Atoms and Molecules
The invisible and unknown form of
matter
The idea of divisibility by Indian
philosophers
Maharishi Kanad He postulated that if we
keep on dividing the matter (called as padarth) we
will get smaller and smaller particles. And soon we will achieve the
smallest of particles (called as parmanu) which may
not divide further.
Pakudha Katyayama He postulated that there
are various forms of matter because the particles of matter exist together in
combinations.
The idea of divisibility by Greek
philosophers
Democritus and Leucippus They
suggested that when we keep on dividing the matter there comes a time when no
more division of particles can take place. Such particles are called atoms
which means being invisible.
But all these ideas were not backed up by many
experimental pieces of evidence until Antoine L. Lavoisier provided two laws of
chemical combination.
Laws of Chemical Combination
1. Law of conservation of mass mass can neither
be created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction
2. Law of constant proportion/Law of definite
proportion the elements are always present in definite
proportions by mass in a chemical substance
For example, Hydrogen and oxygen are present in
water in a ratio of 1:8. So if we decompose 9g of water we will obtain 1g of
hydrogen and 8g of oxygen.
The Atomic Theory
John Dalton proposed an atomic theory which acted
as an explanation of the above two laws. As per the theory, all matter whether
it is an element, a compound or a mixture consists of tiny invisible particles
called atoms.
The postulates of the atomic theory
by John Dalton
1. The matter is made up of tiny particles called
atoms that cannot be divided.
2. Atoms are never formed or destroyed during a
chemical reaction.
3. Atoms of an element exhibit same nature.
They have the same size, mass, and character.
4. Atoms of different elements exhibit variant
nature. They do not have same characteristics.
5. Atoms form compounds by combining in a ratio of
whole numbers.
6. A compound contains a constant number and kinds
of atoms
Atoms
We can call atoms as the building blocks of matter.
Just like bricks are the building blocks of a building.
What is the size of an atom?
Atoms are extremely small. Their size is measured
in nanometers where 1nm = 1/109 m.
|
Atomic radius is measured in nanometers |
|
|
Relative Sizes |
|
|
Radii (in m) |
Example |
|
10-10 |
Atom of hydrogen |
|
10-9 |
Molecule of water |
|
10-8 |
Molecule of haemoglobin |
|
10-4 |
Grain of Sand |
|
10-2 |
Ant |
|
10-1 |
Watermelon |
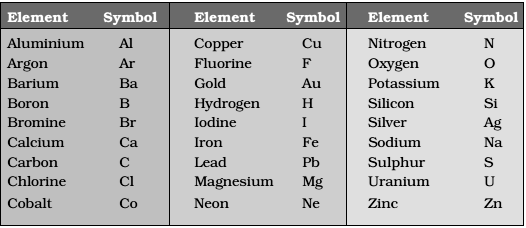
Symbols for Atoms
Here are some examples of the symbols that are used
to represent different atoms
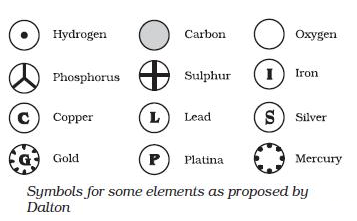
The symbols for representing an atom are generated
from the first two letters of the elements name. The first letter is always in
uppercase (capital letter) while the second letter is written in lowercase.
Here are some examples
The Atomic Mass

The Daltons Atomic Theory suggested that each
element has a distinguishing atomic mass. With this theory, the law of constant
proportions could be explained easily.
But it is indeed difficult to evaluate the mass of
an atom since the size of an atom is relatively small.
Therefore scientists started evaluating the mass of
an atom by comparing it with the mass of a standard atom.
Earlier 1/16 of the mass of an oxygen atom was used
as a standard for calculating the mass of other elements. Now, carbon - 12 is considered
a standard atom for calculating the mass.
Its atomic mass is 12u (12 atomic mass units). Thus
we can say that one atomic mass unit is the mass of 1/12 the mass of a
carbon-12 atom. Here is a list of atomic masses of a few elements.
|
Element |
Atomic Mass |
|
Hydrogen |
1 ΅ |
|
Carbon |
12 ΅ |
|
Nitrogen |
14 ΅ |
|
Oxygen |
16 ΅ |
|
Sodium |
23 ΅ |
|
Magnesium |
24 ΅ |
|
Sulphur |
32 ΅ |
|
Chlorine |
35.5 ΅ |
|
Calcium |
40 ΅ |
Can atoms exist independently?
Atoms cannot survive independently. So, atoms join
together and form molecules or ions.
Molecule
·
A molecule is a collection of various atoms
that combine chemically with each other.
·
These atoms are bound together by certain
forces of attraction.
·
Atoms of the same elements or different
elements can bind together to form molecules.
·
Therefore, a molecule is the smallest
particle of a substance that can exist independently and shows all the
properties of that substance.
Molecules of Elements
·
The molecules of an element are formed by
combinations of similar types of atoms. For example, Helium (He) is made up of
only one atom while oxygen is made up of two atoms.
·
Atomicity the number of atoms in a molecule of
an element is called its atomicity. For example, helium is monoatomic and
oxygen is diatomic.
·
Monoatomic when an element comprises of a single
atom. Example all metals
·
Diatomic when an element comprises of two atoms.
Example all gases
·
Triatomic when an element comprises of three
atoms
·
Tetra-atomic when an element
comprises of four atoms
·
Poly-atomic when an element comprises of more
than two atoms
Here a few examples of atomicity of elements
|
Atomicity of some Elements |
||
|
Name |
Atomicity |
Formula |
|
Argon |
Monoatomic |
Ar |
|
Helium |
Monoatomic |
He |
|
Oxygen |
Diatomic |
O2 |
|
Hydrogen |
Diatomic |
H2 |
|
Nitrogen |
Diatomic |
N2 |
|
Chlorine |
Diatomic |
Cl2 |
|
Phosphorous |
Tetra atomic |
P4 |
|
Sulphur |
Poly atomic |
S8 |
Molecules of Compounds
Molecules of compounds constitute atoms of
different elements that combine together in a fixed proportion. For example,
water comprises of two atoms of hydrogen and one atom of oxygen.

Ions
·
Compounds contain metals as well as
non-metals. These elements include charged species which are known as ions.
·
Thus, ion is a particle that has a positive
or negative charge.
·
Anion negatively charged ion
·
Cation positively charged ion
·
There can be a single charged atom in an ion
or there may be a group of charged atoms in an ion that have a net charge on
the compound.
·
When a group of atoms carries a charge in a
compound it is called as a polyatomic ion.
Chemical Formula
We use a chemical formula to represent the
composition of a compound in the form of symbols. To write a chemical formula
you must know two things
1. Symbols of elements
2. Valency
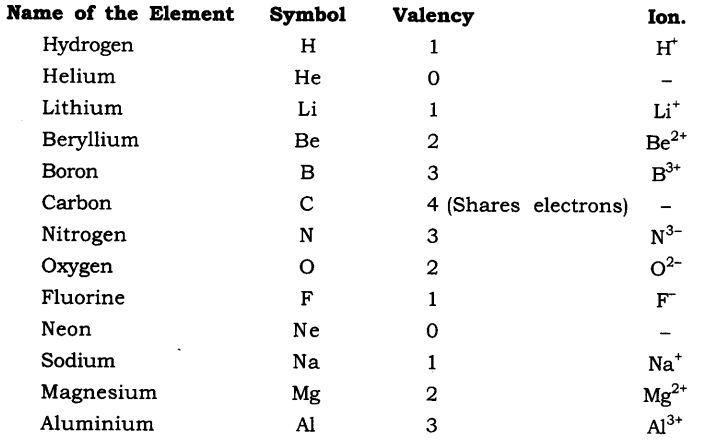
Valency it is also known
as the combining capacity of an element. In other words, valency
explains how atoms of one element will mix with atoms of another element. For
example, the hydrogen ion is represented as H+ which means that its valency is 1. Similarly, the oxygen ion is represented as
O2- which means that its valency is 2. Here is a list
of valancies of various elements.
Rules of writing a Chemical Formula
·
Valencies of on the ions must
balance.
·
In a case where both metal and non-metal
substances are present in a compound, the name of the metal is always written
first in the chemical formula. For example, Sodium Chloride is written as NaCl
·
In case of polyatomic ions, the ion is
written in brackets before writing the number of ions associated to it. In case
of a single ion, there is no need to mention the ion in brackets
Writing the Formulae of Simple Compounds
Binary compounds compounds that consist of two
different elements
How to write a Formula of a Compound
·
Write the symbols of the corresponding
elements of the compound as explained above
·
Write the valencies
of the elements of the compound
·
Crossover the valencies
of the elements
Here are a few examples of writing the chemical
formula

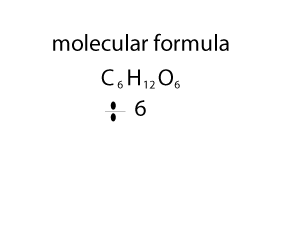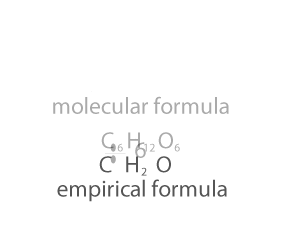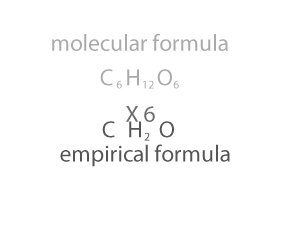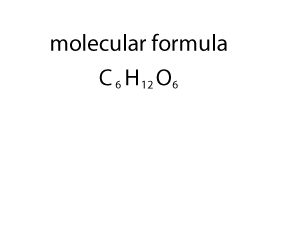
Molecular Mass and the Mole Concept
Molecular Mass summation of all the atomic masses in
a molecule
Molecular mass is expressed in atomic mass units (amu).
