Why Do we Fall Ill?
The activities performed inside our body by the
internal organs are all interconnected. For instance, the heart always forms of
the blood in the body, the brain always thinks, the kidney filters out waste
from our body and so on. If anyone of these activities stops, this would affect
the whole functionality of our body.
What is health?
It is a state of being well so that one can perform
physical, social and mental functions properly. For Example,
we say a person is healthy if they can perform their day to day tasks very
well.
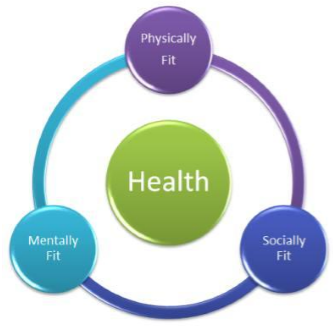
Figure 1: What is health?
Is health dependent on personal and
social issues?
Yes, we cannot achieve health solely on our own.
Every organism in this world depends upon another or the environment for their
better health.
Factors that determine better health:
·
We always stress upon the fact that the
environment surrounding us should be healthy otherwise it may lead to harmful
diseases. Therefore, we can say that public cleanliness is an
important factor for the better health of people in society.
·
Another important factor for proper health
is food. Now, we can have food only if we have the money to buy it
and for that, we need to work. Therefore we can say that good economic
conditions of society and employment are needed for better health.
·
Lastly, we can stay healthy if we are living
a tension free life. How can we expect a healthy environment around us if
everyone keeps on ill-treating each other? Therefore, we can say that a good
social environment is required for better health.
What do you mean by a disease?
·
We can say that a disease is any abnormality
or disturbance caused in our body.
·
A disease is not caused by any external
injury but can be caused by an external factor like germs.
·
Sometimes internal dysfunctionality of our
body may also lead to diseases.
·
A disease generally has some Symptoms and
Signs associated with it, For Example, Pain, Swelling and Fever are
some common symptoms.
How is being disease-free different
from being healthy?

Figure 2: Healthy and Disease-Free
How can we stay disease free?
We can stay disease-free by maintaining good health
that is,
·
by having proper food or a balanced diet
·
by keeping the environment clean
·
maintaining personal hygiene
How can we identify a disease?
·
A disease is associated with symptoms. In
other words, our body shows certain indications with which we can assume that
we may be suffering from a disease.
·
We know that different parts of our body
perform different functions.
·
Any of these functions are disturbed, we can
say that something is wrong within our body or something has changed in it.
This is a symptom of getting a disease.
·
Symptoms just indicate that there is a
disease. They do not indicate the exact type of disease.
·
The doctors often look for the signs of a
disease in order to find out the exact problem. These signs, unlike the
symptoms, are more definite indication of a disease. Sometimes laboratory tests
are also done in order to find a disease.
Types of Diseases: Acute Diseases and
Chronic Diseases
|
Acute Disease |
Chronic Disease |
|
Acute
diseases last for only a short period of time. |
Chronic
diseases last for a long period of time |
|
It
is caused randomly. |
It
is caused in due course of time. |
|
It
does not cause major effect on general health. |
It
causes major effect on general health. |
How chronic diseases affect our
health?
·
Chronic diseases take relatively a long
period of time hence they are likely to affect our general health as well.
·
They may hinder the growth in children or
increase stress in adults.
·
They can make us feel tired all the time.
·
They can also lead to an increase or decrease
in weight.
·
They can also affect our day to day
activities and the ability to learn new things.
·
Hence, we can say that they have long-term
effects on health than acute diseases.
What causes diseases?
We know that, diseases can be caused by two
factors:
Internal factors in our body such as:
·
Hormonal imbalance
·
Allergic Reaction
·
Genetic disorder
·
Malfunctioning of body organs
External factors such as:
·
Unhealthy diet
·
Disease causing germs (bacteria, viruses,
fungi)
·
Pollution in the environment
·
Unhealthy lifestyle
Based on the following there are two broad
categories of causes of diseases –
1. Immediate Causes and Contributory
Causes
|
Immediate Causes |
Contributory Causes |
|
These
are the actual causes that are responsible for a disease. These causes can be
infectious as well as non-infectious. |
These
are not the direct causes but factors that contribute in causing a disease. |
|
For
Example, Bacteria, Fungi, Viruses, Germs etc. |
For
Example Poor diet, Unhealthy lifestyle, Polluted
environment etc. |
2. Congenital and Acquired
Diseases
Congenital diseases are present since birth. For eg hole in heart of an infant. Acquired Diseases occur
after birth. Based on their ability to spread from one individual to another,
Acquired diseases are of two types:
Infectious and Non-infectious causes
of Disease
|
Infectious Causes |
Non-infectious Causes |
|
These are the extrinsic or external disease causing factors. |
These are the intrinsic or internal disease causing factors. |
|
They lead to infectious disease and can affect the whole community as
they are transferable from one person to another. |
They lead to non-infectious diseases and do not affect the whole
community as they are non-transferable from one person to another. |
Difference between Infectious and
Non-infectious Diseases:
|
Infectious or Communicable Diseases |
Non-infectious or Non-Communicable Diseases |
|
They are caused by attack of pathogens. |
They are not caused by pathogens. |
|
The diseases brought about by exitinsic or
external factors. |
The diseases are mostrly brought by
intrinsic or internal factors. |
|
Infectious diseases can pass from diseased person to a heathly person. |
Non-infectious diseases cannot pass from one person to another. |
|
Transmission of infection occurs through direct contact or some medium
(air, water, vectors). |
Transmission is absent, However hereditary diseases are transmitted
from parent to offspring. |
|
Community hygiene can reduce the incidence of infections
diseases |
Community hygiene is ineffective in reducing the incidence of
non-infectious diseases. |
|
Example: Cholera, Tuberculosis (TB), Pneumonia,
Chickenpox. |
Example: High blood pressure, Heart, disease,
Cancer. |
Infectious Agents
The pathogens or microbes that cause infectious
diseases are also called as Infectious Agents.
