Improvement in Food Resources
All living organisms need food because:
·
It provides carbohydrates, fats vitamins and
minerals
·
It allows development of the organisms
·
It is needed to gain energy for everyday
tasks
Main sources of food:
·
Plants – obtained from agriculture
·
Animals – obtained from animal husbandry
The efficiency of crops and livestock is required
in India because:
·
The population of India is growing at a
faster rate hence more amount of food is required to meet the rising demand.
·
The agricultural land is limited as compared
to the growing population.
Efforts made to meet the increase in
food demands
·
Green Revolution – The introduction of
modern technology and equipment, usage of fertilizers and high-quality seeds
·
White Revolution – Increasing the growth of
milk production by introducing dairy development programs
The introduction of these revolutions has led to an
increased use of natural resources hence now sustainable methods of increasing
crops and livestock efficiency are also required.
Improvement in Crop Yields
Different types of crops and their
Nutritional Value
|
Crop |
Examples |
Value |
|
Cereals |
Wheat, rice, maize, millets, sorghum |
Carbohydrates |
|
Pulses |
Gram, black gram, green gram, pigeon pea, lentil |
Proteins |
|
Oilseeds |
Soybean, groundnut, sesame, castor, mustard, sunflower |
Fats |
|
Vegetables, Spices and Fruits |
Carrot, Cinnamon, orange, spinach |
Minerals, vitamins and small amounts of Carbohydrates, fats and
proteins |
|
Fodder crops |
Berseem, oats, sudan grass |
Food for Livestock |
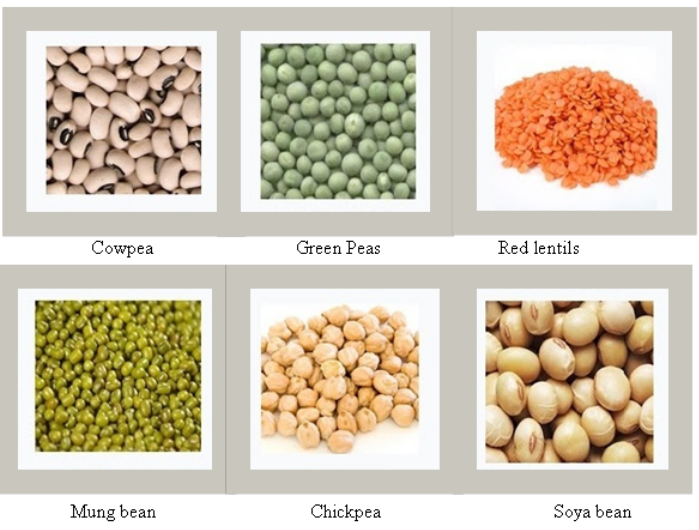

Figure 1 Different types of Crops
Different crops grow in different Seasons because
they require a particular climate temperature and photoperiod for their growth.
|
Crop |
Season |
Example |
|
Kharif |
Rainy
(June to October) |
Rice,
maize, millets |
|
Rabi |
Winter
(November to April) |
Soybean,
pigeon pea, wheat |
|
Zaid |
Summer
(March to June) |
Sugarcane,
Watermelon, Cucumber |
Activities that lead to improvement
in the crop yield:
·
Crop Variety Improvement
·
Crop Production Improvement
·
Crop Production Management
Crop Variety Improvement
In this approach, crops are selected on the basis
of their characteristics. For instance, how well they can respond to
fertilizers, can they produce high yield, how they resist diseases and so on.
Different methods of Crop Variety
Improvement
1. Hybridisation - In this process,
genetically different plants are crossbred.
They can be three types of crossing
·
Intervarietal - Between two
varieties of a plant
·
Interspecific - Between two
species belonging to same genus
·
Inter Generic - Between species
of different genus
2. Introduction of Gene - A gene that can
provide the desirable characteristics to a crop are introduced in this process.
As a result, we obtain genetically modified crops.
Factors on which Crop Yield Generally
Depends
·
The seeds used by the farmers - The seeds that
are of similar variety are preferable.
