurities.
![]() It
is an almost pure form of carbon and is prepared by heating coal in the absence
of air.
It
is an almost pure form of carbon and is prepared by heating coal in the absence
of air.
![]() Coke
is used in blast furnaces for smelting (extracting) iron and also in
blacksmithing.
Coke
is used in blast furnaces for smelting (extracting) iron and also in
blacksmithing.

Coal
tar

![]() Coal
tar is a thick, black liquid with an unpleasant smell.
Coal
tar is a thick, black liquid with an unpleasant smell.
![]() It
is produced by distilling bituminous coal, and contains about 200 substances.
It
is produced by distilling bituminous coal, and contains about 200 substances.
![]() Substances
obtained from coal tar are used as starting materials for manufacturing various
substances used in everyday life.
Substances
obtained from coal tar are used as starting materials for manufacturing various
substances used in everyday life.
![]() It
is used in surfacing of roads, synthetic dyes, medicines & drugs,
explosives, perfumes, plastics, paints, photographic materials, roofing, etc
It
is used in surfacing of roads, synthetic dyes, medicines & drugs,
explosives, perfumes, plastics, paints, photographic materials, roofing, etc
![]() It
contains many chemicals like benzene, naphthalene (moth repellent), aniline,
etc.
It
contains many chemicals like benzene, naphthalene (moth repellent), aniline,
etc.
![]() Nowadays,
coal tar is replaced by bitumen, a petroleum product for surfacing the roads.
Nowadays,
coal tar is replaced by bitumen, a petroleum product for surfacing the roads.



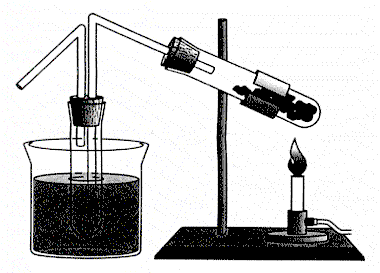
Coal gas
![]() Coal
gas is a mixture of gases like methane, hydrogen and carbon monoxide obtained
during destructive distillation of coal.
Coal
gas is a mixture of gases like methane, hydrogen and carbon monoxide obtained
during destructive distillation of coal.
![]() It
is obtained during the production of coke and is used as a fuel.
It
is obtained during the production of coke and is used as a fuel.
![]() Earlier,
in 1810, coal gas was used for street lighting in London and in 1820 in New
York. Nowadays, it is used as a source of heat.
Earlier,
in 1810, coal gas was used for street lighting in London and in 1820 in New
York. Nowadays, it is used as a source of heat.
Petroleum

![]() Petroleum
is a liquid fossil fuel occurring beneath the earth’s surface that can be
refined and used as a fuel.
Petroleum
is a liquid fossil fuel occurring beneath the earth’s surface that can be
refined and used as a fuel.
![]() Petroleum
products are obtained from petroleum and include gasoline, diesel, petrol, jet
fuel, heating oil, paraffin wax, dyes, lubricating oils, asphalt, etc.
Petroleum
products are obtained from petroleum and include gasoline, diesel, petrol, jet
fuel, heating oil, paraffin wax, dyes, lubricating oils, asphalt, etc.
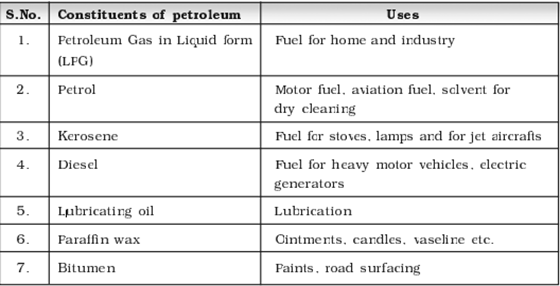
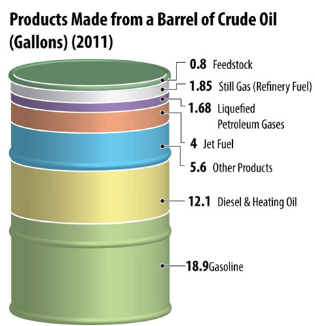
![]() There
are around 6000 items obtained from petroleum.
There
are around 6000 items obtained from petroleum.