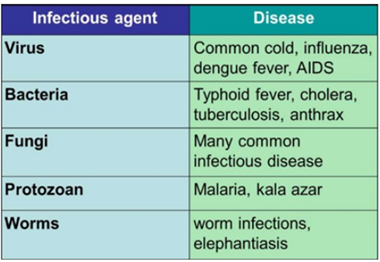
Figure 3: Infectious Agents
Why do we need to understand the
characteristics of these infectious agents?
If we understand the characteristics we can treat
the diseases caused by them in a better way. We can find out which medicine
would work on which infectious agent. Some common characteristics of infectious
agents are:
·
Viruses live inside the host body
·
Bacteria do not generally live inside the
host body
·
Virus, bacteria and fungi multiply quickly
·
Worms do not multiply quickly
How penicillin can help fight against
bacteria?
Antibiotics are generally used to block the growth
of bacteria. The bacteria cells grow by creating a cell wall that protects
them. Penicillin is an antibiotic that prevents the growth of the cell wall and
hence bacteria die easily. Penicillin is used for fighting against different
kinds of bacteria.
Several types of diseases
Based on the means of spread of a disease, we can
classify it into different categories:
|
Type of Disease |
Causing Factor |
Examples |
|
Airborne
diseases |
they
are caused by germs, bacteria or virus in the air |
Common
cold, tuberculosis |
|
Foodborne
diseases |
they
are caused by germs (bacteria, toxins, viruses, fungi) present in the
food |
Food
poisoning, Typhoid |
|
Waterborne
diseases |
They
are caused by drinking contaminated water |
Cholera,
Amoebiasis |
|
Lifestyle
diseases |
they
occur because of poor or unhealthy lifestyle |
Heart
disease, Diabetes |
|
Vector-borne
Diseases |
they
are caused due to animals that carry infectious agents from a sick person to
another person |
Malaria,
Dengue Fever |
|
These
animals that act as an intermediate between disease causing germs and people
are called vectors. |
||
|
Sexually
transmitted diseases |
they
are caused due to sexual contact from one person to another |
AIDS,
Syphilis |
Where do the disease-causing germs
live in our body?
·
There are a number of tissues and organs in
our body where these microbes can get attached to.
·
Generally, the point of entry decides where
they will go. For instance, any microbe that enters through the nose is likely
to settle at the lungs.
·
This can also be seen through the signs and
symptoms of a disease as only those organs and tissues issues seem affected
where these microbes enter.
·
But there are some other common diseases also
that are not tissue-specific.
·
Inflammation – Our body has an
immune system in which it creates the cells that can fight against the
disease-causing germs. This process of recruiting cells to kill the infectious
agents present in our body is called Inflammation. The inflammation
process shows different effects on our body such as fever or swelling.
·
Hence, we can say that the likelihood we are
going to be affected by the disease is determined by the immune system of our
body.
Principles of treatment
Figure 4: Principles of Treatment
We may treat an infectious disease in
two ways:
·
By killing the infectious agents
·
By reducing the effects of the disease or
reducing the symptoms
We can reduce the symptoms in the
following ways:
·
By taking rest to conserve our energy so that
our immune system can fight against the disease
·
By taking medicine to reduce the common
symptoms such as fever or pain and hence reducing the disease
We can kill the infectious agents in
our body in the following way:
·
By taking medicines that can kill them such
as antibiotics or antiviral medicines
Antibiotics aren’t effective against viruses?
Antibiotics commonly work by blocking the
biochemical pathways that are important for bacteria. Thus these inhibit the growth of bacteria, hamper the metabolism and
kill them. Antibiotics do not work on viruses because viruses do not use the
biochemical path and use host cell machinery for making proteins.