·
Climate or Weather Conditions - Crops that can
sustain diverse climatic conditions are preferable.
·
The duality of the Soil - Crops that can
survive in a highly saline soil are preferable.
·
Availability of Water - Crops should be
grown as per the availability of water in the region.
Why do we need to perform a crop
variety improvement?
·
Increasing the yield of the crops
·
Improving the quality of the crop. Different
crops may have different qualities. For Example, pulses have high
protein quality, oilseeds have oil quality fruits and vegetables must have
preserving quality.
·
Improving crop resistance to biotic and
abiotic stresses. Biotic stresses referred to the diseases, insects and
nematodes while abiotic stresses referred to floods, drought, heat and cold
weather conditions.
·
To shorten the maturity period of crops. This
will allow farmers to grow a variety of crops in a year.
·
It would also lead to an increase in the
yield of the crop as it reduces the chances of losses during the harvesting and
simplifies the harvesting period.
·
Achieving the required agronomic
characteristics of crops such as the right height, weight, lodging, resistance
and high yield. In this way, they would consume the right nutrients and would
produce a higher yield.
Crop Production Management
Different farmers can have small or large farms on
which they can use different farming practices. The choice of farming practices
would depend upon the availability of financial resources money. Hence,
production practices can be divided into different levels
1. No cost Production
2. Low-cost Production
3. High-cost Production
Nutrition Management
16 Essential Nutrients that plants need –
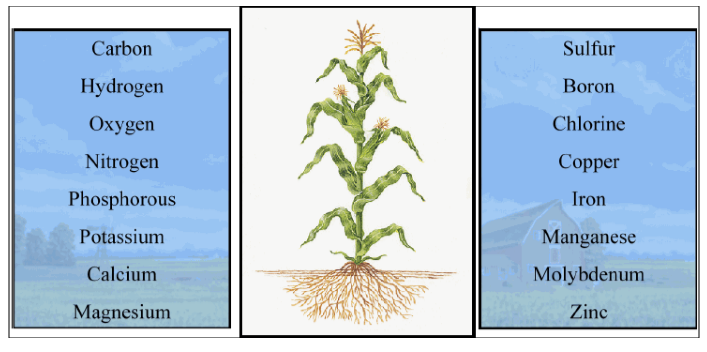
Figure 2 - 16 Essential nutrients for plants
The nutrients that are required in large quantities
are called Macronutrients. The nutrients that are required in small
quantities by the plants are called Micronutrients.
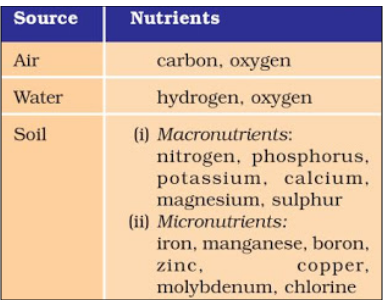
Figure 3 Nutrients provided by air, water and soil
What happens if plants lack in these
nutrients?
·
The yield may be affected as plants won't be
able to reproduce
·
Plant growth can be affected plants can get
diseases easily
How can we increase the yield by
providing all nutrients to the plants?
Using Manure - Manure is prepared by
using animal excreta and plant waste.
Functions or Features of Manure
·
Manure mainly contains organic matter which
increases the fertility of the soil.
·
It also contains nutrients in small quantity
which are then supplied to the soil on adding manure.
·
The soil structure also enhance is due to
manure. It tends to hold more amount of water.
·
The organic matter avoids waterlogging and
drainage in clayey soil.
·
Manure is purely organic hence using more
manure is completely healthy for the plant as well as the environment.
·
Using manure is a way to recycle farm waste.
What is composting?
The process of recycling farm waste material by
decomposing it is called Composting. The product formed on
decomposition is called Compost. The composed has a high variety of
nutrients and organic matter. The material used in the preparation of compost
is animal excreta, sewage waste, vegetable waste and weeds.

