LAWS OF MOTION
Ø Newton’s laws of motion, relations between the forces acting on a body
and the motion of the body, first formulated
by English physicist and mathematician Sir Isaac Newton.

Newton’s first law:
Ø Newton’s first law states that, if a body is at
rest or moving at a constant speed in a straight line, it will remain at rest
or keep moving in a straight line at constant speed unless it is acted upon by
a force.
Ø This postulate is known as the law of inertia.

Newton’s second law:
Ø Newton’s second
law is
a quantitative description of the changes that a force can produce on the
motion of a body.
Ø It states that the time rate of change of
the momentum of
a body is equal in both magnitude and direction to the force imposed on it.
Ø The momentum of a body is
equal to the product of its mass and its velocity.
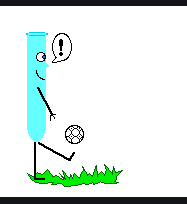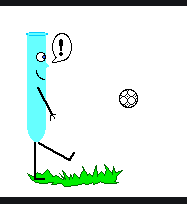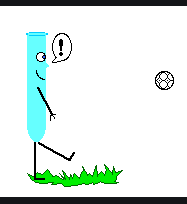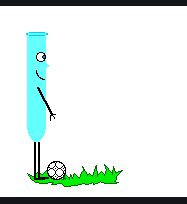
Newton’s third law:
Ø Newton’s third law states that when two bodies interact, they apply forces
to one another that are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. The third
law is also known as the law of action and reaction.
Ø This law is important in analysing problems
of static equilibrium, where all forces are
balanced, but it also applies to bodies in uniform or accelerated motion.
Ø The forces it describes are
real ones, not mere bookkeeping devices.

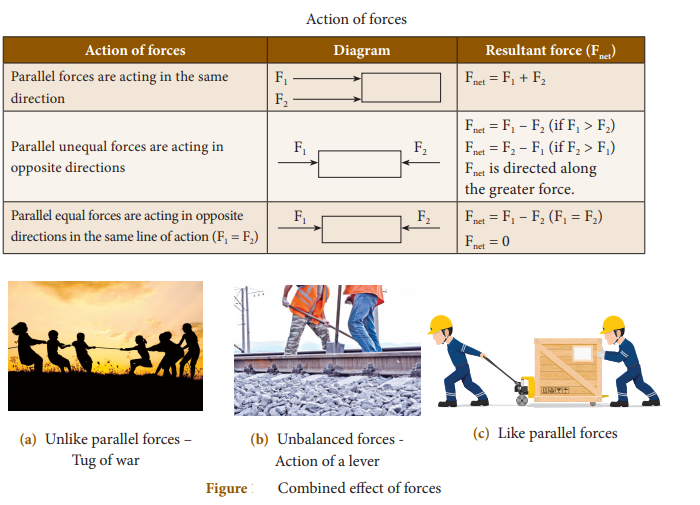
Forces:
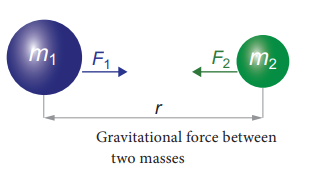
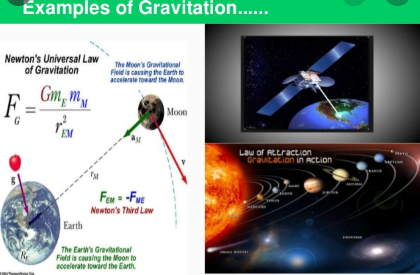
Newton’s universal law of gravitation:
Ø This law
states that every particle of matter in this universe attracts every other
particle with a force.
Ø This
force is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely
proportional to the square of the distance between the centres of these masses.
Ø The
direction of the force acts along the line joining the masses.
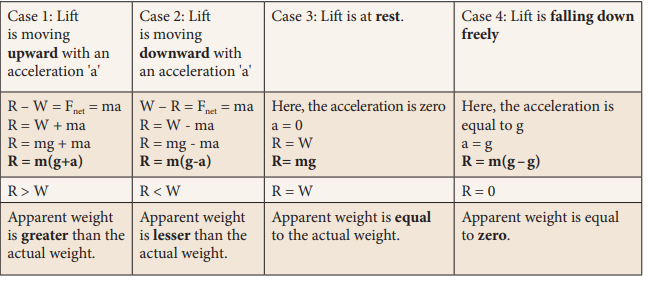
Apparent weight of a person in a moving
lift:
Application of Newton’s law of
gravitation:
1)
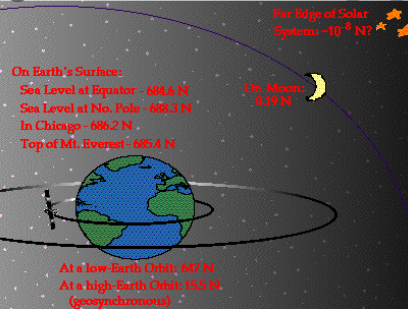
Dimensions of the heavenly bodies can be measured using the gravitation law.
Mass of the Earth, radius of the Earth, acceleration due to gravity, etc. can
be calculated with a higher accuracy.
2) Helps
in discovering new stars and planets.
3) One of
the irregularities in the motion of stars is called ‘Wobble’ lead to the
disturbance in the motion of a planet nearby. In this condition the mass of the
star can be calculated using the law of gravitation.
4) Helps
to explain germination of roots is due to the property of geotropism which is
the property of a root responding to the gravity.
5) Helps
to predict the path of the astronomical bodies.

MIND MAP