However, the most effective way to treat viral
infections and disease is vaccination as it can prevent a person from getting
the disease in the first place.
The principles of prevention
Are there any limitations of treating
infectious agents via medicines?
Yes, there are three limitations:
·
Our body functions might not be able to
recover easily
·
This treatment takes time hence it can affect
our daily activities
·
An infectious disease may transfer from a
person who is suffering the disease to another in the meanwhile of the
treatment
Therefore, we should find out ways to prevent these
diseases in the first place. There are two ways to prevent diseases:
1. Preventing exposure to
these infectious agents
·
Waterborne diseases can be prevented by
always having safe and pure drinking water
·
Airborne diseases can be prevented by
avoiding overcrowded places in keeping the environment clean
·
Vector-borne diseases can be prevented by
keeping our surroundings clean and maintaining public hygiene
2. Strengthening the immune system so
that if any infectious agents enter our body it can fight back. This can be
made possible by having healthy food.
What is the Immune System?
·
The immune system is a network of cells,
tissues and organs that work together in order to protect our body from
diseases. We may consider the immune system as a defence system of our body.
·
The immune system looks out and destroys the
disease-causing germs in our body with the help of special cells called white
blood cells. These cells are present in the blood and hence circulate
throughout the body and monitor it.
·
The germs or any foreign substance that enter
our body are called Antigens. As the immune system recognizes these
antigens, it releases antibodies which lock the antigens and then destroy them
with the help of other cells.
·
The ability of a body to resist a disease
with the help of antibodies is called Immunity.
Discovery of Helicobacter Pylori as a
Reason for Ulcer
A peptic ulcer is a sore that occurs on the inner
lining of the stomach. In 2005, Barry J. Marshall and J. Robin Warren received
a Nobel Prize for discovering that Helicobacter Pylori bacteria are a cause of
such ulcers. Before that, it was believed that stress and lifestyle are a major
cause of such ulcers. The Helicobacter Pylori bacteria weakens the mucous
lining of the stomach which lets the acid present inside the stomach to get
through the inner sensitive lining. The acid and bacteria together irritate the
lining and cause a sore or ulcer.
A Specific Method to Strengthen the
Immune System
·
The above methods were just general ways of
preventing any disease. A specific method to strengthen the immune system and
hence preventing disease is vaccination.
·
Whenever our body is affected by a disease,
our immune system not only fights against it but it also remembers how to
respond when the same disease-causing microbes affect our body the next time.
·
Similarly, vaccination contains an agent that
is similar to the disease-causing agents (weak or killed microbes). As it
enters our body, our immune system learns to fight against it and hence
prevents us from actually getting infected when the actual disease-causing
microbes enter our body.
·
Today, vaccines are available for enhancing
our immune system against various diseases such as polio, chicken pox and
measles.
Diseases - Causes, Control and
Prevention
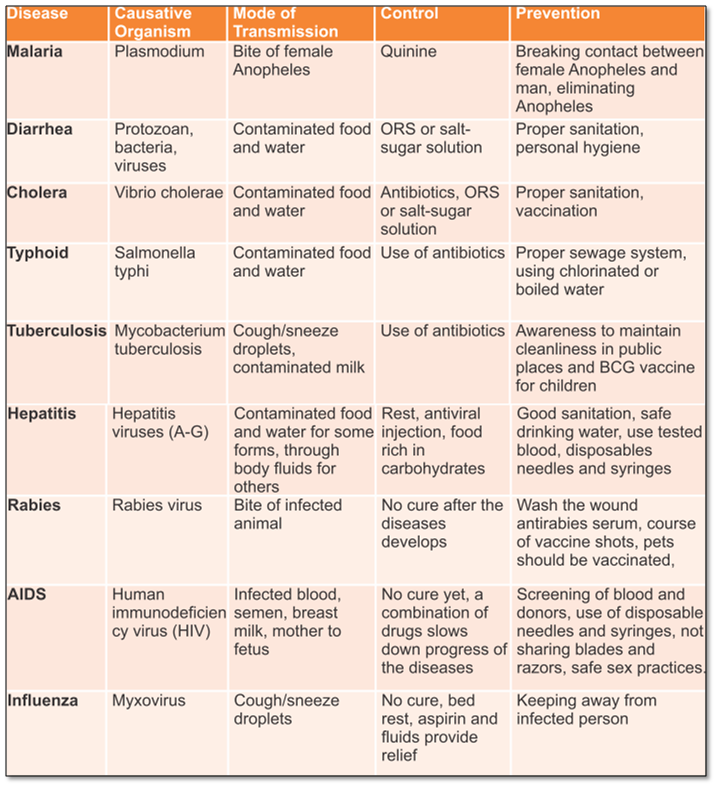
Figure 5: List of Diseases