Universe and Space
Introduction
Our ancestors have
observed and documented the objects seen in the night sky. The field of study
of the universe is called astronomy. We know that there are billions and
billions of stars in the universe, although only about 2000 or so are visible
to naked eye.
Universe is commonly
defined as the totality of everything that exists or is known to exist. Even
though the spatial size of the entire universe is still unknown, it is possible
to measure the observable universe.
The universe consists of
galaxies, planets, stars, meteorites, satellites and all other forms of matter
and energy. And it is a world of wonder. Let us move into this world of wonder
to know more interesting facts about the place of residence of our solar
system.
GEO Centric Theory
Sky is a wonder. Sun,
Moon, stars all appear to rise in the East and move towards the west, giving us
an impression that all these objects are going around the Earth.
When you look at the
night sky you can see lot of twinkling objects. But a few of them differ from
the others. They don’t twinkle and while the other stars hold a fixed pattern
from night to night, these drift. They wander across the sky, moving against
the backdrop of stars. These are called planets.
Our ancestors observed
this and they imagined a universe with the Earth at the center, the stars in
the distant background, and Sun, Moon and the planets orbiting around us.
Two observations
supported the idea that Earth was the center of the Universe. First, from
anywhere on the Earth, the Sun appears to revolve around the Earth once in
a day. While the Moon and the planets have their own motions, they also appear
to revolve around the Earth about once per day. Even the celestial sphere
studded with stars appears to rise and set in the evening, and make one
complete rotation in a year. Second, the Earth seems to be unmoving from
the perspective of an earthbound observer; it feels stationary.

