ELECTRICITY
Electricity is a form of energy that is
associated with electric charges that exists inside the atom.
Electric Current:-
·
The
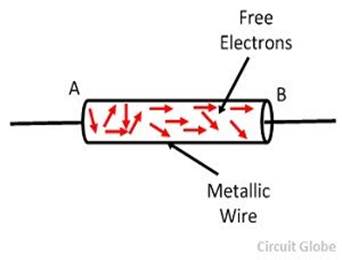
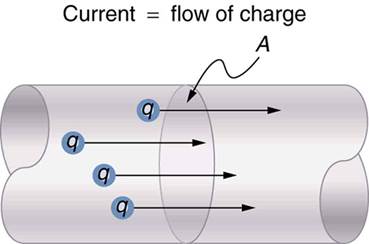
flow of electric charges constitute an electric current.
·
An
electric current is measured by the amount of electric charge moving per unit
time at any point in the circuit. The conventional symbol for current is ‘I’.
Charges
What is a charge? What
is an elementary charge?
·
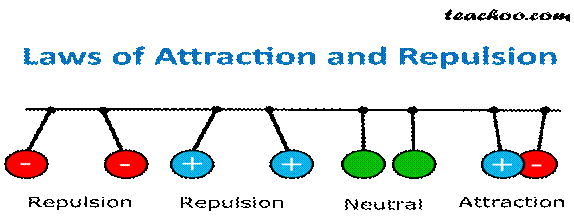
Charge
or electric charge is the basic property of matter that causes objects to
attract or repel each other. It is carried by the subatomic particles like
protons and electrons.
·
Charges
can neither be created nor be destroyed.
·
There
are two types of charges: positive
charge and negative charge.
Protons carry positive charge and the electrons carry negative charge.
·
There
is a force of attraction or repulsion between the charges. Unlike charges
attract each other and like charges repel each other.
·
Electric charge is measured in coulomb (C).
·
Small
amount of charge that can exist freely is called
elementary charge (e). Its value is
1.602 × 10-19 C. This is the amount of charge
possessed by each proton and electron. But, protons have positive elementary
charge (+e) and electrons have negative elementary charge (-e). Since protons
and electrons are equal in number, an atom is electrically neutral.
Transfer Of Charges
How does charges get transferred from one substance to
another?
Electrons in the outermost orbit of an atom
can be easily removed. They can be transferred from one substance to another.
The substance which gains electrons become negatively charged and the substance
which looses electrons becomes positively charged.
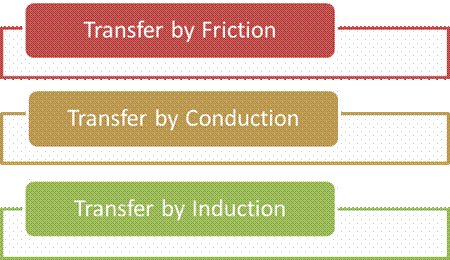
Transfer of
charges takes place in the following three ways
 .
.
Transfer By Friction
When an
ebonite rod (rod made by vulcanized rubber) is rubbed with fur, the fur
transfers electrons to the ebonite rod because the electrons in the outermost
orbit of the atoms in fur are loosely bound as compared to the ebonite rod. The
ebonite rod which has excess electrons becomes negatively charged and the fur
which has deficiency of electrons is positively charged. Thus, when two
materials are rubbed together, some electrons may be transferred from one
material to the other, leaving them both with a net electric charge.
Transfer By Conduction
When the
ebonite rod is rubbed with woollen cloth, electrons
from the woollen cloth are transferred to the ebonite
rod. Now ebonite rod will be negatively charged. When it is brought near the
paper cylinder, negative charges in the rod are attracted by the positive
charges in the cylinder. When the cylinder is touched by the rod, some negative
charges are transferred to the paper. Hence, the negative charges in the rod
are repelled by the negative charges in the cylinder. Thus, charges can be
transferred to on object by bringing it in contact with a charged body. This
method of transferring charges from one body to other body is called transfer
by conduction.

Transfer By Induction
The process
of charging an uncharged body by bringing a charged body near to it but without
touching it is called induction. The uncharged body acquires an opposite charge
at the near end and similar charge at the farther end..
When a
positively charged rod is brought near an uncharged rod, negatively charged
electrons are attracted towards it. As a result there is excess of electrons at
nearer end and deficiency of electrons at the farther end. The nearer end of
the uncharged rod becomes negatively charged and far end is positively charged.