Figure 4 Compost preparation
Classification of Manure
1. Compost and Vermicompost
Manure
|
Compost |
Vermicompost |
|
A
manure prepared from waste materials such as cow dung, sewage, vegetable
wastes and domestic waste |
A
manure that is prepared by using Earthworms |
|
Takes
around 3 to 6 months in formation |
Takes
around 1 to 2 months in formation |
|
The
microbes decay the matter and manure is formed |
Earth
worms reduce the matter and compost is formed |
2. Green Manure – sometimes specific
plants are grown and then ploughed again in the soil. These plants decay and
turn into manure which enriches the soil, mainly with nitrogen and phosphorus.
Plants that are used in the production of green manure are hemp, clover, peas grass
mixtures.
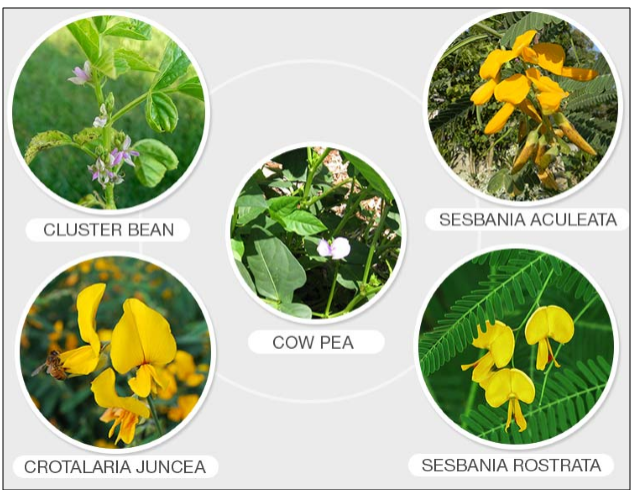

Figure 5 Green Manure Crops
Using Fertilizers
Fertilizers are artificial materials that are
produced on a commercial basis or natural substances that ensure nutrient
benefits to the soil.
·
Organic fertilizers used by Farmers: Limestone, rock
phosphate
·
Artificial fertilizers used by Farmers: Ammonium nitrate,
potassium sulfate
Features of Fertilizers
·
Fertilizers provide important nutrients such
as nitrogen, potassium and phosphorus to the soil.
·
They help in the proper growth of the plants.
·
They are responsible for high yields in the
high-cost farming methods.
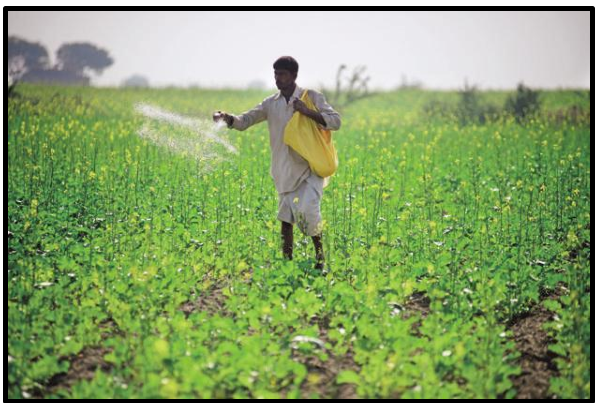

Figure 6 Using fertilizers in fields
Precautions with Fertilizers
·
Fertilizers should be applied in a proper
amount as an excess of fertilizers is not good for the plants.
·
Proper precautions regarding the time of
applying fertilizers should be taken.
·
Excess use of fertilizers can lead to water
pollution as the extra fertilizers get washed away during irrigation.
·
Excess use of fertilizers can destroy the
fertility of the soil as well.
How are fertilizers and manure
different?
|
Manure |
Fertilizers |
|
Manure provides humus to the soil |
Fertilizers do not provide humus to the soil |
|
Manures are less rich in nutrients |
Fertilizers are highly rich in nutrients |
|
Long term usage of manure leads to increment in the fertility of the
soil |
Long term usage of fertilizers can lead to decrease in the soil
fertility |
What is organic farming?
A farming practice which involves no use of
artificial chemicals, fertilizers and pesticides and completely relies upon
organic matter is known as organic farming. Organic farming uses healthy
cropping systems such as crop rotation, intercropping and mixed cropping.
