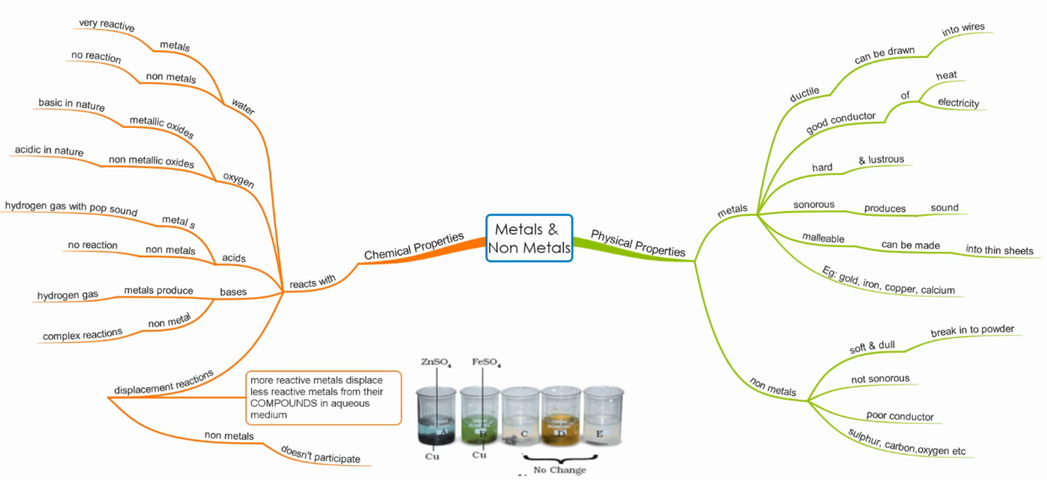
Materials: Metals and Non-Metals
Physical properties of Metals
1a.
Metals can conduct electricity and heat, i.e., they let current and heat pass
through it easily.
1b. Application:
Copper is
used to make electrical wires. Aluminum is used to make cooking utensils.

2a.
Metals are ductile, which means that they can be drawn into wires.
2b. Application:
Copper is
used to make wires.

3a.
Metals are hard because of the packing of its atoms.
3b. Application:
Iron is
used in making buildings.

3c. Exception:
Sodium
and potassium are soft and can be cut with a knife.

4a.
Metals are lustrous (shiny), which means that they reflect light from their
surface and can be polished.
4b. Application:
Metals
are used to make jewelry.

4c. Exception: Pure sodium and potassium are not lustrous.


5a.
Metals are malleable, which means that they can be beaten into thin sheets.
5b. Application: Silver or aluminum foil to keep food warm.


6a. Most metals remain solid at room temperature.
6b. Application: Metals can be used for many things.
6c. Exception: Mercury and gallium which remain liquid at room
temperature.

7a.
Metals produce ringing sounds when they are struck and hence, they are
sonorous,
7b. Application: Bells are made of metals.

7c. Exception: Mercury is not sonorous at room temperature as it
is liquid state.
Physical properties of Non-Metals
1a.
Non-Metals cannot conduct electricity and heat, i.e., they do not let current
and heat pass through it easily.
1b. Use: Handles of cooking utensils are made of rubber.
Resistors are made of non-metals.

1c. Exception: Graphite is a good conductor of electricity.
2a.
Non-Metals are brittle, which means on striking they break.
3a. Most non-metals are soft.
3b.
Diamond is the hardest material found on Earth

4a. Most non-metals are dull in appearance.
4b. Exception: Diamond is shiny.
5a.
Non-metals are easily breakable and hence non-malleable.
6a. Most
non-metals exist in two of the three states of matter at room temperature:
Gases (such as oxygen), and Solids (such as carbon)
7a.
Non-metals do not produce ringing sounds when they are struck.
8.
Despite lacking the properties, non-metals are very useful. Some of the
applications are:
8a.
Essential for life (such as oxygen)
8b. Used
as fertilizers (such as nitrogen and phosphorus)
8c. Used
to purify water (such as chlorine)
8d.
Applied on wounds as an antiseptic (such as purple-colored iodine solution)
8e. Used
in crackers (such as sulphur)
Chemical properties of Metals
A. Reaction with Oxygen
When
metals react with oxygen, they form metal oxide.
Metal + O2 →
Metal Oxide
Examples:
1. Rusting
of Iron

