Welding
Introduction
Welding can be defined as the
process of joining two metal parts by applying heat. In industry, welding
process is primarily used for fabricating works.

Welding
is useful in making permanent joints. It can be performed by applying or not
applying pressure. In some types of welding processes, filler metal is used. In
some other methods, filler metal is not used.
The
process of welding finds application in manufacturing automobiles, aeroplanes,
rail coaches, machine components, metal structures, boilers and ships.
Generally, welding process is applied wherever metal works are performed.
Types of Welding
There are two types by which welding is performed
1.
Plastic welding
2.
Fusion welding
Plastic Welding
In
this type, the metal parts are heated to plastic state. In this stage, pressure
is applied to make a perfect joint. It is also known as pressure welding.

Fusion Welding
The metal parts are heated upto
the point of melting in this type. The joint is made at this stage and the
parts are allowed to cool. On cooling, the molten metal forms a solid joint. No
pressure is applied in this method. Hence, it is also known as pressure less
welding or Fusion welding Arc welding and gas welding fall in this category.
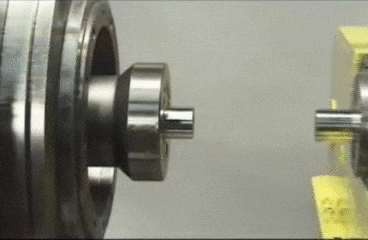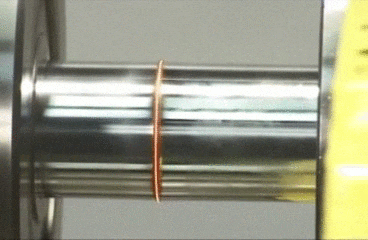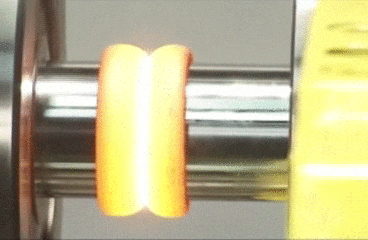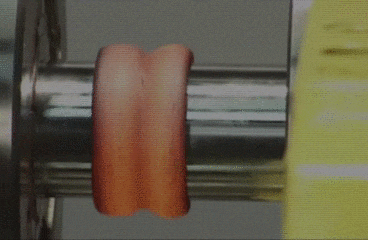
Classification of welding processes
1.
Arc welding
a. Carbon arc welding
b. Metal Arc welding
c. Metal Insert gas welding
d. Tungsten inert gas welding
e. Atomic hydrogen welding
f. Plasma arc welding
g.
Submerged welding
h. Electro slag welding
2.
Gas Welding
a. Oxy – acetylene welding
b. Air – acetylene welding
c. Oxy hydrogen welding
3.
Oxy – acetylene cutting
a. Arc cutting
b. Hard facing
c. Brazing d. Soldering
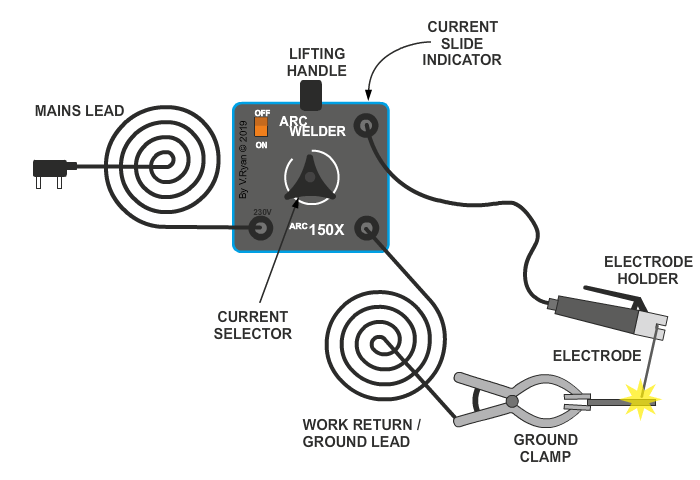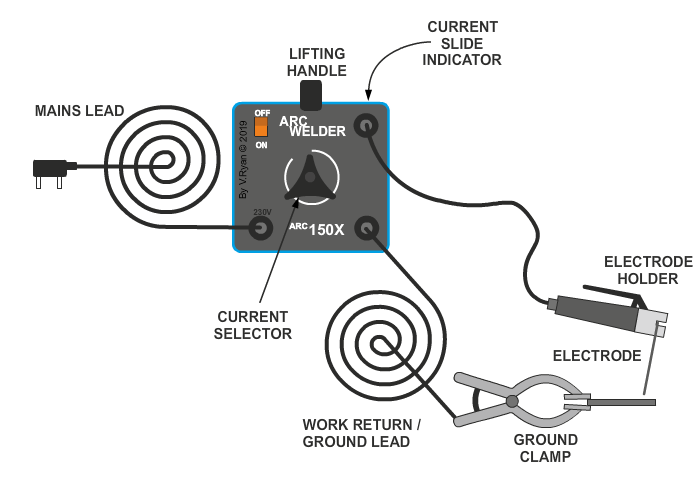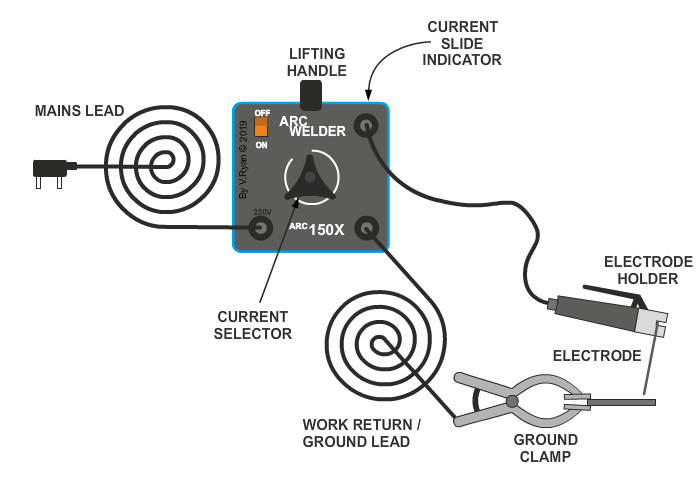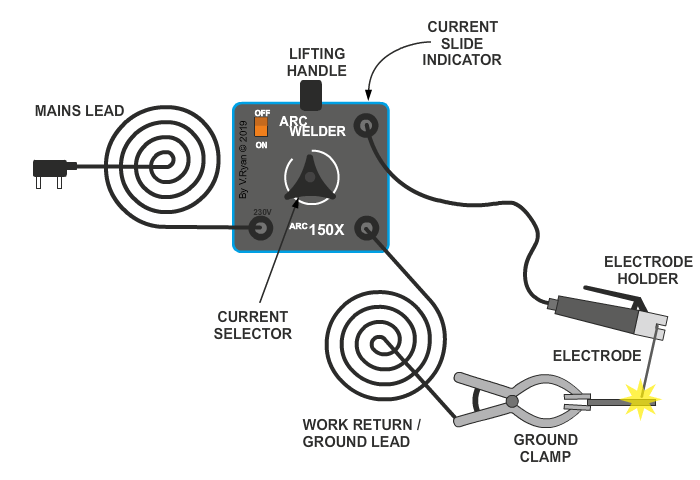
Arc welding
In
arc welding, the edges of two metal parts are melted by an electric arc and the
joint is made. An electrode made of a suitable metal is utilised for this
purpose. The electrode is taken closer to the parts to be joined and electric
current is supplied to both the parts and the electrode. An electric arc is
made between the electrode and the metal parts. This arc generates high
temperature and melts the metal parts. The parts are joined at this molten
state. The filler metal in the form of electrode is deposited along the joint.
The metal parts are joined without the application of any pressure. Electrical
energy is converted into heat energy in arc welding.

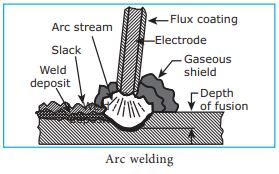
Electric Arc welding
The distance between the metal
parts and the electrode should be around 3mm. The heat generated during arc
welding ranges from 50000 C to 60000 C. A generator or a
transformer supplies the required current to both the electrode and the metal
parts. The electrodes are flux coated to prevent the molten metal from reacting
with the atmosphere.