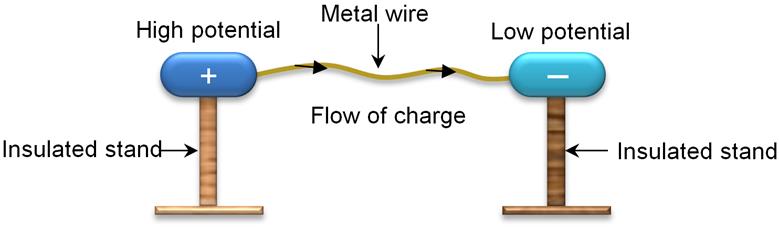
Flow Of Charges
·
Let
us suppose, there are two metallic spheres; one having more negative charge
(excess of electrons) and the other having more positive charge (deficiency of
electrons). When you connect them both with the help of a metallic wire, excess
electrons from the negatively charged sphere will start flowing towards the
positively charged sphere. This flow continues till the number of electrons in
both the sphere is equal.
·
Here, the positively charged sphere is said to
be at higher potential and the
negatively charged sphere is said to be at lower
potential.
·
Hence, electrons flow from lower potential to
higher potential. This is known electric current (flow of electrons).
·
The
difference between these potentials is known as potential difference, commonly
known as voltage.
·
Before
the discovery of electrons it was considered that electric current is due to
the flow of positive charges. Flow of positive charge is called conventional
current. Conventional current flows from higher potential to lower potential.
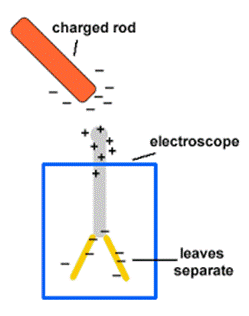
Electroscope
What is an electroscope? Define the principle on which
electroscope works.
§
An
electroscope is a scientific instrument used to detect the presence of electric
charge on a body.
§
There
are two types of electroscope: pith-ball
electroscope and goldleaf electroscope.
§
An
electroscope is made out of conducting materials, generally metal.
§
It
works on the principle that like charges repel each other.
Gold Leaf Electroscope
§
Gold
and silver are used in electroscope because they are the best conductors of
electric current.
Structure Of Electroscope
§
It
is made up of a glass jar. A vertical brass rod is inserted into the jar
through a cork.
§
The
top of the brass rod has a horizontal brass rod or a brass disc.
§
Two
gold leaves are suspended from the brass rod inside the jar.
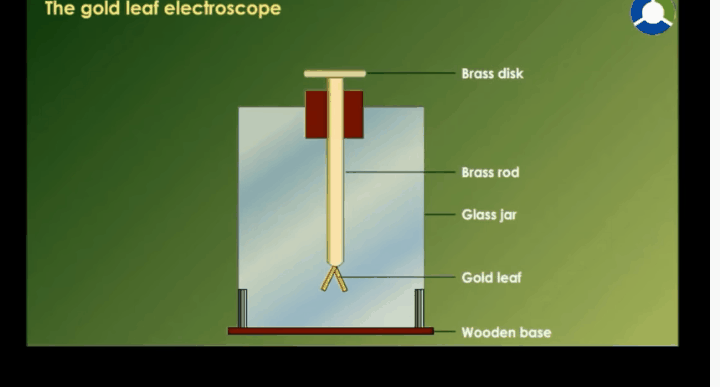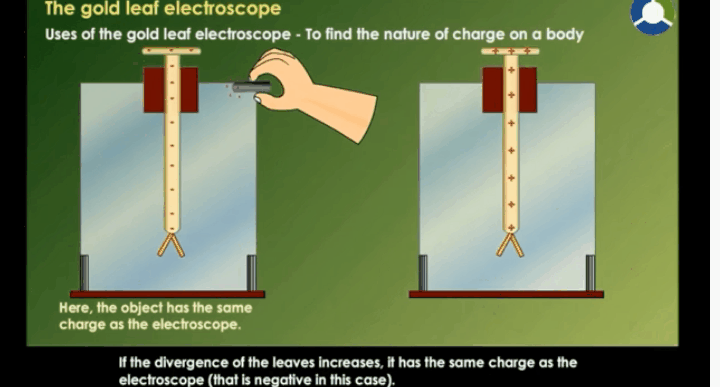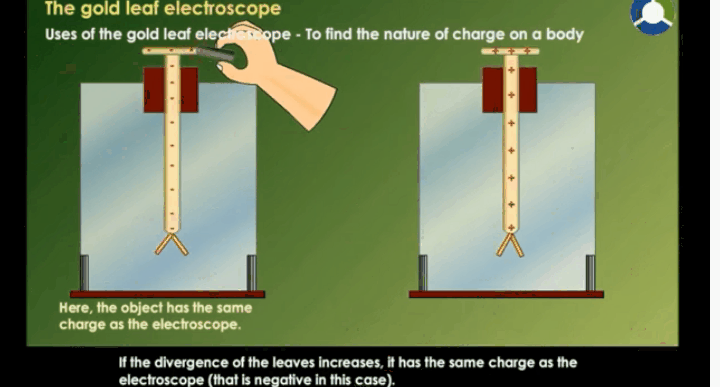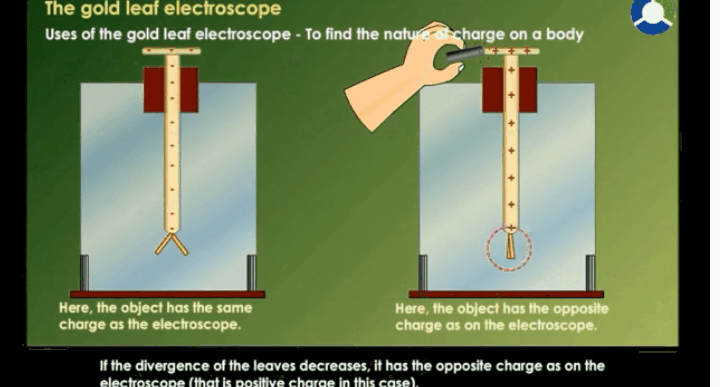
Working Of Electroscope
When the
brass disc of the electroscope is touched by a charged object, electric charge
gets transferred to the gold leaf through the rod. This results in the gold
leaves moving away from each other. This happens because both the leaves have
similar charges.
Charging
Transfer of
charge from one object to another is called charging.
Electrical Discharge
The gold
leaves resume their normal position after some time. This happens because they
lose their charge. This process is called electrical discharge. The gold leaves
would also be discharged when someone touches the brass rod with bare hands. In
that case, the charge is transferred to the earth through the human body.
Lightening And Thunder
How is lightening caused? What is
thunder?
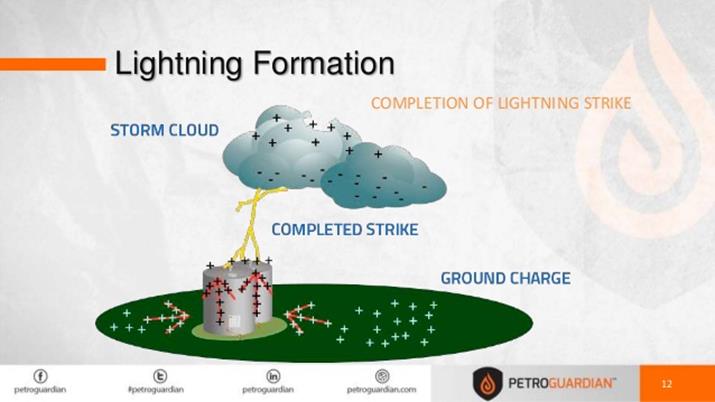
§
Lightning
is produced by discharge of electricity from cloud to cloud or from cloud to
ground. During thunderstorm air is moving upward rapidly. This air which moves
rapidly carries small ice crystals upward. At the same time, small water drops
move downward. When they collide, ice crystals become positively charged and
move upward and the water drops become negatively charged and move downward. So
the upper part of the cloud is positively charged and the lower part of the
cloud is negatively charged. When they come into contact, electrons in the
water drops are attracted by the positive charges in the ice crystals. Thus,
electricity is generated and lightning
is seen.
§
Sometimes the lower part of the cloud which is
negatively charged comes into contact with the positive charges accumulated
near the mountains, trees and even people on the earth. This discharge produces
lot of heat and sparks that results in what we see as lightning. Huge
quantities of electricity are discharged in lightning flashes and temperatures
of over 30,000°C or more can be reached. This extreme heating causes the air to
expand explosively fast and then they contract. This expansion and contraction create
a shock wave that turns into a booming sound wave, known as thunder.
Earthing
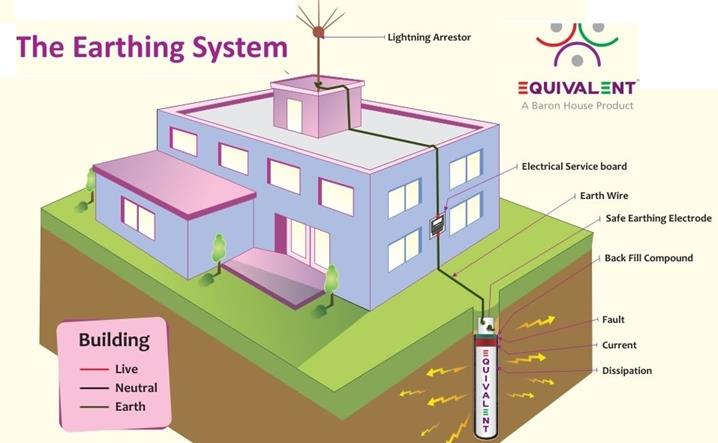
§
A
safety measure devised to prevent people from getting shocked if the insulation
inside electrical devices fails is called Earthing.
§
Electrical earthing
can be defined as the process of transferring the discharge of electrical
energy directly to the Earth with the help of low resistance wire.
§
Usually
an electric appliance such as a heater, an iron box, etc. are fitted with three
wires namely live, neutral and earth.
§
The
earth wire is connected to the
metallic body of the appliance. This is done to avoid accidental shock. Suppose
due to some defect, the insulation of the live wire inside an electric iron is
burnt then the live wire may touch
the metallic body of the iron. If the earth
wire is properly connected to the metallic body, current will pass into the
Earth through earth wire and it will protect us from electric shock.
§
The
Earth, being a good conductor of electricity, acts as a convenient path for the
flow of electric current that leaks out from the insulation.
Lightning Arresters
§
Lightning
arrestor is a device used to protect buildings from the effects of lightning.
§
Lightning
conductor consists of a metallic lightning rod that remains in air at the top
of the building.
§
Major
portion of the metal rod and copper cable are installed in the walls during its
construction. The other end of the rod is placed deep into the soil.
§
When
lightning falls, it is attracted by the metallic rods at the top of the
building. The rod provides easy route for the transfer of electric charge to
the ground.
§
In
the absence of lightning arrestors, lightning will fall on the building and the
building will be damaged.
Electric Circuit
·
We
can draw circuit diagrams using these symbols. Symbols for bulbs, cells and
switches are shown in figure.
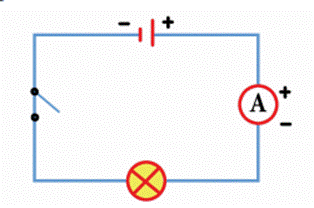
·
In
a cell, the longer line denotes the positive (+) terminal and the short line
denotes the negative (-) terminal. We shall use these symbols to show
components in the circuits we draw. Such diagrams are called circuit diagrams.
Types Of
Electrical Circuits
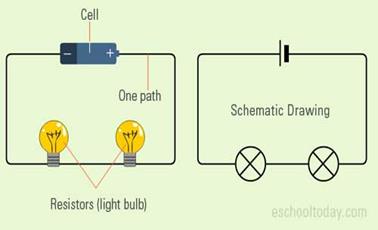
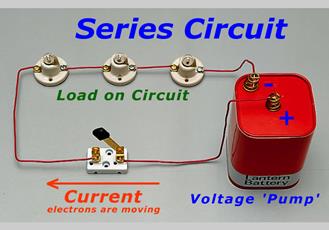
Series Circuit
·
So,
similar looking bulb do not always glow equally bright when connected in
series.
·
The
circuit can be broken at several places. For example, between the cell and the
bulb, between the two bulbs etc.
·
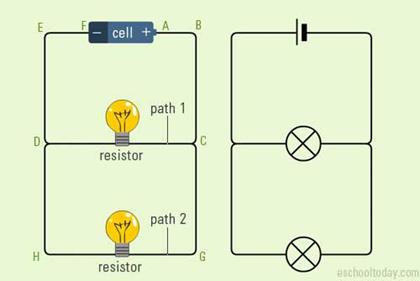
A
series circuit is one in which more than 1 bulbs are connected along 1 path through
which electricity flows.
Parallel Circuit
·
A
circuit in which two bulbs are connected in different places.