Iron
erodes (form a red layer) in presence of oxygen and water thus forming iron
oxide.
Iron (Fe) + Oxygen (O2) + Water (H2O)
→ Ferric Hydroxide (Fe(OH)3)
2. Magnesium
burns in oxygen to form magnesium oxide.

Magnesium (Mg) + Oxygen (O2) →
Magnesium Oxide (MgO)
3. Verdigris
of copper
When a
copper vessel is exposed to moist air for long, it acquires a dull green
coating.

Copper (Cu) + Moist Air (Water (H2O) +
Oxygen (O2) + Carbon Dioxide (CO2)) → Copper
Hydroxide (Cu(OH)2) + Copper Carbonate
(CuCO3)
4. Basic
Nature of Metallic Oxides
A. Reaction with Air
When
ashes of magnesium, after burning in air, is dissolves in water, it changes red
litmus to blue. Thus, it is basic in nature.

In
general, metallic oxides are basic in nature.
B. Reaction with Water
Some
metals react with water to form metal hydroxide and hydrogen gas.
Metal + (cold) Water →
Metal hydroxide + Hydrogen
Metal + Stream → Metal
oxide + Hydrogen
Examples:
1. Sodium
metal is very reactive. It reacts vigorously with oxygen and water. A lot of
heat is generated in the reaction. It is, therefore, stored in kerosene.

Sodium (Na) + Water (H2O) → Sodium
Hydroxide (NaOH) + Hydrogen (H2)+ Heat
2. Metal
hydroxides are basic in nature and turn red litmus to blue.
C. Reaction with Acid
Some
metals react with acid to form metal salts and hydrogen gas.
Metal + Acid → Metal
Salt + Hydrogen
Examples:
1. Reaction
of Magnesium with HCl

Magnesium (Mg) + Hydrochloric Acid (HCl) →
Magnesium Chloride (MgCl2) + Hydrogen (H2)
2. Reaction
of Aluminum with HCl

Aluminum (Al) + Hydrochloric Acid (HCl) →Aluminum
Chloride (AlCl3) + Hydrogen (H2)
3. Reaction
of Iron with HCl
Iron does
not react with hydrochloric acid at room temperature, however it reacts when
heated.
Iron (Fe) + Hydrochloric Acid (HCl) →Iron
Chloride (FeCl2) + Hydrogen (H2)
4. Copper
does not react with hydrochloric acid at room temperature, and even on heating.
However it reacts with H2SO4. (Sulfuric Acid)
Copper (Cu) + Sulfuric Acid ( H2SO4)
→ Copper Sulfate (CuSO4 ) + Sulfur dioxide (SO2)+
Water (H2O)

5.
Presence of hydrogen gas is detected by a ‘pop’ sound.
D. Reaction with Base
Some
metals react with acid to form metal salts and hydrogen gas.
Metal + Acid → Metal
Salt + Hydrogen
Examples:
1. Reaction of Aluminum with Sodium
Hydroxide
Aluminum (Al) + Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH)
+ Water (H2O)→Sodium Aluminate (NaAlO2)
+ Hydrogen (H2)

