Atomic Structure
1.
All the matter is made up of molecules.
The molecules are combination of atoms of different elements or the same
element. Thus, atom is the smallest constituent particle of matter.
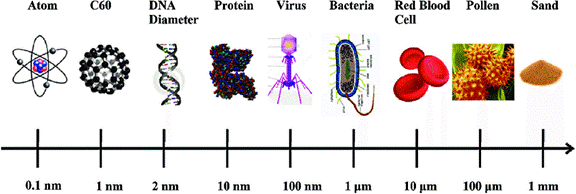
2. Atom has an average diameter of 0.0000000001m or 1×10-9 m
3.
Dalton’s atomic theory
◦
John
Dalton proposed the atomic theory in the year 1808.
◦
He
proposed that matter consists of very small particles which he named atoms.
◦
An
atom is the smallest indivisible particle, it is spherical in shape.
Drawbacks
◦ His
theory does not propose anything about the positive and negative charges of an
atom.
4.
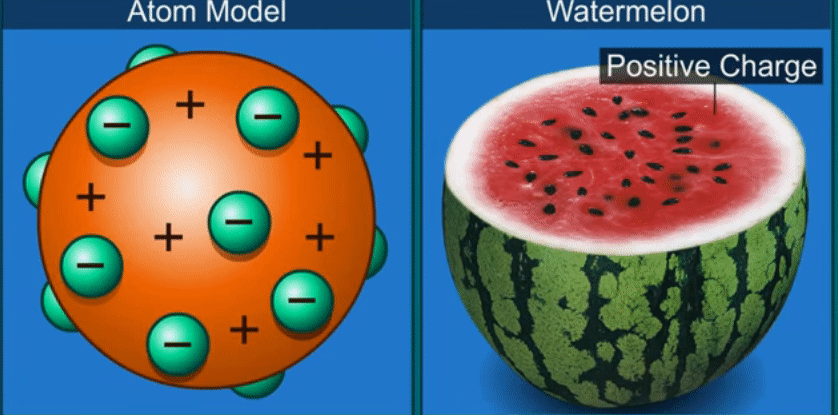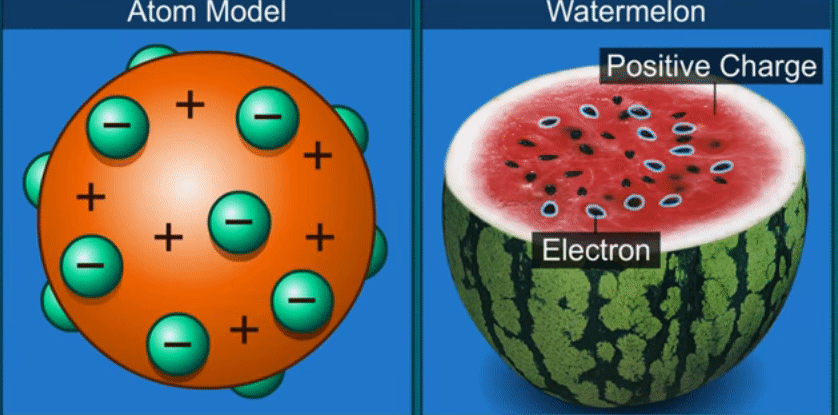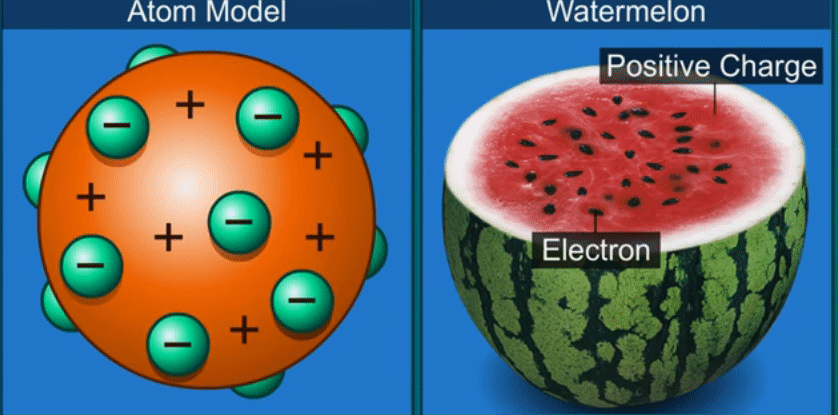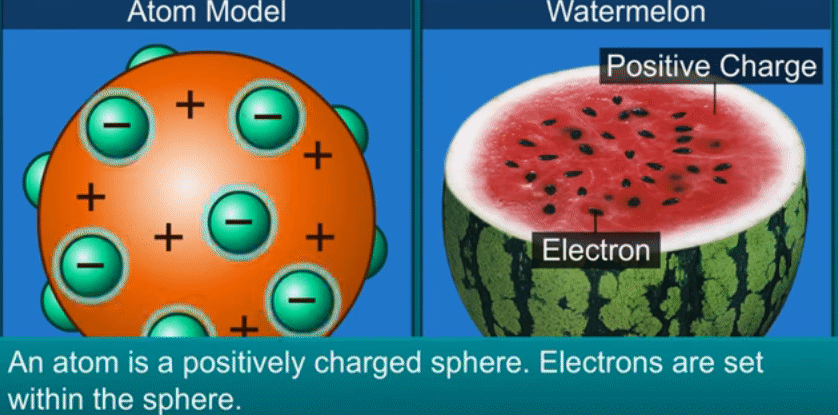