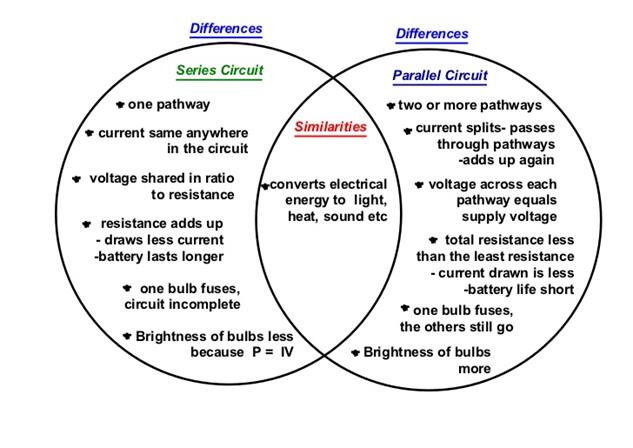
Similarity And Difference Between Series And Parallel Circuit
Chemical Effects Of Electricity
Chemical effects of electric current
We know that when an electric current passes through
solution it ionizes and breaks down into ions. This is because of chemical
reactions that take place when an electric current passes through a
solution. Depending on the nature of the solution and the electrodes used, the
following effects can be observed in the solution:
1. metallic
deposits on the electrodes
2. change
in the colour of the solution
3. a
release of gas or production of bubbles in the solution
Applications of chemical effects of electric
current
Electroplating
·
Electroplating is a process in which
layer of metal is deposited on another material with the help of electricity.
·
Electroplating is used in many
industries for depositing a layer of metal with desired characteristics on
another metal.
·
Different metals used for
electroplating are Nickel, Copper, Gold Silver, Tin, Brass, Zinc, Chromium and
Platinum.
Process of electroplating
·
In order to conduct electroplating
right electrodes and electrolytes must be chosen so that metal can deposit over
a material.
·
For instance, if we want to deposit
copper on a material we need an electrolyte that contains copper in it.
Similarly, if we need gold on a material we need an electrolyte that contains
gold in it.
·
Also, we should make sure that the
electrode that we are choosing is completely clean.
·
The electrodes used are made up of
different materials. One of the electrodes is of the same metal of which the
electrolyte solution is. The second electrode needs to be the material on which
we want to coat another metal.
·
For instance, in case we want to
plate copper upon brass, one electrode should be of Copper and the other
electrode should be of Brass and the electrolyte solution should be any salt
which contains copper in it, for example, copper sulphate
solution. Consider the diagram given below that describes the process of
electroplating of copper.
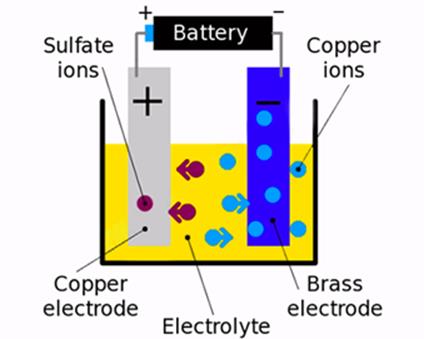
·
Out of these two electrodes the
copper electrode acts as the anode (positive electrode) and brass electrode
acts as the cathode (negative electrode).
·
When electricity is passed through
the solution, the copper sulphate breaks down into
its ions.
·
The copper ions (they have a
positive charge) get attracted by the brass electrode while the sulphur ions
being negatively charged move towards the copper electrode.
·
As a result, copper starts
depositing on the brass electrode.
·
The process of electroplating takes
some time to complete.
·
The amount of time that it will take
depends upon the strength of the current that is being passed through the
circuit and also upon the concentration of the electrolyte.
·
As these two are increased the speed
of the electroplating process also increases.
Applications of electroplating

·
Medical equipment is made up of
nickel which is harmful to the human body hence to avoid it from coming in
contact with our body a coating of platinum or gold is applied on the surface
of nickel.
·
Many kitchen equipments, bath taps,
parts of cars etc. are covered with chromium coating. Chromium is an expensive
metal hence the objects are created with the cheaper metal and chromium coating
is provided. Thus, to bring a shining over the objects and prevent them from
corrosion chromium coating is used.
·
Jewellery
makers often make ornaments of less expensive metals and provide a coating of
gold or silver upon them.
·
The tin cans that are used to store
food are actually made up of iron and have a coating of tin on them. Iron can
easily react with food and spoil it, however, tin prevents the food from
getting reacted with iron and therefore helps in preventing it from getting
spoiled easily.
·
Bridges and various parts of
automobiles are made up of iron because it provides strength. However in order
to prevent iron from getting rusted a coating of zinc is provided over it. This
method is also called galvanization of iron.