Organic matter used in organic farming:
·
manure
·
bioagents such as blue-green
algae
·
biofertilizers
·
Neem leaves and turmeric as biopesticides

Figure 7 Elements of Organic Farming
Irrigation
It is a process of application of water in
controlled amounts at regular intervals to the crops. Irrigation methods are
adopted at various places especially in areas of low rainfall to ensure the
proper growth of crops.

Figure 8 Irrigation of fields
Why do droughts occur?
The scarcity of water or low rainfall often results
in drought conditions. If farmers do not use any irrigation methods and only
rely on rainfalls, draught poses a serious threat to the crops. Areas with
light soils also tend to face drought-like conditions as soils cannot retain
water
Irrigation Methods
|
Wells:
two types of wells are used for irrigation: ·
Tubewell:
tube wells are tube-like structures that are used to extract the underground
water. ·
Dug Wells: dug wells are the wells dug in
the ground in order to extract the underground water. Water from dug well and
tubewell both is lifted by using pumps. |
|
|
Canals: A
canal system is a network created to move water from one source of water such
as a stream or reservoir. The main canal is divided into branches that spread
by through the fields so that water can be distributed everywhere. |
|
|
River
Lift System: A river lift system is used to draw water
from the rivers directly for irrigational purposes. This system is successful
in areas where the canal system is not successful. |
|
|
Tanks: farmers
often use small storage reservoir that can store as well as supply water in
the small fields. |
|
|
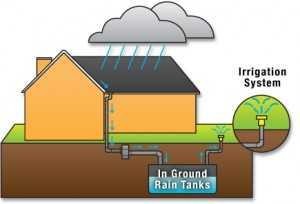
Rainwater
Harvesting: Instead of just letting the rainwater flow
away farmers often store it in the reservoir tank. This water can we for the
used for irrigational purposes. |
|
|
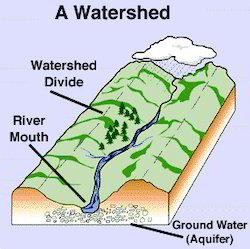
Watershed
Management: Small dams are built on the rivers and
streams in order to increase the ground levels of the area. These check dams
prevent water from flowing away and causing soil erosion. |
|
Cropping Patterns
Different cropping patterns are used by farmers in
order to increase the crop yield:
·
Mixed Cropping
·
Intercropping
·
Crop Rotation
Mixed Cropping
·
It is a cropping pattern in which two or more
crops are grown together in the same field.
·
The main aim of this cropping method is to
ensure some healed even if one of the crops fails to grow properly.
·
The seeds of different crops are combined and
planted together.
·
Same fertilizers are used for all the crops.
·
For Example, wheat and gram, wheat and mustard,
groundnut and sunflower.

Figure 15 (a) Mixed Cropping in same row
Intercropping
·
It is a cropping method in which two or more
crops are grown together in a field but in a specific pattern.
·
The seeds of these crops are not combined
before plantation.
·
Both the crops used different kinds of
fertilizers depending upon their own requirements.
·
The main objective of this method is to
ensure the maximum productivity of the crops.
·
Since the crops have different nutrient
requirements they would use maximum nutrients from the soil.
·
Diseases and pest would also not easily
spread to all the crops.
·
For Example, soybean and maize, finger millets and
cowpea.

Figure 15(b) Intercropping
in specific rows
Crop Rotation
·
In this cropping method, different types of
crops are chosen and irrigated on the same piece of land sequentially.
·
The rotation of crops depends upon the soil,
climate and water retention of the soil.
How is crop rotation useful?
·
If farmers grow the same crop on the land for
long-term the same nutrients keep on depleting from the soil which leads to a
decrease in the soil fertility.
·
But when crops with different nutritional
requirements are grown the soil nutrients get enriched and the fertility of the
land is maintained.
·
Different crops are not susceptible to all
kinds of pests and diseases.
·
Planting different crops on rotation can lead
to a better yield.
·
Crop rotation allows a reduction in the
number of fertilizers and pesticides on the fields.
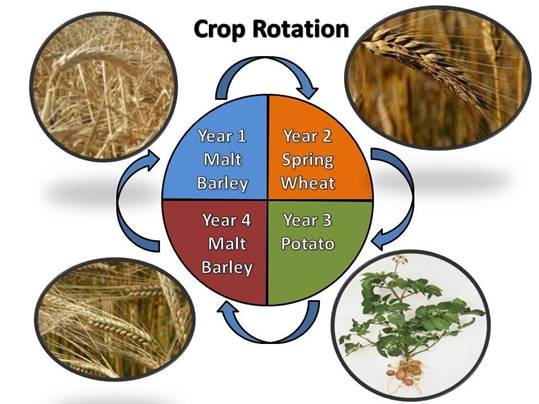
Figure 16 Crop Rotation
Crop Production Management
Factors that can affect the production of crops are
weeds, pests and diseases.
·
Weeds: Along with crops,
sometimes some other plants also grow up which are not needed. These are called
weeds. Weeds can affect the crop as they utilise the nutrients from the soil
that are meant to be used by the crops.
Weed Control Methods:
·
Weedicides are sprayed on the fields that can
kill them as they do not harm any crops.
·
Weeds can be uprooted manually by the
farmers.
·
The crop is sown timely are not affected by
weeds.
·
Using different methods of cropping suggest
crop rotation and intercropping also reduce the chances of growing weeds.

Figure 17 Uprooting weeds manually
2. Pests: Several insects and
pests can affect the crops in different ways:
·
They can cut the parts of the crops like
fruits, leaves and stems.
·
They can get into the stems and roots of the
plants.
·
They suck the cell sap of the plants and
hence destroy them.
Pest Controlling Methods:
·
Pesticides and insecticides are sprayed on
the fields to kill the germs.
·
Crops should be checked timely to ensure
safety against pests.
·
Usage of effective cropping methods such as
crop rotation ensures insect management in the fields.
·
Sometimes summer ploughing is also used to
destroy the weeds and pests.
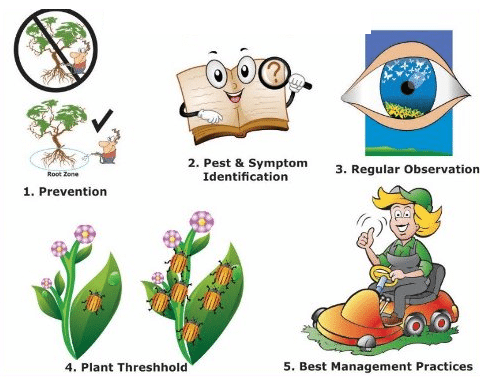
Figure 18 Pest Management
Diseases: Microorganisms such as
fungi, bacteria and viruses often attack the crops and affect them. These
pathogens can be transmitted to the crops via soil, water or air.
Disease Management Methods
·
Selecting the crop that suits the temperature
and climatic conditions of the place.
·
Planting the seeds on right time and in an
environment that favours their growth.
·
Using herbicides such as dicamba
and glufosinate ammonium and fertilizers such as
ammonium nitrate, potassium sulfate.
·
Using crop rotation method and mixed
cropping.
Storage of Grains
Factors that lead to storage losses of crops are:
·
Biotic Factors: Like insects,
fungi, bacteria, rodents and mites
·
Abiotic Factors: Like excessive
temperature and moisture.
How to prevent storage loss?
·
Maintaining the storage houses properly
·
Cleaning the grains properly before storage
·
Drying the grains properly before storage in
sunlight as well as in the shade
Animal Husbandry
In agriculture, animal husbandry is a special field
that deals with rising of the livestock in a controlled, selective environment
by providing them with the right care so that they can stay healthy and disease
free.
There is a need to improve livestock production
because the population of India is tremendously increasing. This means an
increase in demand for eggs, milk and meat.
Animal husbandry includes the
following:
1. Cattle Farming
Cattle are used for two reasons –
·
They provide milk
·
They work as draught labour in the fields
Milch Animals: Animals that provide
milk are called Milch Animals.