J.J. Thomson’s theory
◦
Thomson
compared an atom to a watermelon.
◦
His
theory proposed that the atom has positively charged part like the red part of
the watermelon and in it are embedded, like the seeds, negatively charged
particles which he called electrons.
◦
According
to this theory as the positive and negative charges are equal, the atom as a
whole does not have any resultant charge.
◦
Thomson’s
greatest contribution was to prove by experimentation the existence of the
negatively charged particles or electrons in an atom. For this discovery, he
was awarded the Nobel Prize.
Drawbacks
◦ On
further discovery, it was found that an atom is not like a watermelon.
5.
Rutherford’s theory
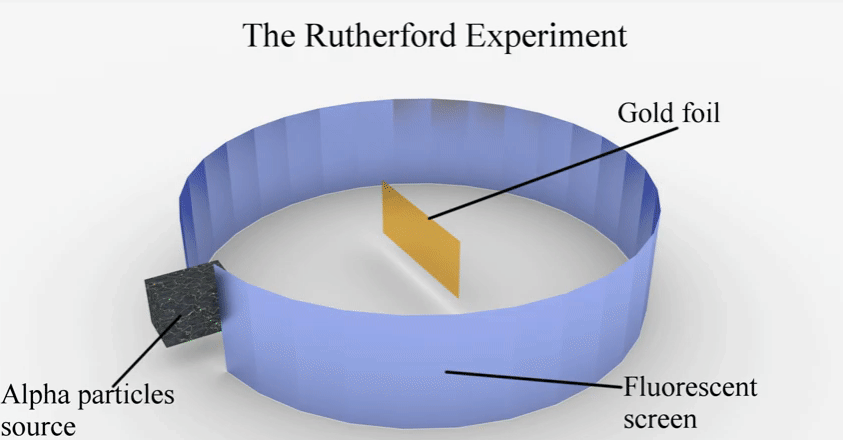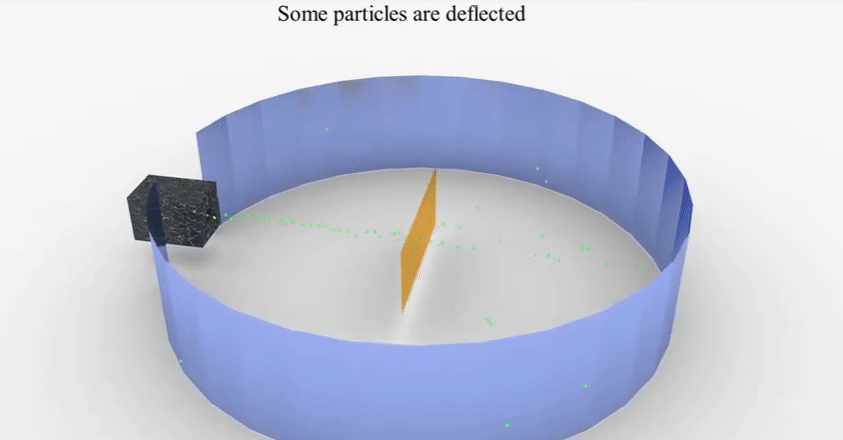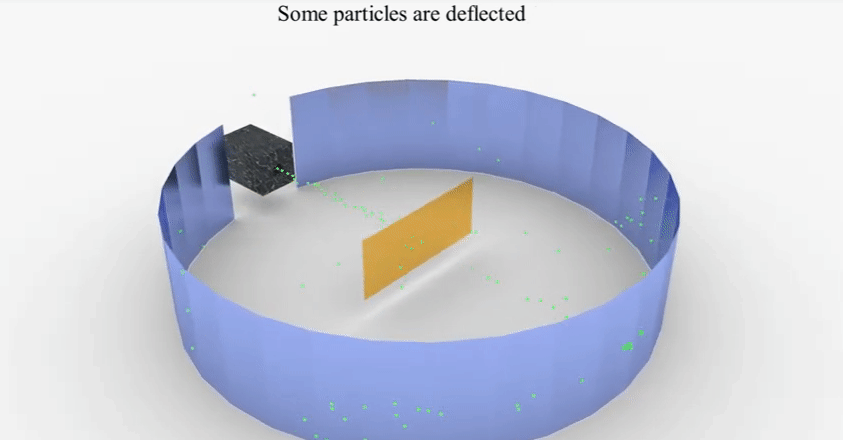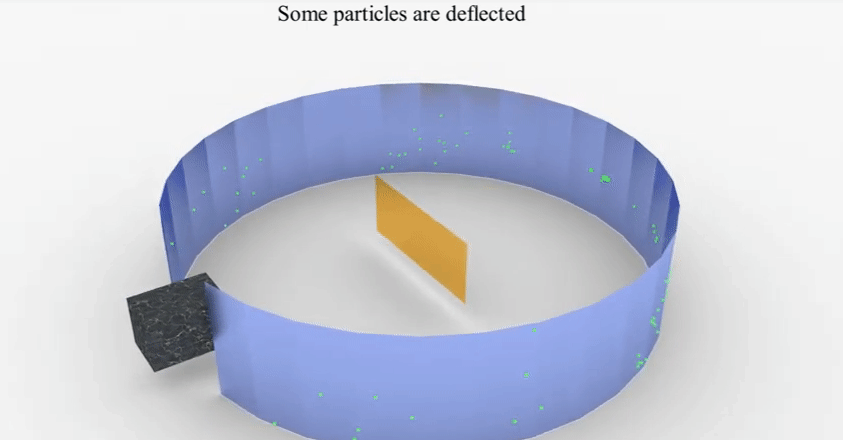
Earnest
Rutherford’s experiment and observations
▪
Set
up: He bombarded a very thin layer of gold with positively charged alpha rays.
▪
He
found that most of these rays which travel at a great velocity passed through
the gold sheet without encountering any obstacles.
▪
A few
are, however, turned back from the sheet. Rutherford considered this remarkable
and miraculous as if a bullet had turned back after colliding with tissue
paper.
Conclusions drawn from
the experiment.
◦ The
fact that most alpha particles pass through the gold sheet means that the atom
consists mainly of empty space.
◦ The
part from which the positively charged particles are turned back is positively
charged but very small in size as compared to the empty space.
◦ For
this theory, he was awarded the Nobel Prize for chemistry.
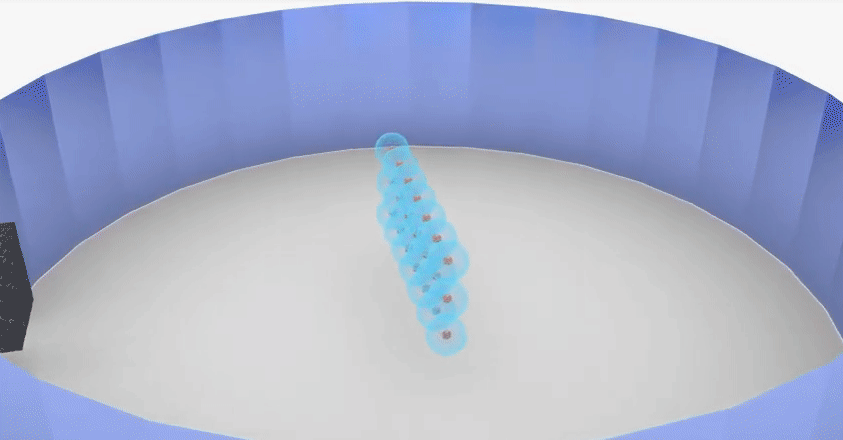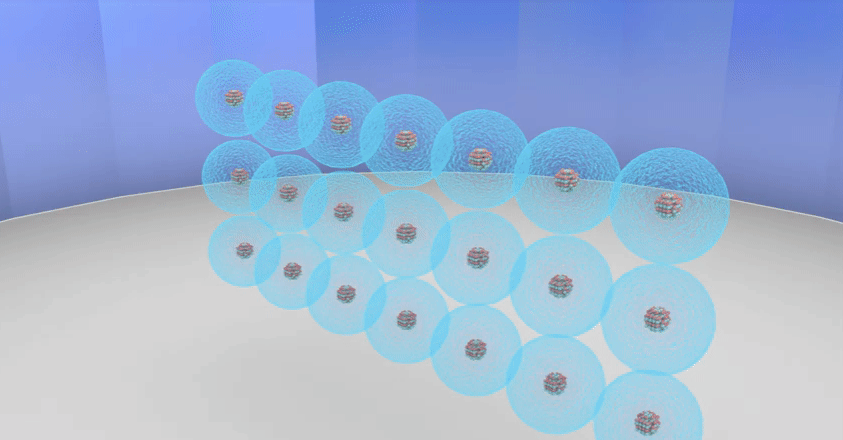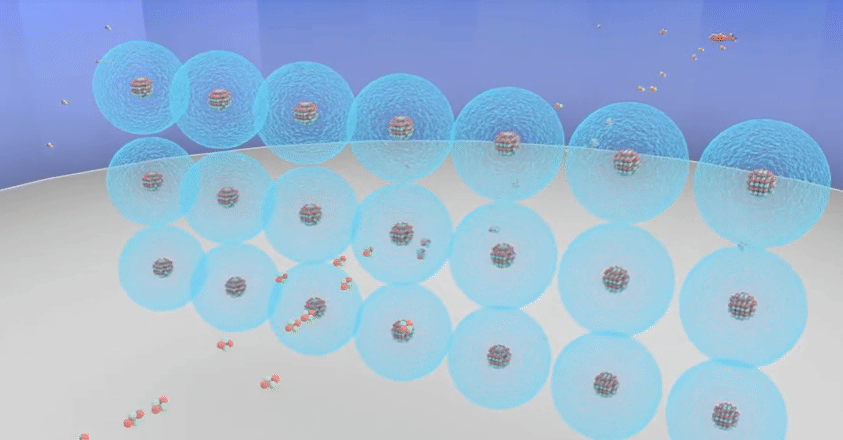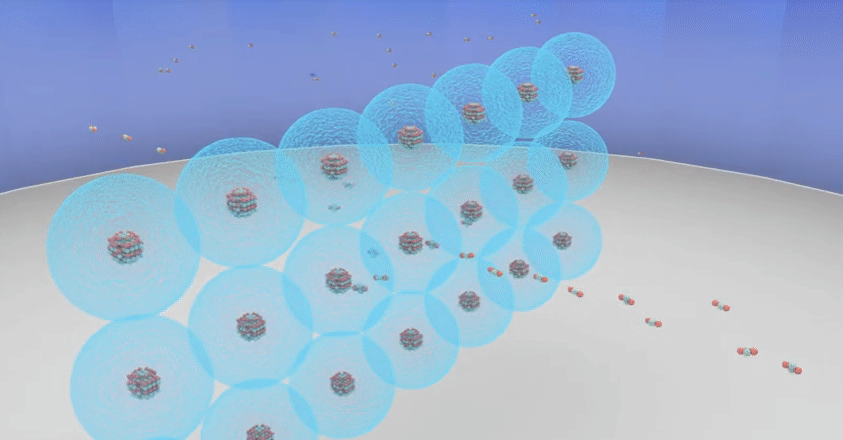
Rutherford’s theory proposes that
◦ The nucleus at the centre of the atom has the
positive charge. Most of the mass of the atom is concentrated in the nucleus.
◦ The negatively charged electrons revolve around
the nucleus in specific orbits.
◦ In comparison with the size of the atom, the
nucleus is very very small
6.
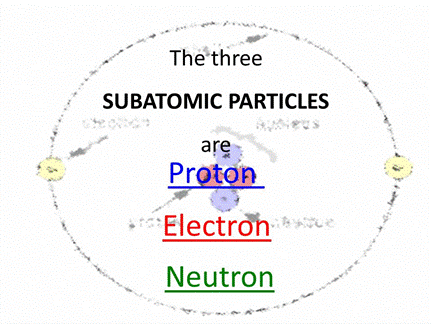
Particles that make up the atom are called
Subatomic Particles. The three main sub-atomic particles are: electron, neutron
and proton.
◦ Proton
(p)
The proton is the positively charged
particle and it’s located in the nucleus. Its positive charge is of the same
magnitude as that of the electron’s negative charge.
◦ Neutron
(n)
Neutron
is inside the nucleus. The neutron does not have any charge. Excepting hydrogen
