Health And Diseases
Abuse
And Types Of Abuse
·
Abuse refers to
cruel, violent, harmful or injurious treatment of another human being.
·
It includes physical, emotional or psychological, verbal, child and sexual abuses.
Child Abuse
·
Constitutes
all forms of physical or emotional ill treatment, sexual abuse, exploitation
resulting in child’s ill health,
survival and development.
·
Physical abuse of a child is defined as those acts that cause
physical harm such as threatening, beating, kicking and hitting the child.
Sexual Abuse
·
A form of
power and dominance of one person over another, which can result in harmful
consequence to the victim.
·
Adolescent
girls and women encounter sexual harassment in different forms.
·
Results in
psychological distress, physical illness and eating disorders in the affected
individuals.
Child Sexual Abuse
·
Verbal
remarks, comments, gestures and looks are the most common forms of sexual abuse.
·
Sexually
abused children show symptoms of genital injury, abdominal pain, frequent urinary
infection and behavioural problems.
Approaches for
Protection of an Abused Child
·
Child helpline
·
Counselling the child
·
Family support
·
Medical Care
·
Legal counsel
·
Rehabilitation
·
Community based efforts
Prevention of Child
Sexual Abuse
·
Do not talk to any suspected person or strangers and to maintain a
distance.
·
Not to be alone with unknown person.
·
To be careful while travelling alone in public or private transport.
·
Not to receive money, toys, gifts or chocolates from known or unknown person
to them without the knowledge of their parents.
·
Not to allow known or unknown person to touch them.
Drug,
Alcohol And Tobacco Abuse
·
The physical and mental dependency on alcohol, smoking and drugs is
called addiction.
·
The addictive potential of these substances pulls an individual into a vicious cycle leading to regular abuse and
dependency.
·
This dangerous behavior pattern among youth can be prevented through
proper guidance.
Drug
Abuse
·
A person who is habituated to a drug due to its prolonged use is called drug addict. This is called drug addiction or drug abuse.
·
A drug that modifies the physical, biological, psychological or social
behaviour of a person by stimulating, depressing or disturbing the functions of
the body and the mind is called addictive drug.
·
Certain drugs called psychotropic drugs which acts on the brain and alter
the behaviour, consciousness, power of thinking and perception.
·
They are referred as mood altering drugs.
·
Persons who consume these drugs become fully dependent on them, they
cannot live without drugs. This condition is referred as drug dependence.
Behaviourial Changes of
Drug Users
·
Drop in academic performance, absence from school or college.
·
Lack of interest in personal hygiene, isolation, depression, fatigue and
aggressive behaviour.
·
Deteriorating relationship with family and friends.
·
Change in food and sleeping habits.
·
Fluctuation in body weight and appetite.
·
Always looking out for an easy way to get money for obtaining drugs.
·
Prone to infections like AIDS and Hepatitis-B.
Drug De-addiction
·
Detoxification
·
Psychotherapy
·
Counselling to family
members
·
Rehabilitation
Tobacco
Abuse
·
Tobacco is obtained
from the tobacco plant Nicotiana tobaccum and Nicotiana rustica.
·
Addiction to tobacco
is due to ‘nicotine’ an alkaloid present in it. Nicotine is a stimulant, highly
harmful and poisonous substance.
·
Inhaling tobacco
smoke from cigars, cigarettes, bidis, pipes, hukka is called smoking.
·
When powdered tobacco
is taken through nose, it is called snuffing.
Smoking Hazards and
Effect of Tobaccos
·
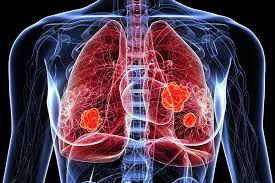
Benzopyrene and
polycyclic hydrocarbons present in tobacco smoke is carcinogenic causing lung
cancer.
·
Causes inflammation
of throat and bronchi leading to conditions like bronchitis and pulmonary
tuberculosis.
·
Inflammation of lung
alveoli, decrease surface area for gas exchange and cause emphysema.
·
Carbon monoxide of
tobacco smoke binds to haemoglobin of RBC and decreases its oxygen carrying
capacity causing hypoxia in body tissues.
·
Increased blood
pressure caused by smoking leads to increased risk of heart disease.
·
Causes increased
gastric secretion which leads to gastric and duodenal ulcers.