As civilization
progressed the early astronomers found two types of motion of celestial
objects. Let us take the case of Moon. On a daily basis Moon appears to rise in
the east and set in the west. Thus, one can say that Moon is going around the
Earth with a period of one day. But for a careful observer, it was clear that
the Moon was also exhibiting another motion. Suppose, the Moon is appearing in
the sky today near the star Asvini, tomorrow we will observe that the Moon is
near the star Bharani, a star east of Asvini. And the next day it will be near
the star Kartikai, east of Bharani. After 27 days, moving little by little
eastwards, the Moon again stations itself near asvini. Thus, everyday Moon
appears to move from east to west in one day where as it appears to go in a
circle from west to east in the background of stars in about 27 days.
These two motions were
puzzling. Very soon astronomers like Aryabhata said that Earth is spinning in
its axis, that is the cause of apparent daily motion from East to West. Whereas
the eastward motion of Moon in the celestial sphere with a period of about 27
days, was seen as the ‘actual’ motion of the celestial objects.
Thus, the geocentric
model (also known as geocentrism), that is a description of the Universe with
spherical and spinning Earth at the center and the Sun, Moon, stars, and
planets all orbits the Earth emerged in various cultures. In Greece, this model
was put forth by the Greek philosopher Plato and his disciple Aristotle in 6th
century B.C. It was standardized by a Greeco Roman mathematician Ptolemy in the
2nd Century A.D. A similar model is seen in the Siddhanthic astronomy in India
like Aryabhateeyam of Aryabhata.
How moon exhibit phases
Astronomers in ancient
times also observed certain facts. The Purananuru (65) of Sangam literature,
the poet Poet Kalathalaiyar singing in appreciation of Cheraman Peruncheralathan
says“
On the day when the full
moon appears, the sunand moon look at each other with their bright light. In
the evening time, one sphere hides behind the mountains.”
On the full moon day,
when the Sun is setting in the west, precisely at the same time, Moon rises at
the East. That is both Sun and Moon are in the opposite side. Likewise when it
is waning half moon, the Moon is rises when it is midnight and the waxing half
moon rises during noon. From such observations and modelling ancient astronomers
could explain why we have waxing and waning of moon.
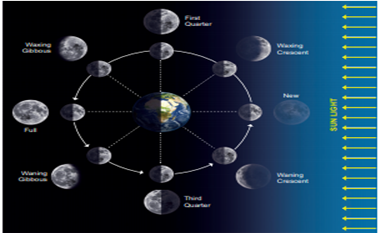
It is probably easier to
understand the waxing and waning of Moon in the order of new moon & full
moon and then how the first and third quarter moon (half moon) appear and then
the phases in between.
Sun is the source of
light. Sun light falls on the spherical earth, but only on the side facing Sun.
The opposite side of Earth is without sunlight. As the Earth spins day and
night follows as different parts of Earth appear before the Sun. That is at all
times one half of Earth is illuminated by Sun and one half is in darkness.
As shown in the above
diagram, when the moon is positioned between the earth and sun, notice all the
illuminated part of Moon is away from Earth. Hence we cannot see any part of
the illuminated side of the Moon. Only the dark side of Moon is towards Earth.
When the moon is in this position, we have new moon.
Now look at the moon
when it is behind the Earth. Now the portion of the moon illuminated by sun is
totally towards Earth. The dark side is away from the Earth. This means the
moon will appear to be round in the sky. This is full moon.
When the Sun, Earth and
Moon are in 90 degree angle .Now if you look at the portion of moon facing
Earth, we will see half if it illuminated and half is dark side. Thus, the moon
will appear as half moon. The half moon during the waxing period is called as
first quarter and the half moon during the waning period is called as third
quarter. (figure sun moon and earth are at right angles)
Epicycles
Moon going around Earth
with 27 day period nicely explained its motion. However astronomers in ancient
times faced problem in explaining the motion of the then known five planets-
Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter and Saturn.
Moon in the background
of stars moved everyday eastwards nicely. However for example, if we were
observing the motion of Mars from January , it would appear to move eastward in
the background stars. That is the position of mars today will be near a star
which is east of the star near which it was yesterday. However on June 28 , we
will see a change. From that date the Mars would appear to move west rather
than its normal eastward motion. This reversal of direction of planets is
called as ‘retrograde motion’. If we continue to observe, on August 28 once
again the Mars would appear to reverse the direction and again on its usual
eastward motion in the celestial sphere. Usually Jupiter is brighter than Mars,
however, around the period of retrograde motion the Mars was much bright than
other times; even brighter than Jupiter.
Other planets also
exhibited number of puzzling behaviours. Venus and Mercury always appeared very
close to Sun, and hence never appeared in the midnight sky. The brightness of
Jupiter also varied again when it exhibited retrograde motion. For example in
2018, Jupiter reversed its direction of motion on March 9, 2018 and again
resumed its normal eastward motion on July 11, 2018.
The simple geocentric
model, where planets go around the Earth could not explain why the brightness
of the planets changed, and why they reversed their directions. Change in
brightness and retrograde motion would be impossible if we assumed that the
planets were at the same distance at all times from Earth.
To explain the puzzling
phenomena astronomers in early times proposed a change in the simple geocentric
model. This is called as epicycle model.
Ptolemy (2nd cent) in
Greece, Aryabhatta in India and others used the epicycle model to explain the
motion of the celestial objects. Their models were improved by generation of
astronomers like Tycho Brahe and Neelakanta Somayaji.
Although, the model
explained many phenomena there were number of mismatches. The model was
becoming messy.
Arrival of telescope
Ø Telescope
was invented by Hans Lippershey but Galilio used it for studying the sky for
the first time.
Ø The
telescope showed more universe was than visible to naked eye. With his simple
telescope matching toy telescopes of today, Galilio was able to see mountains
on the Moon, small dim stars invisible to naked eye, sunspots on the face of
Sun.
Ø He
was able to demonstrate that the milky way, an hazy bright patch in the sky is
nothing but thousands of stars huddled together, Jupiter had moons going around
it and Saturn had mysterious appendage which we now know as rings.
Ø One
of the most startling observations he made was related to telescopic
observation of Venus. This convinced him to accept the theory of the Polish
Astronomer Nicolus Copernicus, that it is not Sun, planets and Stars that go around
Earth, but it is Earth and other planets that go around the Sun- heliocentric
theory.
Heliocentric model
Dissatisfied with the
messy epicycle model Nicolus Copernicus, radically proposed that the model will
become simple if we assume Sun is at the center and all planets, including
Earth, go around it.
Suppose, Earth and Mars
are on the two sides of the Sun, then Mars would be far and appear dim,
compared to when they are on the same side. Earth orbit around Sun in 365 days,
whereas Mars takes 687 days.
This implies at times
Earth will overtake Mars. When the Earth is approaching and overtaking Mars,
the Mars would appear to exhibit retrograde motion. In short all the observed
phenomena could be explained in a simple way.
How do we know that actually Sun is at the center or not?
Galileo found that his
observation of Venus gave the observational evidence to support the
heliocentric theory. Galileo observed Venus in 1610-1611 with a telescope. To
naked eye, Venus is just a gleaming bright spot.
However, through a
telescope, the shape of the planet can be seen. Galilio was startled to find
like Moon Venus too exhibited phases. The shape varied from crescent to
gibbous. Also, the size of the planet varied.
When the planet was in
gibbous phase the size was small, and when it was thin crescent the size was
many folds higher.
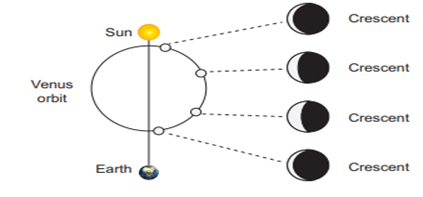
As
the Venus went around the epicycle, as shown in the diagram Venus would exhibit
phases. Thus, the variation in the brightness can also be explained. It became
clear to Galilio that the geocentric epicycle model will not help in accounting
for the observed phases of the Venus.
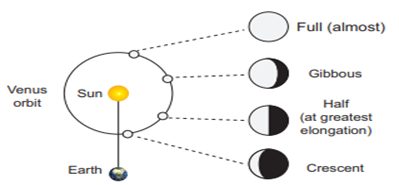
Look at the above
diagram. If the Venus was going around the Sun, and its orbit is inside that of
Earth, Venus would appear always near the Sun in the sky. It can never be seen
in the midnight sky.. If the Venus was revolving around the Earth, we can never
see the gibbous phase of the Venus and it would be seen only if it is orbiting
the he Sun.
This clinching
observational evidence proved that at the least Venus orbited around the Sun.
Further evidences collected by astronomers using telescope and other advanced
modern instruments gave enough evidence that all planets revolve around the
Sun.
If Galileo were around
today, he would surely be amazed at exploration of our solar system and beyond
by ISRO, NASA, Russian space agency and others.
Now we can observe
planets orbiting around other stars (called exoplanets), proving that not only
planets orbit around the Sun in solar system, but all around the universe such
planetary systems exist.
Origin of the Universe
Our Sun is a star with a
planetary system. Billions of such stars consitute a system called as galaxy.
The name of our galaxy is, Milky Way. Like Milky Way, there are at least
hundreds of billions of galaxies in the Universe.