Draught Animals: Animals that work in the fields for
irrigation, carting and tiling are called Draught Animals.

Figure 19 Cattle Farming
Can we increase milk production in
cattle?
·
Milk production can be enhanced by increasing
the lactation period in the cattle.
·
Crossbreeding of foreign breeds and local
breeds can provide cattle with qualities of increased lactation period and
resistance to diseases.
·
Shelters of the cattle should be kept neat
and clean in order to keep the cattle healthy.
·
The cattle should be kept clean and should be
provided with a covered shelter that can protect them from harsh weathers.
·
The floor of the shelters to be kept a dry
and clean
Food requirements of dairy animals:
·
Maintenance requirements: the food that is
required to keep the animals healthy
·
Milk production requirements: the food that
is needed in the lactation period
·
Animal feeds
o
Roughage – contains fibre
o
Concentrates – contains low
fibre but high nutritional value
o
Feed Additives – includes food that
contains micronutrients that can promote health and milk production
Protecting the Cattle from Diseases:
·
Diseases can lead to a reduction in the
production of milk and even the death of cattle.
·
Mainly parasites can affect the health of the
cattle. These parasites can be found in the animals or they may attack them
externally.
·
The internal parasites generally damage the
liver and stomach of these animals. For example, worms and flukes.
·
The external parasites cause skin diseases in
cattle.
·
Sometimes bacteria and virus also called
several diseases in the cattle.
·
A good way to prevent diseases is
vaccination.
2. Poultry Farming
Poultry farming includes different kinds of
domesticated birds. Different types of poultry are:
·
Chicken
·
Duck
·
Goose
·
Pigeon
·
Turkey
It is mainly done for:
1. getting eggs through
layers
2. getting chicken meat
through broilers
Examples of Poultry Birds:
·
Indigenous breeds: Aseel, Burosa
·
Foreign breeds: Leghorn, Black
Minorca
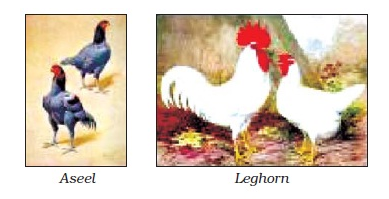
Figure 20 Poultry Animals
Crossbreeding is a way to achieve this. Generally,
foreign breeds of chicken are crossed with Indian breeds to achieve high
quality. It thus has better traits such as:
·
Increase in a number of chicks.
·
They can tolerate high temperatures.
·
They do not require much maintenance
·
They can survive cheap diets
Egg and broiler production
Broiler Chicken
·
They need a diet with a high quality of
Vitamins A and K, proteins and fats.
·
They need special care to maintain feathering
and avoiding death.
·
Proper hygiene and temperature conditions
should be provided to the broiler chicken.
Layers
·
They do not require such nutrient-rich diet.
·
They just need a controlled diet.
·
The layers require more space and lightning
as compared to the broilers.
Disease Control methods should also be adopted
against the diseases that are generally caused by bacteria, fungi and parasites
in broilers and layers. Disinfectants can be sprayed regularly to avoid such
diseases. Sometimes deficiency of nutrition can also need to diseases.
Vaccination is a good way to protect the poultry fowl from diseases.
3. Fish Production
Fish can be obtained in two ways:
·
From Natural Resources - Capture Fishing
·
From Fish Farming - Culture Fishing
Marine Fisheries
·
Marine fishes are caught using fishnets and
mechanical capturing techniques.
·
The main source of marine fishes is marine
water or salt water.
·
Generally, large numbers of fishes can be
captured at a time through mariculture.
·
For Example, tuna, Bombay duck, prawns
Inland Fisheries
·
Fishes found in lakes, ponds, lagoons and
rivers are captured.
·
The main source of Inland fisheries is
freshwater and brackish water.
·
The yield is not as high in these sources
hence large numbers of fishes are captured through aquaculture.