![]() Due
to its great commercial importance, petroleum is called black gold.
Due
to its great commercial importance, petroleum is called black gold.

![]() Petroleum
was formed from organisms living in the sea.
Petroleum
was formed from organisms living in the sea.
![]() As
these organisms died, their bodies settled under the sea and got deposited with
layers of sand and clay.
As
these organisms died, their bodies settled under the sea and got deposited with
layers of sand and clay.
![]() Over
millions of years, in the absence of air, high temperature and pressure
transformed them to petroleum and natural gas.
Over
millions of years, in the absence of air, high temperature and pressure
transformed them to petroleum and natural gas.
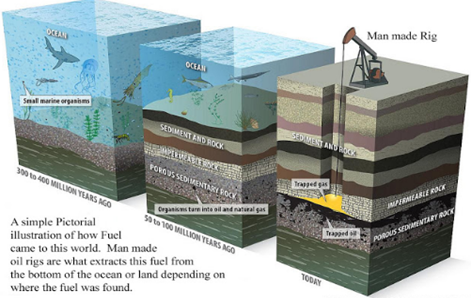
![]() Petroleum
is insoluble in water and has lesser density than water. So, it forms a
separate layer above that of water.
Petroleum
is insoluble in water and has lesser density than water. So, it forms a
separate layer above that of water.
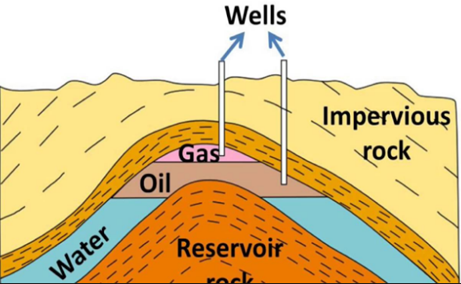
![]() The
world’s first oil drill was in Pennsylvania in 1859.
The
world’s first oil drill was in Pennsylvania in 1859.

![]() In
1867, oil was found at Makum in Assam.
In
1867, oil was found at Makum in Assam.