When
we observed other galaxies we found a strange behavior. All the galaxies were
appearing to move away from us. Further, farther they are faster they appear to
move. Cosmologists , scientists who study the structure and evolution of
universe that is cosmos, reason that this imply at one point of time in the
past all matter was confined in a single point and since then it has started to
expand.
The event when the
matter confined in a single point and began to expand is called ‘big bang’.
This is considered as the origin of our universe as we know it.
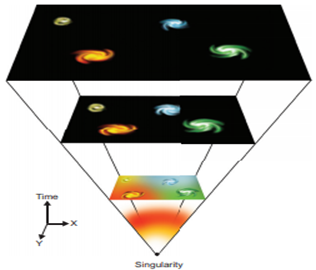
The Big Bang Theory is
the prevailing model of the evolution of the Universe. Under this theory, space
and time emerged together about 14 billions of years ago. At that time, the
entire Universe was inside a bubble that was thousands of times smaller than a
pinhead.Then it suddenly expanded. The present Universe emerged .Time, space
and matter all began with the Big Bang.
In a fraction of a
second, the Universe grew from smaller than a single atom to bigger than a
galaxy. And it kept on growing at a fantastic rate. It is still expanding
today. Over the next three minutes, the temperature dropped below 1 billion
degrees Celsius. After 300 000 years, the Universe had cooled to about 3000
degrees. Atomic nuclei could finally capture electrons to form atoms. At that
stage of the evolution of the Universe, it was filled with clouds of hydrogen
and helium gas. Giant clouds of hydrogen and helium were gradually drawn to the
places where dark matter was most dense, forming the first galaxies, stars, and
everything else seen today
We cannot see anything
that happened during the first 300000 years of the Universe. Scientists try to
work it out from their knowledge of atomic particles and from computer models.
The only direct evidence of the Big Bang itself is a faint glow in space,
called cosmic microwave background.
As millions of years
passed, the dense areas pulled in material because they had more gravity.
Finally, about 100 million years after the Big Bang, the gas became hot and
dense enough for the first stars to form. New stars were being born at a rate
10 times higher than in the present-day Universe. Large clusters of stars soon
became the first galaxies.
Building Blocks of Universe
Ø As
stated above universe is constituted of galaxies, just as lot of houses in our
locality constitute a village or a city.
Ø We
have lot of things such as rooms, furniture etc. in our homes.
Ø Likewise
lot of stellar objects such as stars, planets, asteroids and meteors are the
building blocks of our universe.
Galaxies
A galaxy is a large
collection of stars or cluster of stars and celestial bodies held together by
gravitational attraction. There are about billions of galaxies in the universe.
Types of galaxies
There are various types
of galaxies such as spiral, elliptical, barred spiral and irregular
1. Spiral Galaxy
Ø Spiral
galaxies consist of a flat, rotating disk containing stars, gas and dust, and a
central concentration of stars known as the bulge.
Ø These
are often surrounded by a much fainter halo of stars.
Ø Spiral
galaxies are named by their spiral structures that extend from the center into
the galactic disc.
Ø The
spiral arms are sites of ongoing star formation and are brighter than the
surrounding disc because of the young, hot stars that inhabit them.