(protium), the nuclei of all atoms contain neutrons.
◦ Electron
(e)
This
is a negatively charged particle. Electrons revolve around the nucleus of the
atom in specific orbits.
7.
Characteristics of the sub-atomic particles:
◦ Protons
and Neutrons are the two types of particles in the nucleus of an atom. They are
called nucleons.
◦ The
total negative charge of all an electrons outside the nucleus is equal to the
total positive charge in the nucleus. That makes the atom electrically neutral.
◦ The
mass of an electron is negligible as compared to that of a proton or neutron.
Hence, the mass of an atom depends on the number of protons and neutrons in the
nucleus
8.
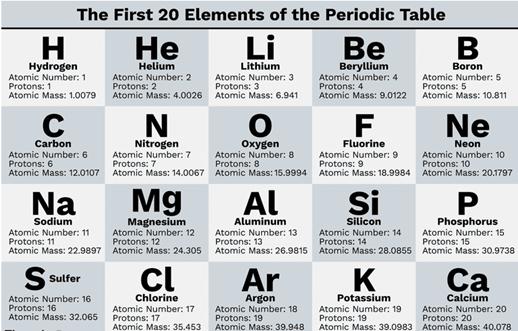
Atomic number (Z)
◦ The number of electrons or protons in an atom is
called the atomic number of that atom.
◦ It is represented by the letter Z.
◦ Thus, if we know the atomic number of an atom,
we know the number of electrons or protons in it.
9. Mass number (A) is equal to the sum of
the number of protons (p) and neutrons (n) in the nucleus.
