Water
Introduction
Water is one of the basic
substance present in the earth. It plays a vital role in the evolution and
survival of life. It is impossible to imagine life on the earth without water.
Water helps to regulate the temperature of our planet. It also helps to
maintain the temperature in organisms.
Where and how water is found on the earth?
Water
is available in nature in three forms – Solid, Liquid ,
Vapour.
Ø Solid form of water
- Ice - It is
present in ice bergs and ice caps on top of tall mountains, galaciers
and polar regions.
Ø Liquid form of water – Water – It is present in oceans,
seas, lakes, rivers and even underground.
Ø Gaseous form of water – Vapour – It is present in the air
around us.
Availability of water
We know
that nearly ¾th of the surface of the earth is covered by water. Most of the water, that is 97% of the total amount of water that exits
on earth is found in seas and oceans. Can we drink the water available in the
sea? Sea water is salty. But water used for our daily purposes is not salty. It
is known as fresh water. Water obtained from ponds, puddles, river, tube-wells
and taps at home is usually fresh water. If the total water on earth be 100%,
let’s see what percent would be the availability of fresh water. Look at the
pie chart given below
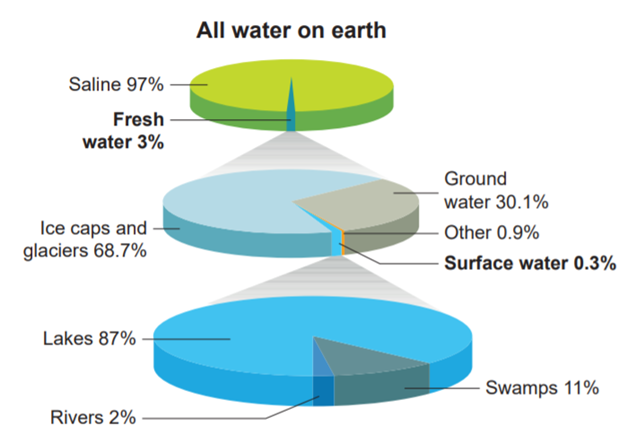
From the pie chart, it can also be noted
that 97% water is saline water. Only 3% found is the freshwater and that too in
polar ice caps and glaciers. So this portion of water is not readily available
for drinking.
The distribution of the
totally available freshwater is as follows:
· Polar
ice caps and glaciers 68.7%
· Ground
water 30.1%
· Other
sources of water 0.9%
· Surface
water 0.3 %
The distribution
of total surface water is as follows:
· Lakes
87%
· Rivers
2%
· Swamps
11%
Thus the above pie chart
explains that we have a very small amount of fresh water available for human
usage and so maintaining the water table and the conservation of water is very
essential.
Composition of water
Water
is a transparent, tasteless, odourless and nearly colourless chemical substance. It is composed of two atoms
of hydrogen combined with one atom of oxygen. The molecular formula of water is
H2O. However, the physical composition of water changes from place to place. It
can be clear or cloudy, oxygenated or not very oxygenated and it can be fresh
or salty. The amount of salt in water is termed as salinity. Based on its
salinity water is classified into three main categories such as freshwater,
brackish water and sea water. Fresh water contains 0.05% to 1% of salt.
Brackish water contains upto 3% of salt and seawater contains more than 3% of
salt. Ocean water is composed of many substances. The salts include sodium
chloride, magnesium chloride and calcium chloride.
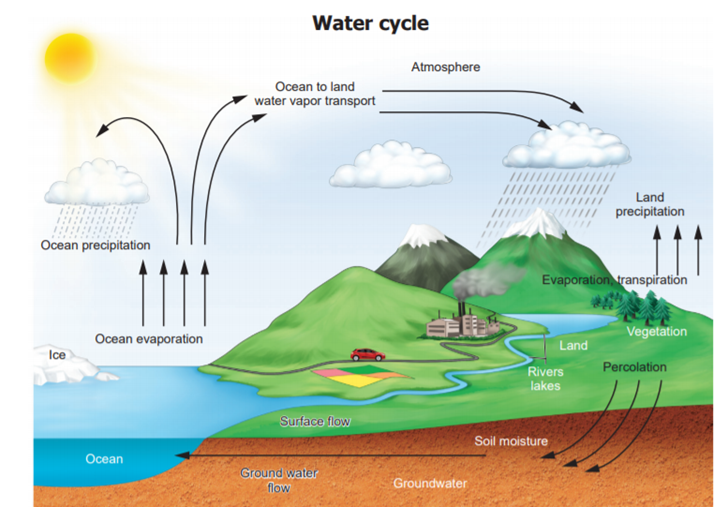
Water cycle
The water
on the earth evaporates into the atmosphere due to the heat of the sun. The
water vapour in the atmosphere forms clouds. From the clouds water falls on the
earth in the form of rain or snow. By this natural process, water gets renewed.
This is called water cycle. Water cycle is a continuous process. It involves
three stages - evaporation, condensation and precipitation. It is also called
the hydrological cycle. Evaporation : Water from
oceans, lakes,ponds and rivers evaporates due to the
heat of the sun. Condensation : Water vapour which
enters into the atmosphere by evaporation moves upward with air, gets cooled
and changes into tiny water droplets that form clouds in the sky
Precipitation :
The
millions of tiny droplets collide with one another to form larger droplets.
When the air around the clouds is cool these drops of water fall in the form of
snow or rain.
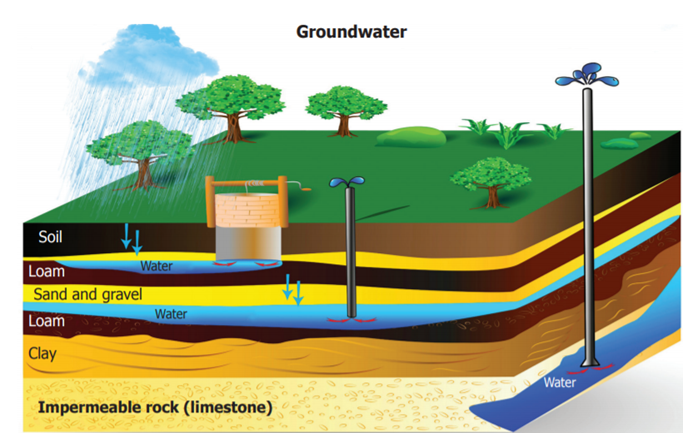
Natural Sources of fresh water
Three
types of natural sources of fresh water are available on the earth.
v Surface water
Water
present on the surface of the earth such as river,lake,ponds, streams or fresh water wetland is called
surface water.

v Frozen water
Water that is present in the
frozen form as polar ice-caps and glaciers are called frozen water. A larger
portion of water is 68.7% of the total available fresh water is in frozen
state.

v Ground water
Ground water is the water
present beneath Earth's surface in soil. This water is obtained through
springs, open wells, tube wells, or hand pumps etc.,
Conservation of water
There
is no change in the total quantity of water available on the earth. It remains
the same. But the water useful for plants, animals and man is decreasing day by
day. It is called scarcity of water.
The main reasons for water scarcity
· Population
explosion
· Uneven
distribution of rainfall
· Decline
of ground watertable
· Pollution
of water
· Careless
use of water
Methods of water conservation:
Mainly, two methods can be
followed for the conservation of water.
Ø Water management
· Bringing
awareness about the bad effects of throwing wastes into the water bodies
· Recycling
of water by separating pollutants.
· Minimizing
the use of chemical fertilizers in agriculture. It reduces the pollution of
underground water.
· Controlling
deforestation
· Adopting
drip irrigation and sprinkler irrigation in agriculture. By this way lesser
amount of water can be used for the irrigation
Ø Rainwater harvesting
· Collecting
water from where it falls.
(e.g):
Collecting water from the roof tops of the houses or buildings (Roof water
harvesting).
· Collecting
flowing rain water
(e.g):
Collecting rainwater by constructing ponds with bund.
Importance of water
Ø Human body
Our
body uses water in all its cells, organs and tissues to help regulate its
temperature and maintain other bodily functions. On an average, the human body
requires 2 – 3 litres of water per day for proper
functioning. Water helps in digestion of food and removal of toxins from the
body.
Ø Domestic
Apart from drinking, people use
water for many other purposes. These include: cooking, bathing, washing
clothes, washing utensils, keeping houses and common places clean, watering
plants, etc.
Ø Agriculture
Water is also essential for the
healthy growth of farm crops and farm stock and is used in the manufacture of
many products.
Ø Industry
Industry depends on water at all levels of
production. It is used as a material, a solvent and for generating electricity.