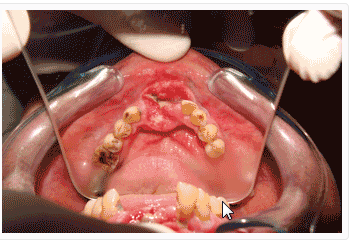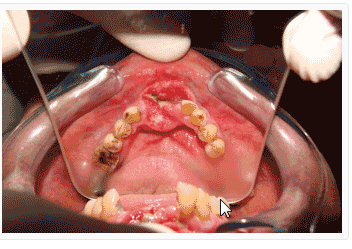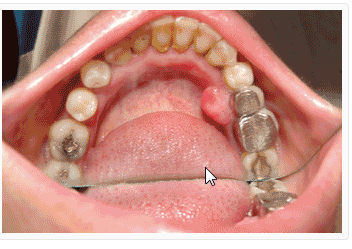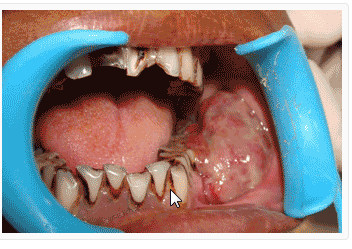
·
Tobacco chewing
causes oral cancer (mouth cancer).
Prevention of Smoking
·
Knowing the dangers of
smoking and chewing tobacco adolescents and the old people need to avoid these
habits.
·
Proper counselling
and medical assistance can help an addict to give up the habit of smoking.
Alcohol
Abuse
·
The dependence of
alcohol is called alcoholism and the addict is termed as alcoholic. It is
called alcohol abuse.
·
Drinking of alcohol
impairs one’s physical, physiological and psychological functions.
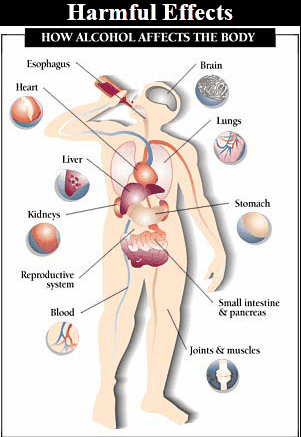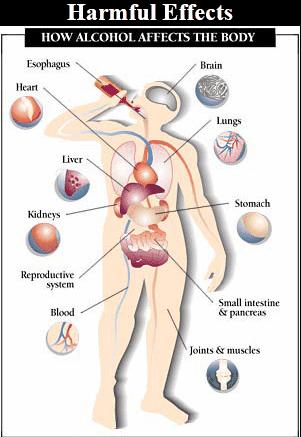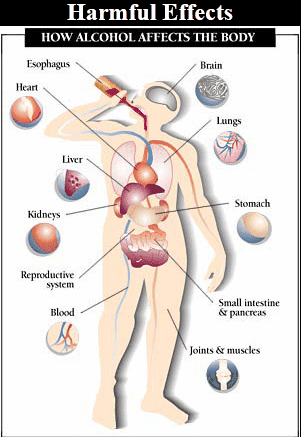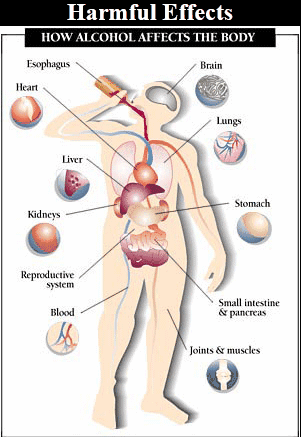
Harmful Effects of
Alcohol to Health
·
Nerve cell damage
resulting in various mental and physical disturbances.
·
Lack of co-ordination
of body organs.
·
Blurred or reduced
vision, results in road accidents.
·
Dilation of blood
vessels which may affect functioning of the heart.
·
Liver damage
resulting in fatty liver which leads to cirrhosis and formation of fibrous tissues.
·
Body loses its
control and consciousness eventually leading to health complications and
ultimately to death.
Rehabilitation Measures for
Alcoholics
·
Education and counselling.
·
Physical activity.
·
Seeking help from
parents and peer groups.
·
Medical assistance.
·
Alcohol de-addiction
and rehabilitation programmes are helpful to the individual so that they could
get rid of the problem completely and can lead a normal and healthy life.