Atomic mass or mass number = Number
of Protons + Number of Neutrons
A
= p+n
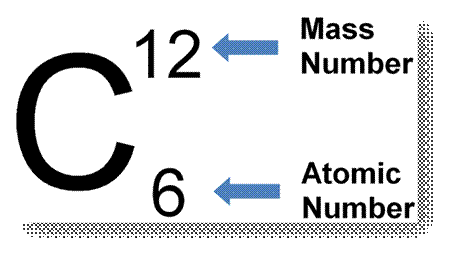
10. When writing the symbol of an element, its
atomic number (as subscript) and atomic mass (as superscript) number are also
written. For example, the symbols of hydrogen, carbon and oxygen are written as
1H1 (atomin number – 1, atomic mass -1), 6C12
(atomic number – 6, atomic mass – 12), 8O16 (atomic
number – 8, atomic mass – 16) respectively.
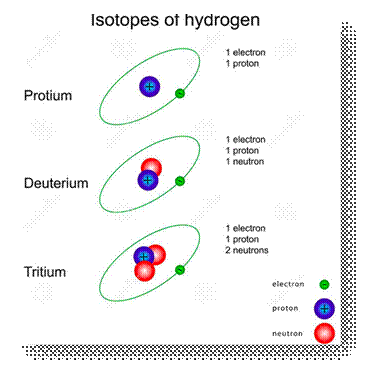
11. Isotopes
◦ Atoms
of the same element can have different number of neutrons. Such atoms will have
same atomic number but different mass numbers. These atoms are called isotopes.
◦ For
example, Hydrogen has three isotopes: Hydrogen (1H1),
Deuterium (1H2), and Tritium (1H3).
12.
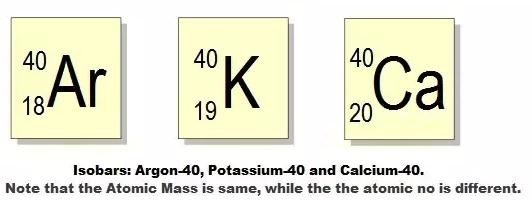
Isobars
◦ Atoms
that have the same mass number but different atomic numbers.
◦ For
example: Calcium – 40 and Argon – 40
13. Isotones
◦ Atoms that have the same number of neutons but
different number of protons.
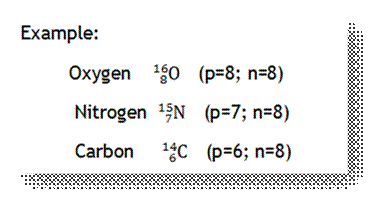
14.