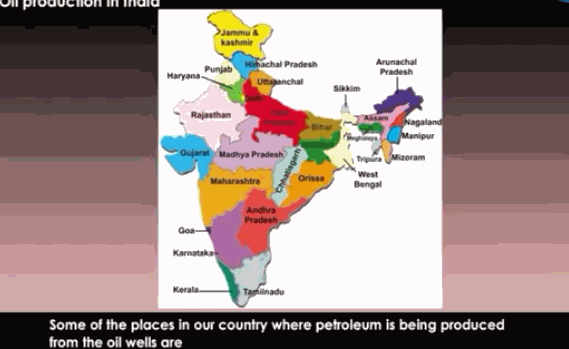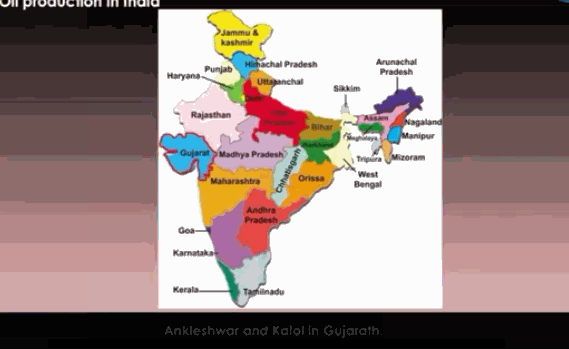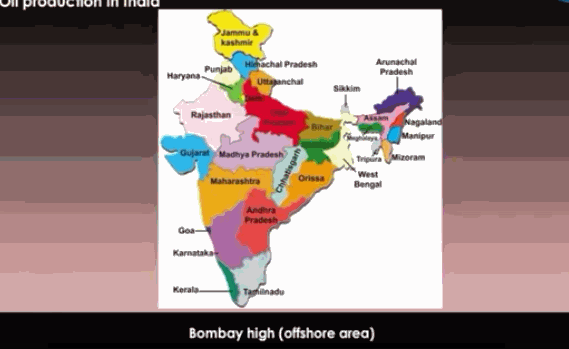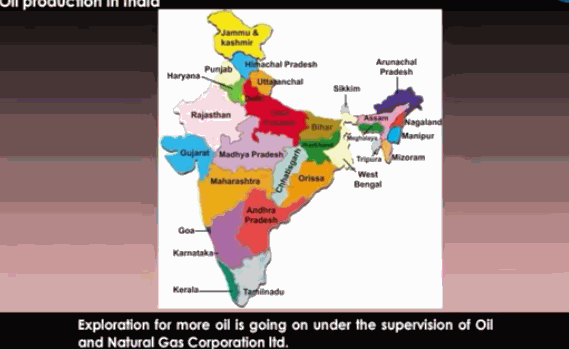
![]() In
India, oil is found in Assam, Gujarat, Mumbai High, and in river basins of
Krishna and Godavari.
In
India, oil is found in Assam, Gujarat, Mumbai High, and in river basins of
Krishna and Godavari.
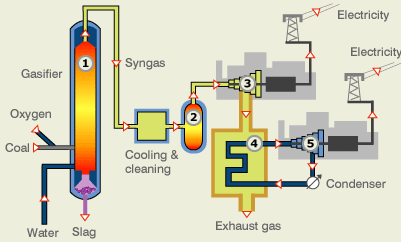
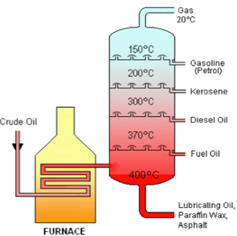
Refining of petroleum
![]() The
process of separating various constituents or fractions of petroleum is known
as refining. It is carried out in petroleum
refineries.
The
process of separating various constituents or fractions of petroleum is known
as refining. It is carried out in petroleum
refineries.

![]() The
crude petroleum obtained from drills is transformed into gasoline, petrol,
diesel, etc.
The
crude petroleum obtained from drills is transformed into gasoline, petrol,
diesel, etc.
![]() Petroleum
refineries involve many different processing units and storage tanks.
Petroleum
refineries involve many different processing units and storage tanks.

![]() Each
refinery has its own arrangement and processing methods based on its location,
crude oil availability, economic considerations, etc.
Each
refinery has its own arrangement and processing methods based on its location,
crude oil availability, economic considerations, etc.
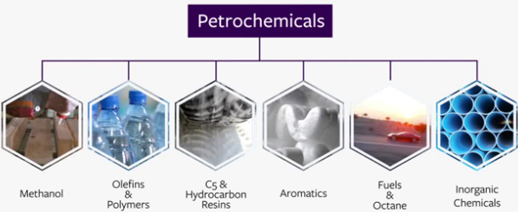
Petrochemicals
![]() Petrochemicals
are the substances obtained from petroleum and natural gas.
Petrochemicals
are the substances obtained from petroleum and natural gas.
![]() They
are used in manufacturing detergents, fibres like polyester, nylon, acrylic,
plastics, paints, wax, etc.
They
are used in manufacturing detergents, fibres like polyester, nylon, acrylic,
plastics, paints, wax, etc.