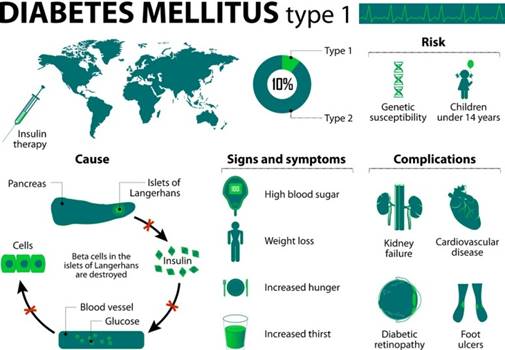
Diabetes
Mellitus
·
Diabetes mellitus is
a chronic metabolic disorder.
·
It is characterized
by increased blood glucose level due to insufficient, deficient or failure of insulin
secretion.
·
The most common
pancreatic endocrine disorder.
Type-1 Insulin Dependent
Diabetes Mellitus (IDDM)
·
IDDM accounts for 10
to 20% of the known diabetics.
·
This is caused by the
destruction of β-cells of the pancreas.
·
It is characterized
by abnormally elevated blood glucose levels (hyperglycemia) resulting from
inadequate insulin secretion.
·
Genetic inheritance
and environmental factors are the cause for this condition.
Type-2 Non-Insulin Dependent
Diabetes Mellitus (NIDDM)
·
This is also called
as adult onset diabetes and accounting for 80 to 90% of the diabetic
population.
·
Insulin production by
the pancreas is normal but its action is impaired.
·
The target cells do
not respond to insulin. It does not allow the movement of glucose into cells.
·
The causes are
multifactorial which include increasing age, obesity, sedentary life style,
overeating and physically inactive.
Symptoms
·
Increased blood glucose
level (Hyperglycemia).
·
Increased urine
output (Polyuria) leading to dehydration.
·
Loss of water leads
to thirst (Polydipsia) resulting in increased fluid intake.
·
Excessive glucose
excreted in urine (Glycosuria).
·
Excess hunger
(Polyphagia) due to loss of glucose in urine.
·
Fatigue and loss of
weight.
Prevention and Control
of Diabetes
·
Low carbohydrate and
fibre rich diets are more appropriate. Carbohydrates should be taken in the
form of starch and complex sugars.
·
Management with
insulin.
·
Physical activity.
·
Education and
Awareness.
Obesity
·
The state in which
there is an accumulation of excess body fat with an abnormal increase in body
weight.
·
A complex
multifactorial chronic disease developing from influence of social,
behavioural, psychological, metabolic and cellular factors.
·
Over weight and
obesity are conditions where the body weight is greater than the mean standard
weight for age and height of an individual.
·
Body mass index (BMI)
is an estimate of body fat and health risk.
BMI = ![]()
Causes and risk factors
·
Due to genetic
factors, physical inactivity, eating habits (overeating) and endocrine factors.
·
A positive risk
factor in development of hypertension, diabetes, gall bladder disease, coronary
heart disease and arthritis.
Prevention and Control
of Obesity
·
Low calorie, normal
protein, vitamins and mineral, restricted carbohydrate and fat, high fiber diet
can prevent overweight.
·
Meditation, yoga and
physical activity can also reduce stress related to overeating.
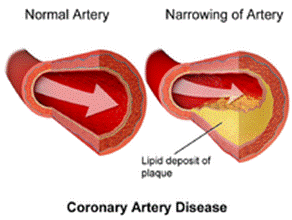
Heart
Diseases
·
Cardiovascular
disease (CVD) is associated with diseases of the heart and blood vessels.
·
Coronary heart
disease (CHD) is the most common form and is caused by deposition of
cholesterol in the blood vessels.
·
It leads to sudden
ischemia (deficient blood supply to heart muscle) and myocardial infarction
(death of the heart muscle tissue).
Causes
·
Hypercholesterolemia
(High blood cholesterol)
·
High blood pressure
(Hypertension)
·
Heridity (family
disorder)
·
Diet rich in
saturated fat and cholesterol
·
Obesity
·
Cigarette smoking
·
Emotional stress
·
Excessive alcohol
consumption
·
Physical inactivity
Symptoms
·
Shortness of breathe
·
Headache
·
Tiredness
·
Dizziness
·
Chest pain
·
Swelling of leg
·
Gastrointestinal
disturbances
Prevention and Control of
Heart Disease
·
Reduction in the
intake of calories, low saturated fat and cholesterol rich food, low
carbohydrates and common salt are some of the dietary modifications.
