Electricity
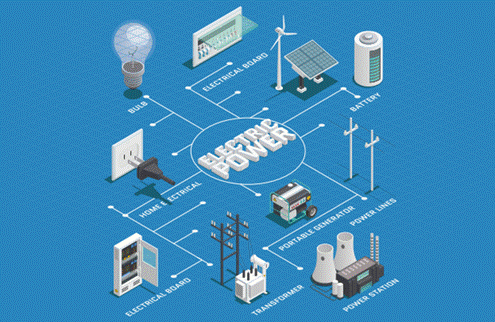
Introduction
We use
electricity in our day to day life. Have we ever wondered from where do we get
this electricity? How does this electricity work?
2.1 Sources of Electricity
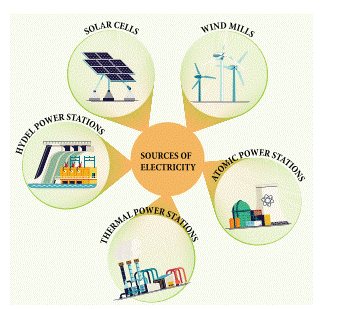
·
Any device from which electricity is
produced is called the source of electricity. We get electricity from different
sources.
·
The Major Electric power stations in
Tamilnadu are:
o
Thermal stations (Neyveli in Cuddalore
District, Ennore in Thiruvallur District), Hydel power stations (Mettur in
Salem District, Papanasam in Tirunelveli District), Atomic power stations
(Kalpakkam in Kanchipuram District, Koodankulam in Tirunelveli District), and
Windmills (Aralvaimozhi in Kanyakumari District Kayatharu in Tirunelveli
District).
·
Apart from these Solar panels which are
prevalent in many places are used to produce electricity.
Let us discuss in short about working power stations.
1. Thermal
Power stations

In
thermal power stations, the thermal energy generated by burning coal, diesel or
gas is used to produce steam. The steam thus produced is used to rotate the
turbine. While the turbine rotates, the coil of wire kept between the
electromagnet rotates. Due to electromagnetic induction electricity is
produced. Here heat energy is converted into electrical energy.
2. Hydel power stations

In
hydel power stations, the turbine is made to rotate by the flow of water from
dams to produce electricity. Here kinetic energy is converted into electrical
energy. Hydel stations have long economic lives and low operating cost.
3. Atomic
power stations

In atomic power stations, nuclear
energy is used to boil water the steam thus produced is used to rotate the
turbine. As a result, electricity is produced. Atomic power stations are also
called as nuclear power stations. Here nuclear energy is converted into
mechanical energy and then electrical energy.
4. Wind mills
In wind
mills, wind energy is used to rotate the turbine to produce electricity. Here
kinetic energy is converted into electrical energy.
2.2 Cell
·
A device that converts chemical energy
into electrical energy is called a cell.
·
A chemical solution which produces
positive and negative ions is used as electrolyte.
·
Two different metal plates are inserted
into electrolyte as electrodes to form a cell.
·
Due to chemical reactions, one
electrode gets positive charge and the other gets negative charge producing a
continuous flow of electric current.
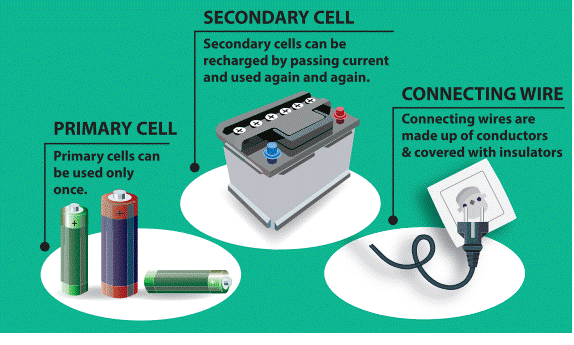
·
Depending on the continuity of flow of
electric current cells are classified into two types. They are primary cells
and secondary cells.
1.
Primary Cells
They cannot be recharged. So they can be used
only once. Hence, the primary cells are usually produced in small sizes.
Examples cells used in clocks, watches and toys etc., are primary cells.

2. Secondary
Cells
A cell that can be recharged many times is
called secondary cell.
These cells can be recharged by passing
electric current. So they can be used again and again. The size of the
secondary cells can be small or even large depending upon the usage. While the
secondary cells used in mobiles are in the size of a hand, the cells used in
automobiles like cars and buses are large and very heavy. Examples Secondary
Cells are used in Mobile phones, laptops, emergency lamps and vehicle
batteries.