![]() Petrochemicals are a collection of pure
chemical compounds, whereas petroleum products are complex mixtures.
Petrochemicals are a collection of pure
chemical compounds, whereas petroleum products are complex mixtures.
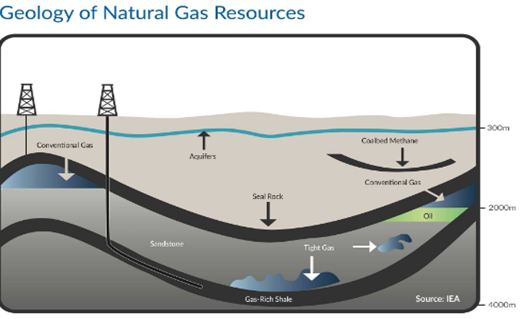
Natural
gas

![]() Natural
gas or fossil gas is a gas consisting of mainly methane and a small percentage
of carbon dioxide, nitrogen, helium, etc.
Natural
gas or fossil gas is a gas consisting of mainly methane and a small percentage
of carbon dioxide, nitrogen, helium, etc.
![]() It
was formed from layers of decomposed plant and animal matter exposed to high
temperature and pressure over millions of years.
It
was formed from layers of decomposed plant and animal matter exposed to high
temperature and pressure over millions of years.
![]() Natural
gas is used as a starting material for manufacture of chemicals and
fertilizers.
Natural
gas is used as a starting material for manufacture of chemicals and
fertilizers.
![]() Hydrogen
gas obtained from natural gas is used for production of fertilisers like urea.
Hydrogen
gas obtained from natural gas is used for production of fertilisers like urea.
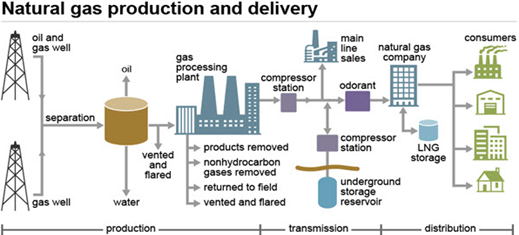
![]() Natural
gas can easily be transported through pipelines and is used in homes and
industries as it can be directly used for burning.
Natural
gas can easily be transported through pipelines and is used in homes and
industries as it can be directly used for burning.

![]() Pipeline
network exists in some parts of Delhi, Vadodara, and some other places.
Pipeline
network exists in some parts of Delhi, Vadodara, and some other places.
![]() It
is usually stored under high pressure as compressed natural gas (CNG).
It
is usually stored under high pressure as compressed natural gas (CNG).
![]() CNG
is nowadays used as fuel in vehicles as it is a cleaner and less polluting
fuel.
CNG
is nowadays used as fuel in vehicles as it is a cleaner and less polluting
fuel.
![]() In
India, natural gas is found in Tripura, Rajasthan, Maharashtra, and in Krishna
and Godavari delta.
In
India, natural gas is found in Tripura, Rajasthan, Maharashtra, and in Krishna
and Godavari delta.
Conservation of natural
resources

![]() Fossil
fuels are non-renewable or exhaustible resources and it is necessary to
conserve them.
Fossil
fuels are non-renewable or exhaustible resources and it is necessary to
conserve them.
![]() The
known reserves of these resources could last only a few hundred years, but they
take millions of years to be formed.
The
known reserves of these resources could last only a few hundred years, but they
take millions of years to be formed.
![]() These
fuels cannot be prepared in laboratories or by artificial methods.
These
fuels cannot be prepared in laboratories or by artificial methods.
![]() The
burning of fossil fuels causes air pollution and global warming. So they should
be used only when absolutely necessary.
The
burning of fossil fuels causes air pollution and global warming. So they should
be used only when absolutely necessary.
![]() This
will help to prolong their availability and reduce environmental damage.
This
will help to prolong their availability and reduce environmental damage.
PCRA (Petroleum Conservation Research Association) advises people to save petrol by:-
![]() Driving
at a constant and moderate speed
Driving
at a constant and moderate speed
![]() Switching
off the engines during traffic
Switching
off the engines during traffic
![]() Ensuring
correct tyre pressure
Ensuring
correct tyre pressure
![]() Ensuring
regular maintenance of the vehicle.
Ensuring
regular maintenance of the vehicle.