·
For Example, silver carp, common carp
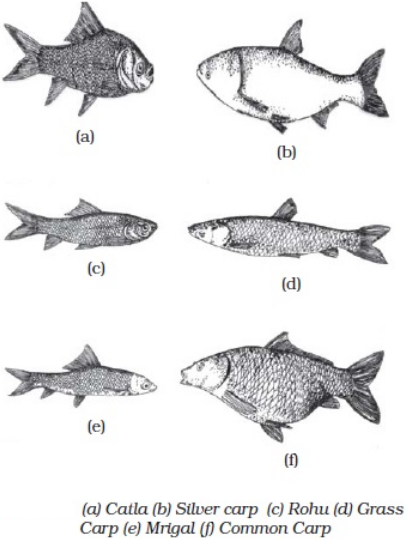
Figure 21 Inland Fisheries
Aquaculture: It is a method of
farming aquatic animals under controlled circumstances. It is performed in both
freshwater and saltwater bodies.
Mariculture: It is a branch of
aquaculture hence a method of fish farming under control environment. Mariculture is often performed in the ocean, a particular
section of the ocean or in the tanks that are filled with seawater only.
Composite fish culture
·
In a composite fish culture, fishes are grown
along with rice crop in the paddy fields.
·
In this method, a combination of 5 - 6 local
as well as foreign fishes is grown in a single pond.
·
Such species are selected because they have
different food habits and would not compete for the food with each other.
·
Some of them are surface feeders; some are
middle zone feeders while others are bottom feeders.
·
They would rather eat all the food in the
pond.
·
As a result, the fish yield in the pond
increases
For Example, Catlas (surface
feeders), Rohu (middle feeders), Mrigal
(bottom feeders), Common Carps (bottom feeders), Grass Craps (aquatic weed
eaters) are often grown together in composite fish culture.
4. Beekeeping
Bee farming is performed in bee farms or apiaries.
Many farmers perform beekeeping as a means of generating additional income
because:
·
Honey is a widely used product
·
Bee farming is not very expensive
·
They also generate wax along with honey
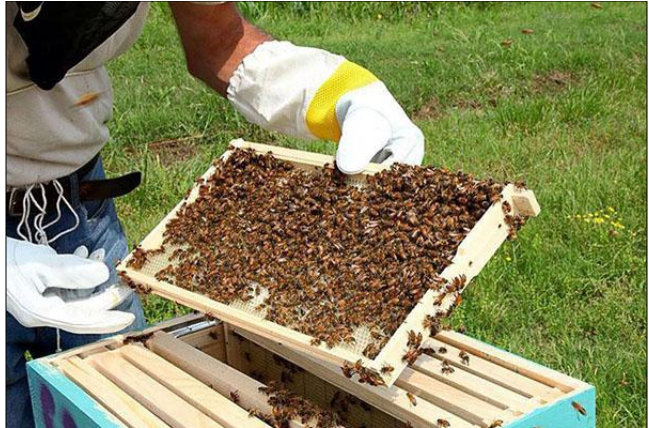

Figure 22 Bee Farming
Bees used for commercial and honey
production
·
Apis Cerana Indica - Indian bee
·
A. Dorsata - The
rock bee
·
A. Florae - The little bee
·
A. Mellifera –
Italian variety of bee

Figure 23 Honey Bee examples
Castes in Honey Bee
The honey bees build a nest which is called as a
bee-hive. A hive contains almost 10,000 to 60,000 bees. The bees live together
in a colony and divide themselves into 3 different castes.
·
Queen bee: the fertile, functional female of all is
the queen bee. It is the supreme bee in the colony.
·
Drone bees: they are the smaller male bees of the
colony. Their main task is to maintain the hive.
·
Worker bees: they are the smallest in size but the most
active members of the hive. They perform different functions such as collecting
pollens and nectar, constructing the comb, cleaning the cells of the
hive.
Why Italian bees are popular in bee
farming?
·
They produce large amounts of honey.
·
They do not sting much.
·
The breeding period in Italian bees is long.
Factors that determine the quality of
honey
·
Along with the choice of selection of the bee
species, the flowers decide the quality quantity and taste of the honey
produced.
·
There should also be enough pasturage or
availability of flowers to the bees so that they can collect enough nectar and
pollen.