2.
Presence of hydrogen gas is detected by a ‘pop’ sound.
E. Reaction of Metals with Solutions of
Other Metal Salts
Metal A +
Salt Solution of Metal B → Salt Solution of Metal A + Metal B
1. More
reactive metals replaces less reactive metals.
2. Less
reactive metals cannot replace more reactive metals.
3. The
order of reactivity of metals is:
Potassium > Sodium > Calcium > Magnesium >
Aluminum > Zinc >Iron > Lead > Copper > Silver > Gold
4. This
is called a displacement reaction.
Examples:
1. Reaction
of Copper Sulphate and Iron
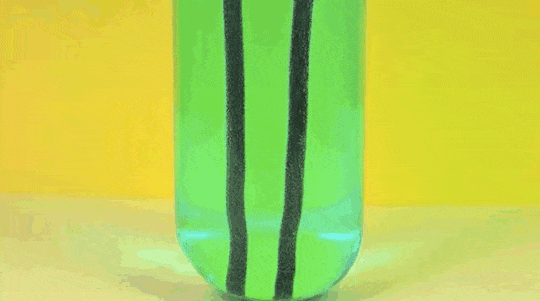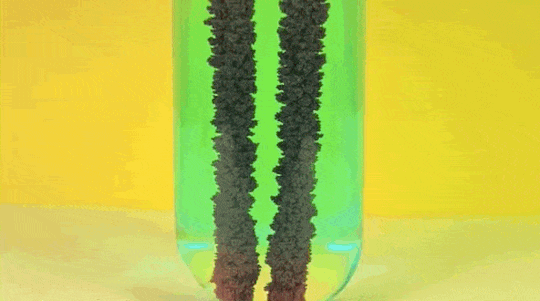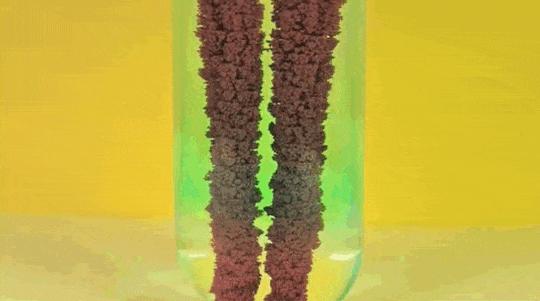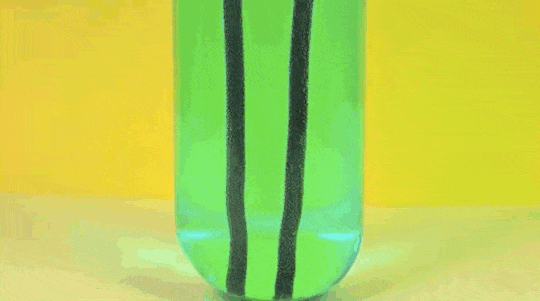
Iron (Fe )+ Copper Sulfate (
CuSO4) → Iron Sulfate ( FeSO4) + Copper (Cu)
2. Reaction
of Copper Sulphate and Zinc

Copper Sulphate (CuSO4) + Zinc (Zn) →
Zinc Sulphate + Copper (Cu)
3. Iron +
Zinc Sulfate → No reaction
4. Copper
+ Zinc Sulfate → No reaction
5. Copper
+ Iron Sulfate → No reaction
Chemical Properties of Non-Metals
A. Reaction with Oxygen
When
non-metals react with oxygen, they form metal oxide.
Non-Metal + O2 →
Non-Metal Oxide
Example:
1.
Reaction of Sulphur with Oxygen
Sulphur (S) + Oxygen (O2) → Sulphur
dioxide (SO2)
2. The
ashes of sulphur on mixing with water turns blue litmus red, thus indicating
their acidic nature.
In
general, non-metallic oxides are acidic in nature.
Sulphur dioxide (SO2) + Water (H2O)
→Sulphurous acid (H2SO3)
B. Reaction with Water
1.
Non-metals do not react with water.
2.
Phosphorus is a very reactive non-metal. It catches fire if exposed to air. To
prevent the contact of phosphorus with atmospheric oxygen, it is stored in
water.
C. Reaction with Acids
1.
Non-metals generally do not react with acid.
2.
Example: Charcoal reacts with concentrated sulphuric acid
Charcoal (C) +conc. Sulphuric Acid (H2SO4)
→ Carbon Dioxide (CO2) + Sulphur Dioxide (SO2) +
Water (H2O)
D. Reaction with Bases
1.
Reaction of non-metals with bases are complex.
Summary