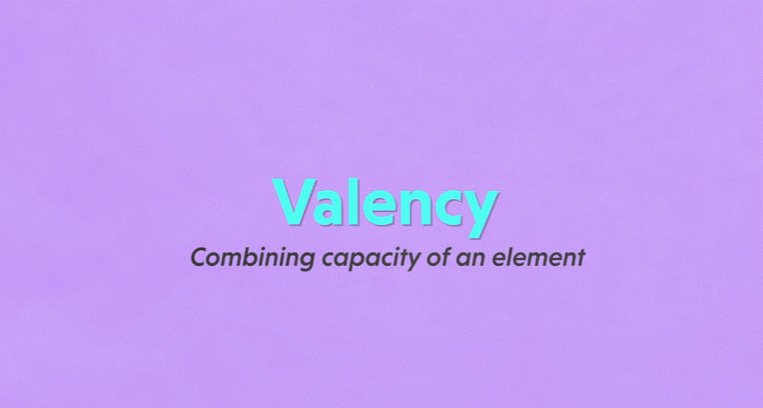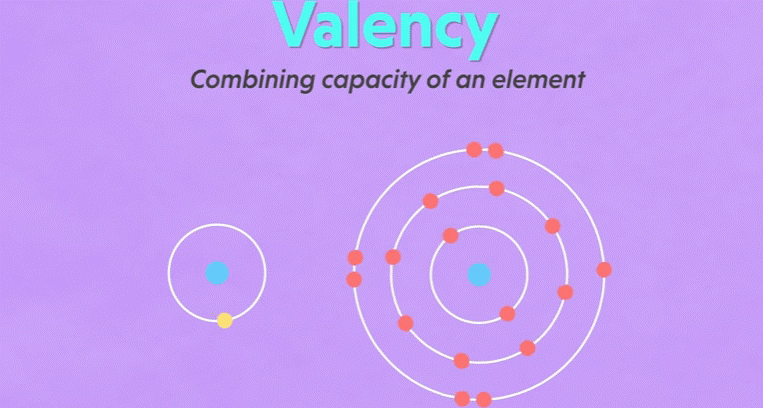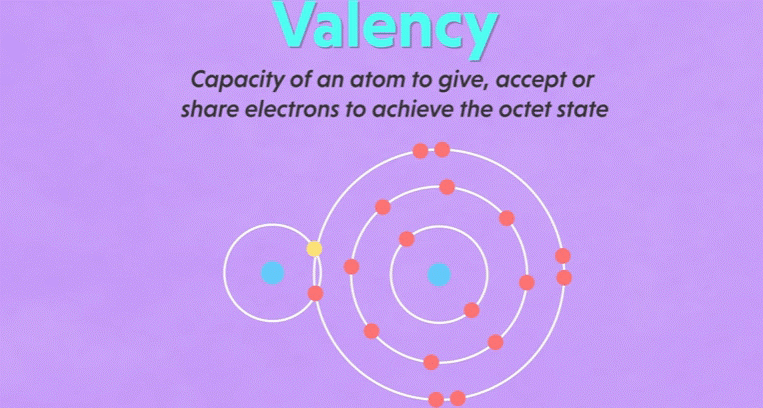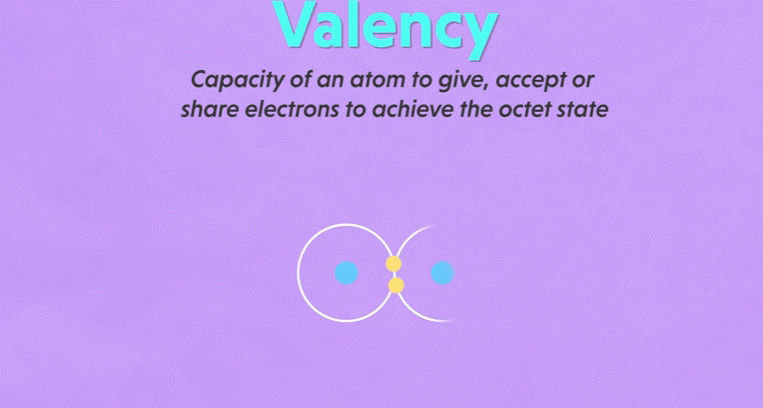
Valency
▪ It
is defined as the combining capacity of an element.
▪ Atoms
of different elements combine with each other to form molecules.
▪ Valency
determines the number of atoms of an element that combines with atom or atoms
of another type.
▪ It
is a measure of how many hydrogen atoms an atom can combine with.
15. For example: Oxygen can combine with two
hydrogen atoms and create water molecule, the valency of oxygen atom is two.
16. Classification
of elements on the basis of its valency.
◦ The
element having valency one is called monovalent. For example: Hydrogen and
Sodium.
◦ The
elements having valency two are called divalent. For example: Oxygen and
Beryllium.
◦ The
elements having valency three are called trivalent. For example: Nitrogen and
Aluminium.
◦ Some
elements exhibits more than one valency. For example: Iron combines with oxygen
to form two types ferrous oxide (exhibits valency 2) and ferric oxide (exhibits
valency 3).
17. When atoms of different elements combine
with each other than molecules of compounds are formed.