·
Increase in the
intake of fibre diet, fruits and vegetables, protein, minerals and vitamin are
required.
·
Physical activity
·
Addictive substance
avoidance
Cancer
·
The study of cancer
is called Oncology (Oncos - Tumor).
·
Cancer is an abnormal
and uncontrolled division of cells that invade and destroy surrounding tissue
forming a tumor or neoplasm (new growth).
·
The cancerous cells
migrate to distant parts of the body and affect new tissues. This process is
called metastasis.
|
More
to Know |
|
World
Cancer Day - 4th February |
Types of Cancers
·
Carcinomas arise from
epithelial and glandular tissues. They include cancers of skin, lung, stomach
and brain.
·
Sarcomas are occur in
the connective and muscular tissue. They include the cancer of bones,
cartilage, tendons, adipose tissue and muscles.
·
Leukaemia are
characterized by an increase in the formation of white blood cells in the bone
marrow and lymph nodes. Leukaemia are called blood cancers.
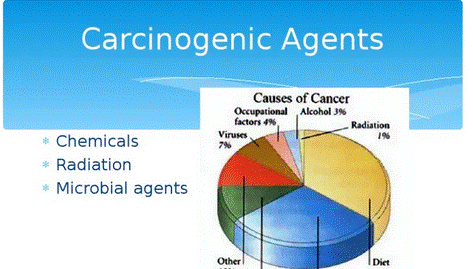
Carcinogenic Agents
·
Cancer causing agents
are called carcinogens.
·
Heavy smoking causes
lung cancer and cancers of oral cavity, pharynx (throat) and larynx. Betel and
tobacco chewing causes oral cancer. Excessive exposure to sunlight may cause
skin cancer.
·
Nicotine, caffeine,
products of combustion of coal and oil, pesticides, asbestos, nickel, certain
dyes and artificial sweetners induce cancer.
·
Ionizing radiations
like X-rays, gamma- rays, radioactive substances and non-ionising radiations
like UV rays cause DNA damage leading to cancer.
·
Cancer causing
viruses are called oncogenic viruses.
Treatment of Cancer
·
Surgery
·
Radiation therapy
·
Chemotherapy
·
Immunotherapy
Preventive measures for Cancer
·
Cancer control programmes
should focus on primary prevention and early detection.
·
Tobacco smoking is to
be avoided.
·
Excessive exposure to
radiation is to be avoided.
AIDS
(Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome)
·
A severe viral
disease and caused by Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV).
·
A condition in which
immune system fails and suppress the body’s disease fighting mechanism.
·
They attack the
lymphocytes and the affected individual is prone to infectious diseases.
Transmission of HIV
·
Sexual contact with
infected person.
·
Use of contaminated
needles or syringes especially in case of intravenous drug abusers.
·
By transfusion of
contaminated / infected blood or blood products.
·
From infected mother
to her child through placenta.
Symptoms and Treatment
of AIDS
·
Symptoms : Infected individuals become immunodeficient. Swelling of
lymph nodes, damage to brain, loss of memory, lack of appetite and weight loss,
fever, chronic diarrhoea, cough, lethargy,
pharyngitis, nausea
and headache.
·
Diagnosis : The presence of HIV virus can be confirmed by Western Blot
analysis or Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA).
·
Treatment : Anti-retroviral drugs and immunostimulative
therapy can prolong the life of the infected person.
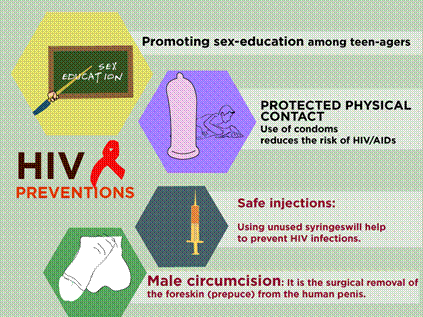
Prevention and Control of
AIDS
·
Screening of blood
from blood banks for HIV before transfusion.
·
Ensuring the use of
disposable needles and syringes in hospitals and clinics.
·
Advocating safe sex
and advantages of using condoms.
·
Creating awareness
campaign and educating people on the consequences of AIDS.
·
Persons with HIV/AIDS
should not be isolated from the family and society.
Mind
Map