For example, the molecular mass of HNO3 can be
calculated as:
Atomic mass of H =1u
Atomic mass of N =14u
Atomic mass of O =16u
Molecular mass of HNO3 = 1 + 14 + (16*3) = 63u
Formula Unit Mass
The sum of atomic masses of all atoms in a formula
unit of a compound is called as its formula unit mass. The formula unit
mass is used in case of substances that constitute ions. For example, formula
unit mass of Sodium Chloride (NaCl) can be calculated
as: (1*23) + (1*35.5) = 58.5u
Mole Concept
How do we interpret a chemical equation?
2C + O2 = 2CO2
We say that two molecules of carbon combine with
one molecule of oxygen to form two molecules of carbon dioxide.
We can also say that 24u of Carbon molecules
combine with 32u of oxygen molecules to form 56u of carbon dioxide molecules.
Therefore, we can characterize the quantity of a
substance by its mass or by its number of molecules.
A chemical equation directly indicates the number
of molecules participating in the reaction. Thus, it is convenient for us to
refer to the number of substances in a chemical reaction as numbers of
molecules or atoms.
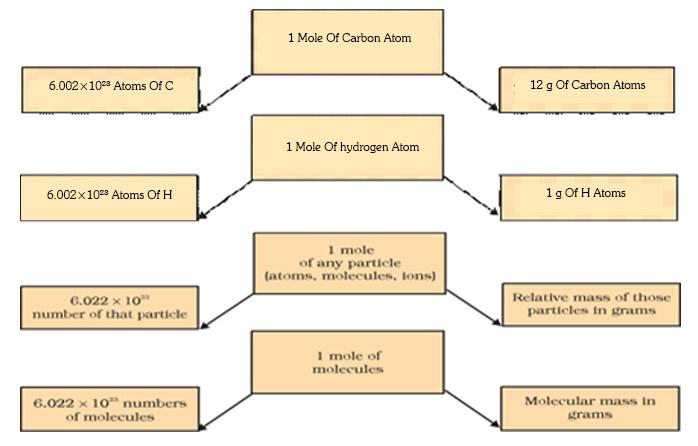
Mole
Mole is a numerical quantity that has a mass equal
to the atomic or molecular mass of species (atoms, molecules, ions or
particles).
1 mole of any substance = 6.022 X 1023 number of
particles (atoms, ions or molecules)
This is called the Avogadro number or
Avogadro Constant which is represented as N0
The mass of 1 mole of a substance is the same as
that its atomic mass or molecular mass expressed in grams.
Gram atomic mass of a substance the atomic mass
of a substance when expressed in grams is known as its gram atomic mass.
Gram molecular mass of a substance the molecular
mass of a substance when expressed in grams is known as its gram molecular
mass.
For example, the atomic mass of Sulphur is 32u.
Gram atomic mass of Sulphur is 32g.
Also, 32u of Sulphur has 1 atom of Sulphur. 32g of
Sulphur has 1 mole atoms, that is, 6.022 X 1023 atoms of Sulphur.
Similarly, we can say that the gram molecular mass
of Carbon Dioxide is 56g.
But we know that in the case of chemical equation
mole is the measuring unit.
Therefore, 1 mole = 6.022 Χ 1023 number = Relative
mass in grams
Wilhelm Ostwald introduced the word mole which
actually means a heap or a pile. Therefore, we consider a substance as a heap
of atoms or molecules.
Consider these formulae
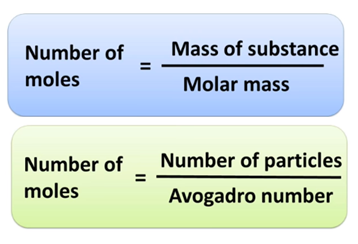
A quick review of how mole, Avogadro number and
Mass are related to each other