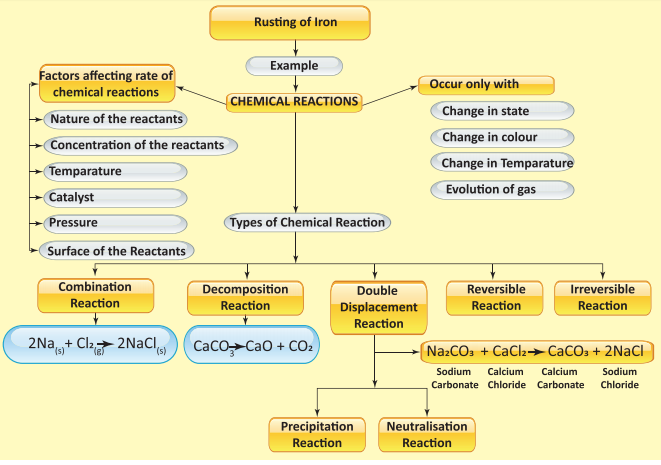
TYPES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS
Ø In a chemical reaction, the atoms of the
reacting molecules or elements are rearranged to form new molecules.
Ø Old chemical bonds between atoms are broken
and new chemical bonds are formed.
Ø Bond
breaking absorbs energy whereas bond formation releases energy.
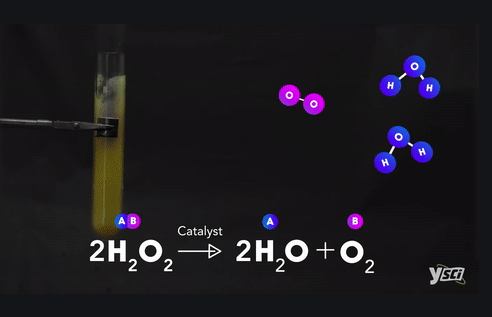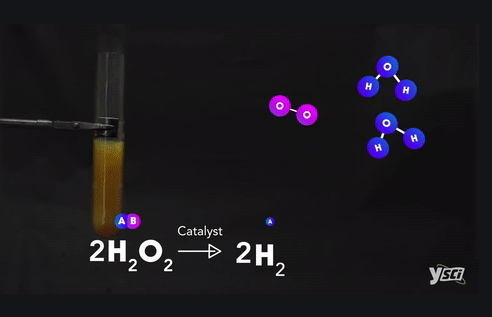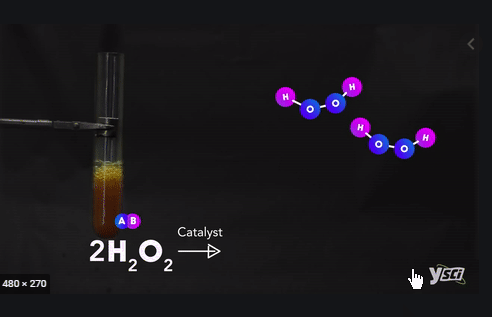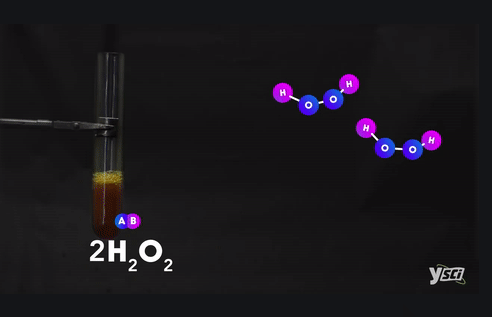
Example :
Ø Methane + Oxygen → Carbon dioxide +
Water
TYPES
OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS -
Combination
reactions:
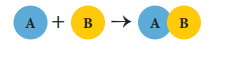
Ø A
combination reaction is a reaction in which two or more reactants combine to
form a compound.
Ø It is
otherwise called 'synthesis reaction' or 'composition reaction'.
Ø When a
reactant ‘A’ combines with ‘B’, it forms the product ‘AB’.
Ø The
generalised scheme of a combination reaction is given below:
Decomposition
reactions:
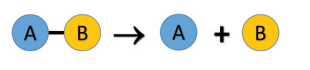
Ø In a decomposition reaction, a single
compound splits into two or more simpler substances under suitable conditions.
Ø It is the opposite of the combination
reaction.
Ø The generalised scheme of a decomposition
reaction is given below:
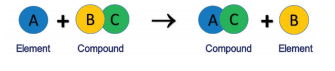
Single
Displacement Reactions:
Ø It is a
reaction between an element and a compound.
Ø When they
react, one of the elements of the compound-reactant is replaced by the
element-reactant to form a new compound and an element.
Ø The
general schematic representation of a single displacement reaction is given as:
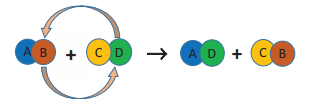
Double
Displacement Reactions:
Ø When two
compounds react, if their ions are interchanged, then the reaction is called
double displacement reaction.
Ø The ion
of one compound is replaced by the ion of the another
compound.
Ø Ions of
identical charges are only interchanged, i.e., a cation can be replaced by
other cations.
Ø This
reaction is also called ‘Metathesis Reaction’.
Ø The
schematic representation of a double displacement reaction is given below:
Combustion Reactions:
Ø A combustion reaction is one in which the
reactant rapidly combines with oxygen to form one or more oxides and energy
(heat).
Ø So in combustion reactions, one of the
reactants must be oxygen.
Ø Combustion reactions are majorly used as heat
energy sources in many of our day to day activities.
Ø For instance, we use LPG gas for domestic
cooking purposes.
Ø We get heat and flame from LPG gas by its
combustion reaction of its constituent gases.

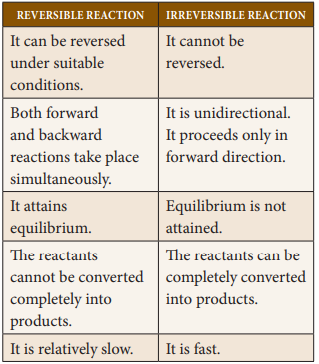
Differences
between reversible and irreversible reactions: