Measurement
1 a. Measurement is the process of finding an unknown physical
quantity by using a standard quantity.
b.
We need three things for a perfect measurement. They are
(i) An instrument,
(ii) A standard quantity
(iii) An acceptable unit.

Eg: To measure the length of a book,
we’ll need a ruler. Here, a ruler is the ‘instrument’.
Say the book is 15cm long, then 15
is the ‘magnitude’ and ‘cm’ is the unit. This process is called “Measurement”.
2.
Different Systems of Units
a.
FPS - System (Foot for length, Pound for mass and second for time)
b.
CGS -System (Centimeter for length, Gram for mass and second for time)
c.
MKS - System (Meter for length, Kilogram for mass and second for time)
3.
International System of Units
a.
For the sake of uniformity, the standard unit for physical quantities was
introduced. These standard units are also called S.I. Units.
b.
Seven physical units and their standard units were defined under the
International System of Units.
4. S.I.
Units
The
seven quantities and their units are:
Length
- meter (m)
Mass
- kilogram (kg)
Time
- second (s)
Temperature
- kelvin (K)
Electric
Current - ampere (A)
Amount
of Substance - mole (mol)
Luminous
Intensity - candela (cd)
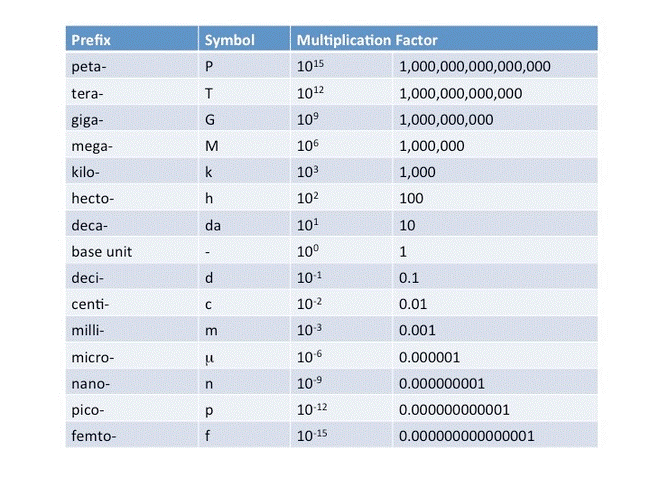
5. The ‘CGS’, ‘MKS’ and SI
units are metric systems of units and ‘FPS’ is not a metric system. It is a
British system of units.
6.
Temperature
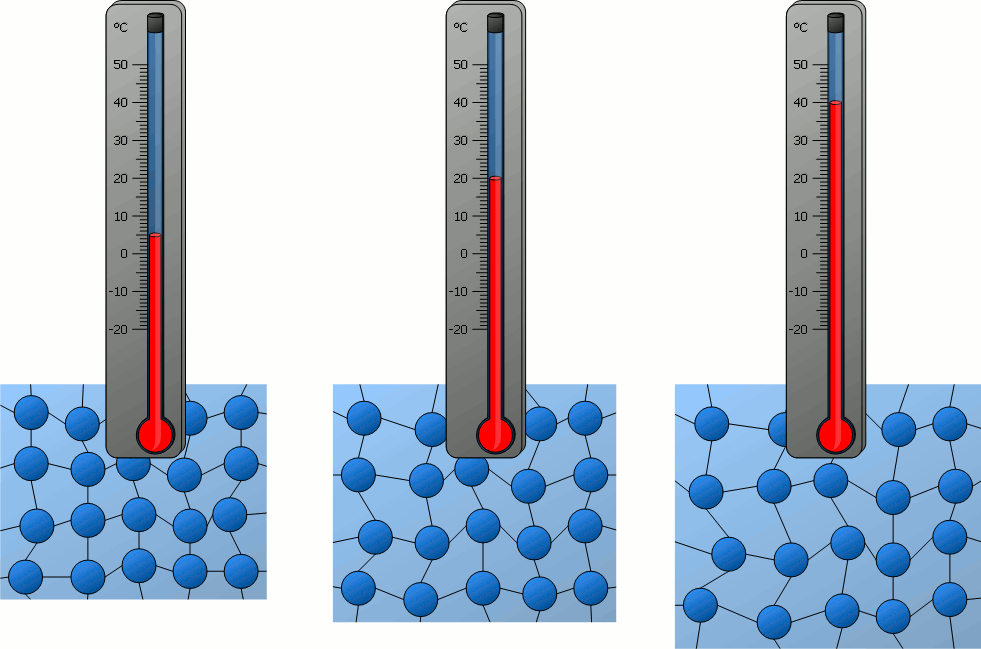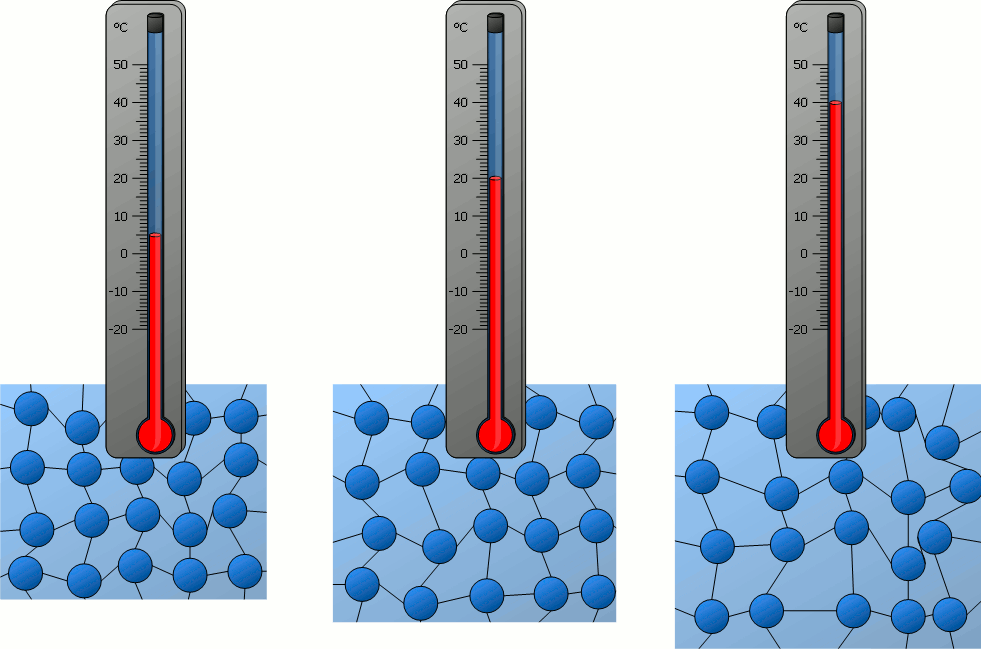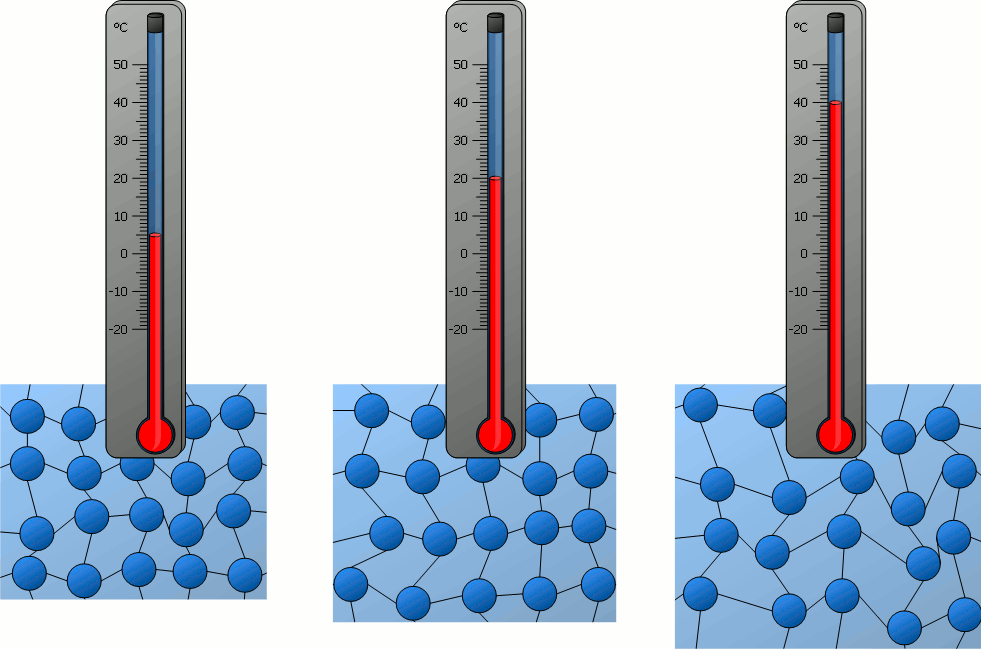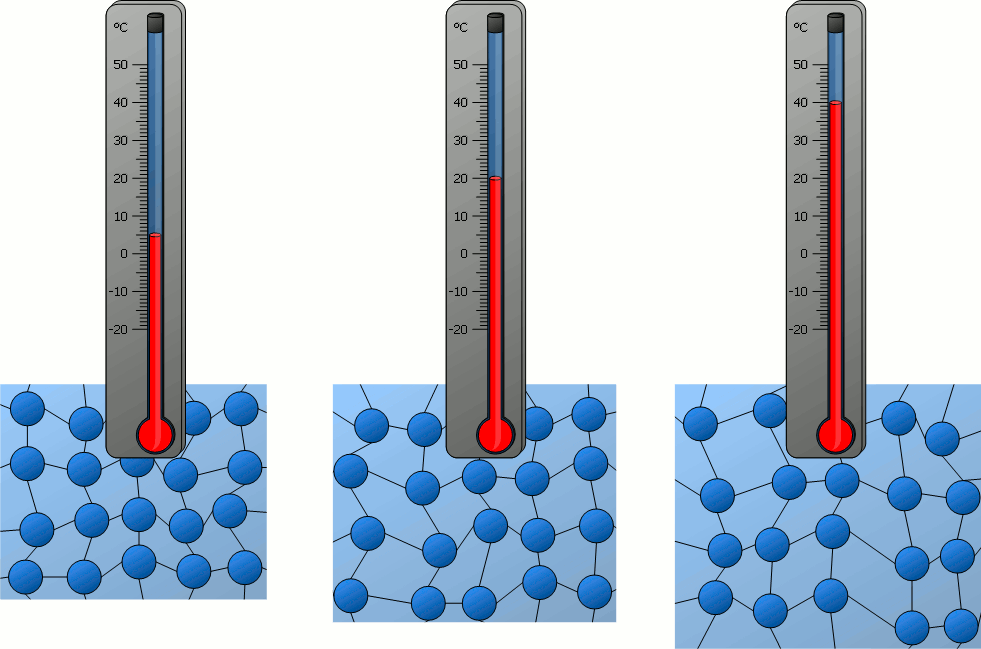
a. Meaning:
Temperature is a physical quantity that measures
the degree of hotness or coldness of a substance.
b. The relation between heat and temperature:
Heat given to a substance will increase its temperature. The
heat removed from a substance will lower its temperature.

c. Scientific Definition:
Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy
of the particles in a system.
d. SI Unit and other units:
The SI unit of temperature is Kelvin. Celsius
and Fahrenheit are other common units used to measure temperature.
e. Instrument used:
Thermometer is used to
measure temperature.

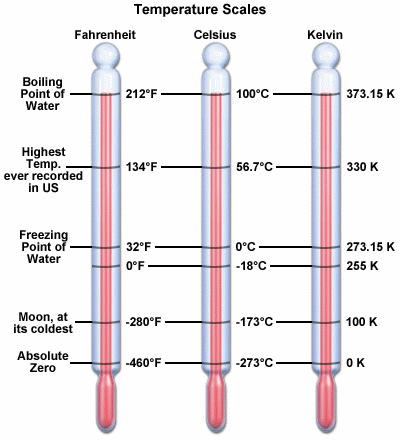
7. The relation
between different units of Temperature
The
three units of temperature, Kelvin (K), Celsius (C) and Fahrenheit (F), are
related by the formula:
![]()
8.
Application of thermometers
a. Physicians use ‘clinical
thermometers’ which uses the Fahrenheit Scale.
b. Scientists are using
thermometers with the Kelvin scale.
c. Common temperature measurements
are made in the Celsius scale.
d.
Infrared thermometer measures the temperature of an object without any physical
contact.
9.
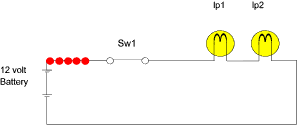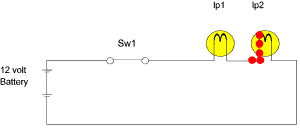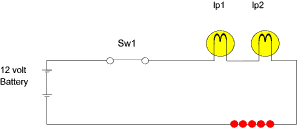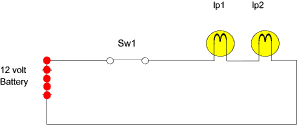
Electric Current
a.
Definition:
Flow of electric charges per unit time, in a particular
direction is known as ‘electric current’.
b.
SI Unit:
SI unit of electric current is ‘ampere’ and it is denoted as
A. Unit of charge is coulomb.
c.
1 A of
current:
One ampere is defined as one ‘coulomb’ of charge moving in a
conductor in one second.
d.
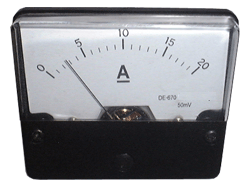
Instrument:
Ammeter is a device used to measure electric current.
10.
Superconductors:
At very low temperature, around 30 K (-243.2° C), some
conductors conduct electric current without any loss. These conductors are
known as Super Conductors.

Uses:
a. The superconductors are used to
levitate trains from the track.
b. Superconductors can be used as memory
or storage element in the computers.
11. Amount
of Substance
a. Definition:
Amount of substance is a measure of the number of entities
(particles) present in a substance.
Generally, the amount of substance is directly
proportional to the number of atoms or molecules.
b. SI Unit:
The SI unit of amount of substance is mole and it is denoted
as ‘mol’.
c. Definition of 1 mol:
Mole is defined as the amount of substance, which contains
6.023 x 1023 entities (also known as Avogadro number)
12. Plane
and Solid angle
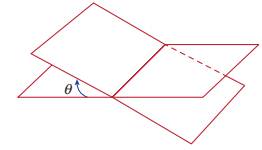
a.
Plane
angle:
It is the angle between the intersection
of two straight lines or intersection of two planes.
b.
SI Unit of
plane angle:
The SI unit of Plane Angle is ‘radian’ and is denoted
as ‘rad’. Another unit to measure plane angle is the degree.
c.
Radian:
Radian is the angle subtended at the center of a
circle by an arc whose length is equal to the radius of the circle.
d.
The
relation between radian and degree.
π
radian = 180°
1
radian
= 180°/ π
e.
Solid
angle:
It is the angle formed by three or more planes intersecting
at a common point. It can also be defined as ‘angle formed at the vertex of the
cone’
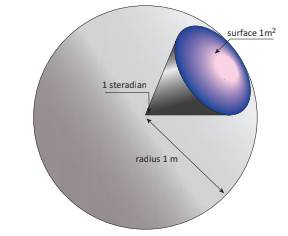
f.
SI Unit:
The SI unit of solid angle is ‘steradian’ and is denoted
as ‘sr’.
g.
Steradian:
Steradian is the solid angle at the center of a sphere subtended
by a portion whose surface area is equal to the square of its radius of the
sphere.
12.
Luminous Intensity
a.
Definition:
The measure of the power of the emitted light, by a light
source in a particular direction, per unit solid angle is called Luminous
Intensity.

b.
SI Unit:
The SI unit of luminous intensity is candela and is
denoted as ‘cd’.
c.
Instrument:
Luminous intensity is measured by a ‘photometer’

13.
Clock:
Clock is an
instrument used to measure time.
14. Classification of clocks based on display:
a.
Analog
clock:
Time is displayed by three hands of the clock: the hour's
hand, the minute's hand, and the second's hand.

Hours
Hand: It is short and thick.
Minutes
Hand: It is long and thin.
Seconds
Hand: It is long and very thin, and is always moving. It makes one rotation in
one
Minute
and 60 rotations in one hour.
b.
Digital
clock:
A digital
clock displays the time directly. It shows the time in numerals or other
symbols. It may have 12 hours or 24 hours display.
They
are also called electronic clocks.

15. Classification of clocks
based on its working mechanism:
a.
Quartz
clock:
It is activated by ‘electronic
oscillations’, which are controlled by a ‘quartz crystal’. These clocks have an
accuracy of one second in every 109 seconds.
b.
Atomic
clock:
It is activated by periodic vibrations occurring within the
atoms. These clocks have an accuracy of one second in every 1013 seconds.
Use:
Atomic
clocks are used in the Global Positioning System (GPS), Global Navigation
Satellite System (GLONASS) and International time distribution services.
16. Time Zones in the World
a. The
Earth is divided into 24 zones, each of a width of 15-degrees longitude. These
regions are called ‘Time Zones’. Time difference between two adjacent time zones is 1 hour.
b. The zero degrees longitude passes through
Greenwich in London. Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) is the mean solar time at this
location.
c.
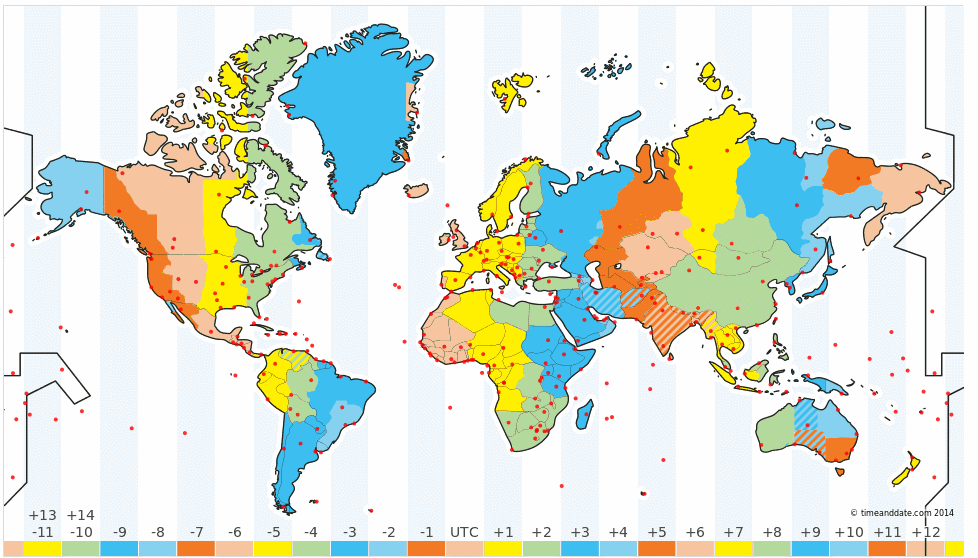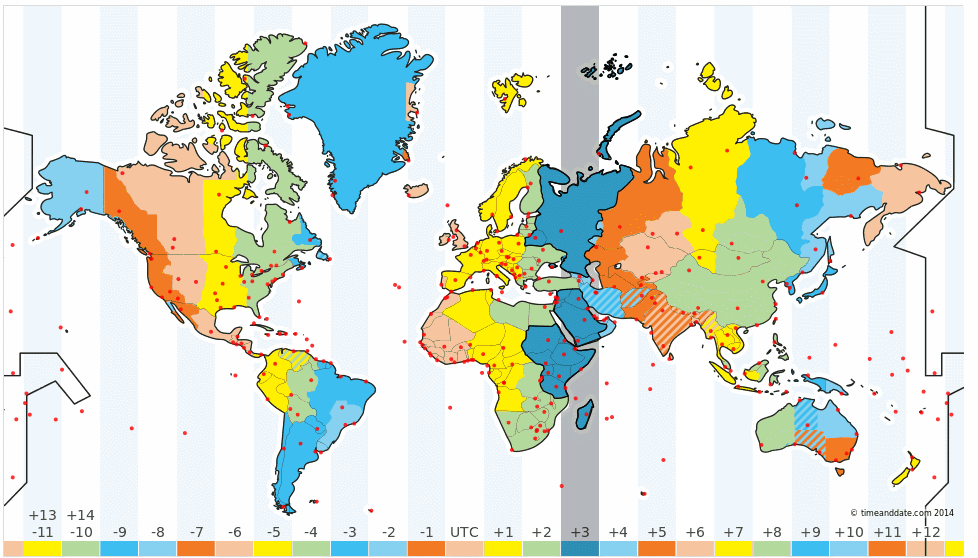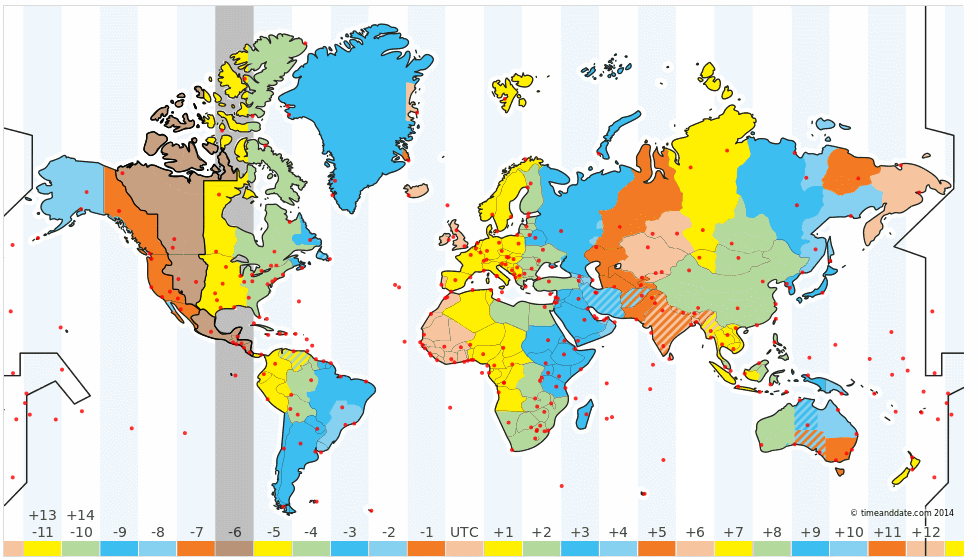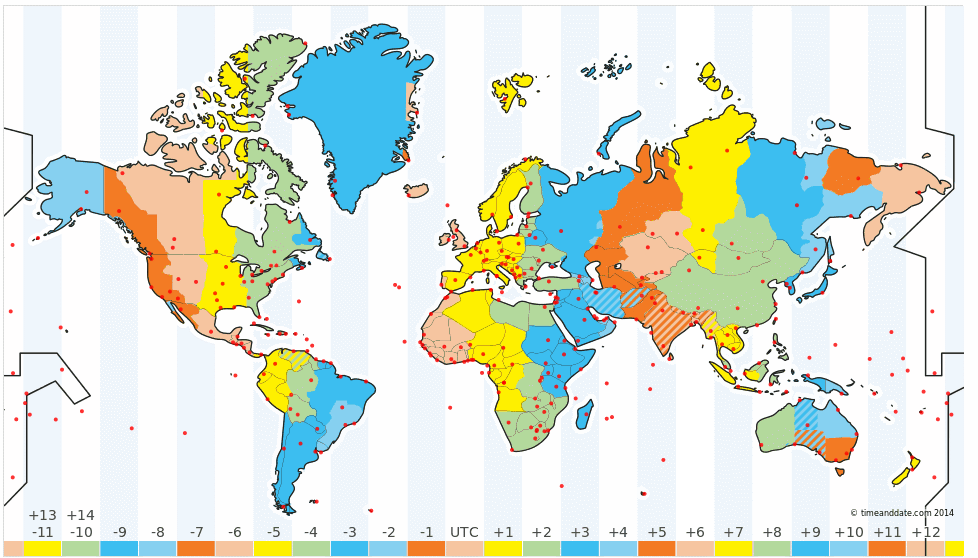
Indian
Standard Time (IST):
The location of Mirzapur in Uttar Pradesh is taken as the
reference longitude of the Indian Standard Time. It is located at 82.5-degree
longitude.
IST
= GMT + 5:30 hours
17.
Accuracy in Measurements
a.
The value of every measurement contains some uncertainty. These uncertainties
are called as ‘Errors’.
b.
The difference between the real value and the observed value is called an
error.
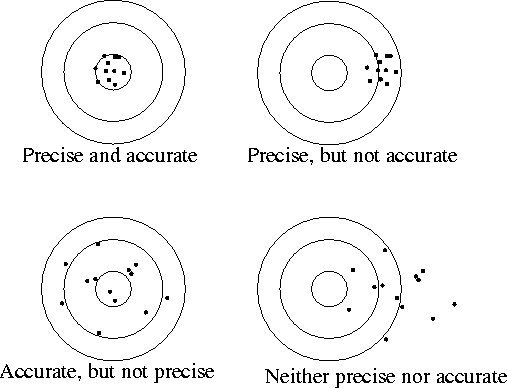
c.
Accuracy is the closeness of a measured value to the actual value or true
value.
d. Precision is the
closeness of two or more measurements to each other.
e.
18.
Approximation
a.
The approximation is the process of finding a number, which is acceptably close
to the exact value of the measurement of a physical quantity.
b.
One of the ways to approximate is to use estimation, i.e., a number obtained by
rounding off a number to its nearest place value.
c. Rules for rounding off
• Decide
which the last digit to keep is.
•
Leave it the same, if the next digit is less than 5.
•
Increase it by one, if the next digit is 5 or greater than 5.