2. Elliptical Galaxy
Ø An
elliptical galaxy is a type of galaxy having an approximately ellipsoidal shape
and a smooth image.
Ø Unlike
flat spiral galaxies with organization and structure, elliptical galaxies are
three-dimensional, without much structure, and their stars are in somewhat
random orbits around the center.
Ø Elliptical
galaxies tend to be surrounded by large numbers of globular clusters.

3. Irregular Galaxy
Ø An
irregular galaxy is a galaxy that does not have a distinct regular shape,
unlike a spiral or an elliptical galaxy, they are often chaotic in appearance,
with neither a nuclear bulge nor any trace of spiral arm structure.
Ø Cosmologists
say that some irregular galaxies were once spiral or elliptical galaxies but
were deformed by an uneven external gravitational force.
Ø Irregular
galaxies may contain abundant amounts of gas and dust.

4. Barred Spiral
Ø A
barred spiral galaxy is a spiral galaxy with a central bar-shaped structure
composed of Stars. Bars are found in approximately in two-thirds to one third
of all spiral galaxies.
Ø The
Milky Way Galaxy, where our own Solar System is located, is classified as a
barred spiral galaxy.

Milky Way
Ø The
Milky Way is the galaxy in which our solar system is located.
Ø The
diameter of Milky Way is over 100,000 light years.
Ø The
Milky Way includes stars smaller than our Sun as well as many other stars that
are thousands of times bigger than the Sun.
Ø It
includes many other celestial bodies of gases, clouds of dust, dead stars,
newly born stars, etc. It is also thought to contain at least 100 billion
stars.
Ø The
galaxy that is closest to our Milky Way is Andromeda.
Ø The
descriptive “milky” is derived from the appearance from Earth of the galaxy – a
band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars that cannot be
individually distinguished by the naked eye.
Ø In
Indian mythology, this patch called as Akasha Ganga.
Ø From
the Earth, the Milky Way appears as a band because its disk-shaped structure is
viewed from within.
Ø Galileo
Galili first resolved the band of light into individual stars with his
telescope in 1610.
Ø Until
the early 1920s, most astronomers thought that the Milky Way contained all the
stars in the Universe.
Ø Observations
by Edwin Hubble showed that the Milky Way is just one of many galaxies.
Ø The
Milky Way does not sit still, but is constantly rotating.
Ø Our
solar system is located within the disk of the galaxy, about 27,000 light years
away from the centre of the galaxy.
Ø The
solar system travels at an average speed of 828,000 km/h. Even at this rapid
speed, the solar system would take about 230 million years to travel all the
way around the Milky Way.
Ø When
the solar system was in the same spot as it is now, there were no humans, no
Himalayan mountain on Earth and the dinosaurs were roaming around the Earth.
Ø Tucked
inside the very center of the galaxy is a monstrous black hole, billions of
times as massive as the sun.
Constellation
A constellation is a
recognizable pattern of stars in the night sky when viewed from the Earth.
International Astronomical Union has classified 88 constellations to cover the
entire celestial sphere. Many of the old constellations have Greek or Latin
names and are often named after mythological characters.