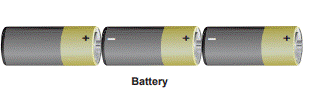
3. Battery
Often, we call cells as ‘batteries’.
However only when two or more cells are combined together they make a battery.
A cell is a single unit that converts chemical energy into electrical energy,
and a battery is a collection of cells.
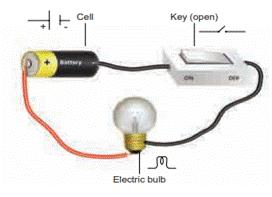
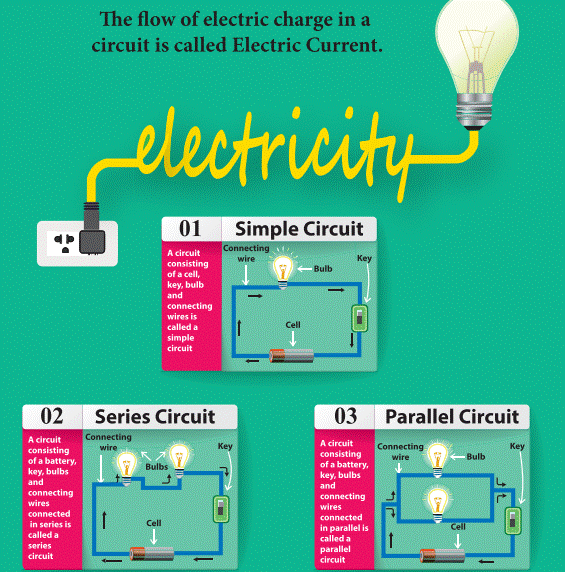
2.3 Electric Circuits
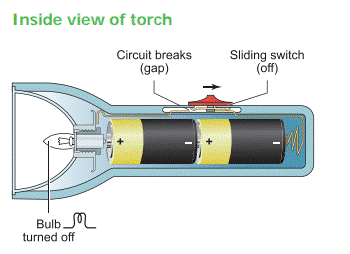
An
electric circuit is the continuous or unbroken closed path along which electric
current flows from the positive terminal to the negative terminal of the
battery. A circuit generally has:
a)
A cell are battery- a source of electric current
b)
Connecting wires- for carrying current
c)
A bulb- a device that consumes the electricity
d)
A key or a switch- this may be connected anywhere along the circuit to stop or
allow the flow of current.
a. Open
Circuit
In
a circuit if the key is in open (off) condition, then electricity will not flow
and the circuit is called an open circuit. The bulb will not glow in this
circuit.
b. Closed Circuit
In
a circuit if the key is in closed (on) condition, then electricity will flow
and the circuit is called a closed circuit. The bulb will glow in this circuit.

Types of Circuits:
1.
Simple Circuit
2.
Series Circuit
3.
Parallel Circuits
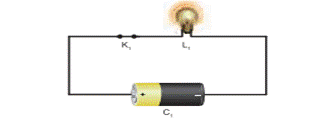
1. Simple Circuit
A circuit consisting of a cell, key,
bulb and connecting wires is called a simple circuit.
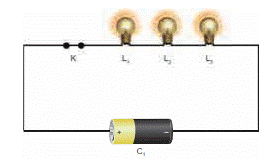
2. Series Circuit
If
two or more bulbs are connected in series in a circuit, then that type of
circuit is called series circuit. If any one of the bulbs is damaged or
disconnected, the entire circuit will not work.
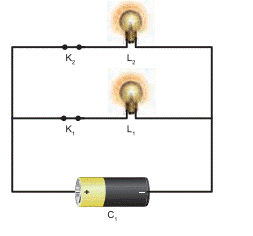
3. Parallel Circuit
If two or more bulbs are connected
in parallel in a circuit, then that type of circuit is called parallel circuit.
If any one of the bulb is damaged or disconnected the other part of the circuit
will work. So parallel circuits are used in homes.
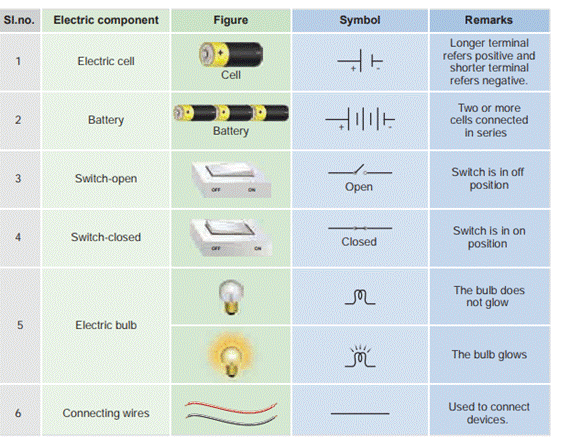
Symbols of Electric
Components
In the circuits discussed above, we
used the figures of electric components. Using electric components in
complicated circuits is difficult. So, symbols of the components are used
instead of figures. If these symbols used in electric circuits, even
complicated circuits can be easily understood.
2.4 Conductors and
Insulators
Will
electric current pass through all materials? If an electric wire is cut, we
could see a metal wire surrounded by another material. Do you know why it is
so?
1.
Conductors
The
rate of flow of electric charges in a circuit is called electric current. The
materials which allow electric charges to pass through them are called conductors.
Examples: Copper, iron, aluminum, impure water, earth etc.,

2.
Insulators (Non-Conductors)
The materials which do not allow electric
charges to pass through them are called insulators or nonconductors. Examples:
plastic, glass, wood, rubber, china clay, ebonite etc.,

Safety measures to
safeguard a person from electric shock
I.
Switch off the power supply.
II.
Remove the connection from the switch.
III.
Push him away using non - conducting materials.
IV.
Give him first aid and take him to the nearest health center.