Ursa
Major (Saptha Rishi Mandalam) is a large constellation and it covers a large
part of the sky. The most striking feature of this constellation is a group of
seven bright stars known as big dipper (seven Sages in Indian astronomy).
Ursa Minor in Lattin
means ‘the little bear’ it lies in the northern sky. The Pole star – Polaris
(Dhrua) lies within this constellation. The main group, ‘little dipper’,
consists of seven stars and is quite similar to that found in Ursa Major.
Orion was a hunter in
Greek mythology. The constellation comprises around 81 stars out of which all
but 10 are too faint to be seen with naked eye.
Different constellations
become visible in the sky at different times in the year. This happens due to
the revolution of the Earth around the Sun.
Unlike galaxy,
constellations are mere optical appearance and not real objects. In galaxy
stars are bound by gravity and constitute a system. In a constellation, one
star may be near and another very very far, but because they are in the same
direction appear to be near to each other in the sky.
![]() Name of
Constellations
Name of
Constellations

![]() Indian
Name English Name
Indian
Name English Name
Mesham Aeries
Rishabham Taurus
Midhunam Gemini
Kadakam Cancer
Simmam Leo
Kanni Virgo
Thulam Libra
Vrischikam Scorpio
Dhanusu Sagittarius
Makaram Capricorn
Kumbam Aquarius
Meenam Pisces
Stars
Ø A
Star is a luminous heavenly body that radiate energy.
Ø With
naked eyes, we can see nearly 3000 stars in the night sky and many more with
the help of a telescope.
Ø The
stars are remotely located and appear as tiny dots of light. Their light
travels long distances to reach us.
Ø The
atmosphere disturbances do not allow light to reach us in a straight line path.
Because of this the stars appear to twinkle.
Ø The
Sun is the nearest star to the Earth.
Ø The
next nearest star is Alpha Centauri.

Satellites
An object that revolves
around a planet in a stable and consistent orbit is called a satellite.
Satellites can be classified into two categories – natural and artificial.
Natural satellites
Ø All
natural objects revolving around a planet are natural satellites. They are also
called moons.
Ø Most
moons are spherical, the ones that are not usually asteroids or meteors that
were captured by the strong gravity of a planet.
Ø All
planets except mercury and Venus in our solar system have moons.
Ø Earth
has only one moon- whereas planets like Jupiter and Saturn have more than 60
moons.

Artificial satellites
Ø Artificial
satellites are man-made objects placed in an obit to rotate around a planet –
usually the Earth.
Ø The
world’s first artificial satellite launched was Sputnik-1 by Russia, Aryabhatta
was the first satellite launched by India.
Ø These
satellites are used in television and radio transmission, studying agriculture
yield, locating mineral resources, weather forecasting, locate different places
on earth.

ISRO
Ø The
Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is the space agency of the Government
of India headquartered in the city of Bangalore.
Ø Its
vision is to “harness space technology for national development while pursuing
space science research and planetary exploration”.
Ø Formed
in 1969, ISRO superseded the erstwhile Indian National Committee for Space
Research (INCOSPAR) established in 1962 by the Scientist Vikram Sarabhai.
Ø The
establishment of ISRO thus institutionalized space activities in India.
Ø It
is managed by the Department of Space, which reports to the Prime Minister of
India.

Ø ISRO
built India’s first satellite, Aryabhatta, which was launched by the Soviet
Union on 19 April 1975. It was named after the Indian astronomer Aryabhata.
Ø In
1980, Rohini became the first satellite to be placed in orbit by an Indian-made
launch vehicle, SLV-3.
Ø ISRO
subsequently developed two other rockets: the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle
(PSLV) for launching satellites into polar orbits and the Geosynchronous
Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV) for placing satellites into geostationary
orbits.
Ø In
January 2014, ISRO used an indigenous cryogenic engine in a GSLV-D5 launch of
the GSAT-14. ISRO sent a lunar orbiter, Chandrayan -1, on 22 October 2008 and a
Mars orbiter, Mars Orbiter Mission, on 5 November 2013, which entered Mars
orbit on 24 September 2014, making India the first nation to succeed on its
first attempt to Mars, and ISRO the fourth space agency in the world as well as
the first space agency in Asia to reach Mars orbit.
Ø On
18 June 2016 ISRO set a record with a launch of 20 satellites in a single
payload. On 15 February 2017, ISRO launched 104 satellites in a single rocket
(PSLV-C37) and created a world record.
Ø ISRO
launched its heaviest rocket, Geosynchronous Satellite Launch VehicleMark III
(GSLV-Mk III), on 5 June 2017 and placed a communications satellite GSAT-19 in
orbit. With this launch, ISRO became capable of launching 4 ton heavy
satellites.
Ø ISRO
launched Chandran 2 on July 22, 2019, Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle
(GSLV-Mk III). It entered the Moon’s orbit on August 20, 2019 and its lander
landed on the Moon on September 7.