Arc welding equipments
The following equipments are used for the process
of arc welding
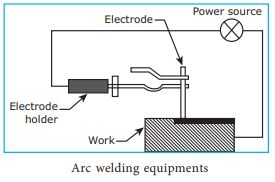
i.
D.C welding generator (or) AC transformer
ii.
Cables
iii.
Electrode cable
iv.
Work cable
v.
Electrode holder
vi.
Electrode
vii.
Gloves
viii.
Protective shield (or) Goggles
ix.
Apron for the operator
x.
Wire brush
xi.
Chipping hammer
Differences between DC generator and AC transformer
|
DC generator |
AC transformer |
|
Low
efficiency |
High efficiency |
|
High
power cost |
Low power cost |
|
High
machine cost |
Low machine cost |
|
Runs
on low voltage |
Runs on high voltage |
|
Safe
equipment |
The chances of accidents is
high |
|
Uncoated
electrodes may be used |
only flux coated electrodes are used |
|
DC generator |
AC transformer |
|
Joints
are made with ferrous and nonferrous metal parts |
Non-ferrous metal parts cannot
be joined |
|
Noisy
functioning |
No noise during operation |
|
The
cost of the process is low |
High process cost |
|
Easy
maintenance of equipments |
Requires proper maintenance |
|
Thin
metal parts can easily be welded |
Difficult to weld thin parts |
Specification of electrodes
Electrodes
- figure
Generally, the size of the
electrodes is specified by the length and its diameter. They are available to a
maximum of 12 mm diameter and 45mm length. The size of the electrode increases
with the current used. In manual welding, the size of the electrode changes
according to the thickness of the metal parts. Spring like electrodes are used
in automatic welding

Types of electrode
The electrodes used in arc welding are two types
1.
Consumable electrode
2.
Non – consumable electrode
There are three types of consumable electrodes.
They are
1.
Bare electrodes
2.
Lightly coated electrodes
3.
Heavily coated electrodes
Non – consumable electrodes are used in the processes
of atomic hydrogen welding and TIG welding
Selection of electrodes
The material used for manufacturing electrodes
depends upon the material to be welded. Given is the list indicating suitable
materials for manufacturing electrodes for welding different metals.
|
S.
No Material to be welded |
Electrode
material |
|
1 Wrought iron Low Carbon Steel Rod 2 Mild Steel Mild Steel, Copper coated
Rod 3 Alloy Steel Nickel Steel Rod 4 Cast Iron Cast Iron Rod 5 Aluminium Cast Aluminium Alloy Rod 6 Carbon Steel Steel wire (0.15% Carbon &
0.025%) Phosperous
& Sulphur 7 Copper Copper Rod 8 Brass Brass Rod |
|
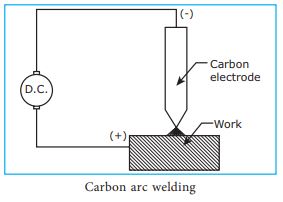
Carbon arc welding
In carbon arc welding, the
process of welding is carried out by an electric arc. The arc formed between
the electrode and the work piece generates high amount of heat. In D.C electric
supply, the carbon electrode is connected to the negative terminal and the positive
terminal is connected to the work piece. During the formation of the electric
arc, the temperature of the positive terminal is 40000 C and the
negative terminal will be around 30000 C. Carbon, the electrode
material will not fuse with the work piece materials. This prevents the joint
from becoming weak. A lengthy arc produces carbon – monoxide at the location of
welding and prevents the molten metal from reacting with the atmospheric air.
Both ferrous and non- ferrous
metals can be welded by this method. Steel sheets, copper and its alloys, brass
and aluminium parts are welded using carbon arc welding. This method of welding
can also be done automatically. Starting of the electric arc is easy and the
temperature is controlled easily. The disadvantage of this method is the
presence of blow holes in the joint.
Gas welding
Gas welding is the process of
melting and joining metal parts by means of a gas flame. Generally pressure is
not applied during the process of gas welding. Oxygen and acetylene gases are
made to pass through the welding torch. These gases are mixed at the required
ratio at the torch and the tip of the welding torch is ignited to produce the
flame. Because of the heat generated by the flame, the edges of the metal parts
are melted. Filler rod provides the additional metal required for making the
joint. The flux coated on the electrodes prevents oxidation and removes
impurities. This method is suitable in welding metal parts of thickness varying
from 2mm to 50mm. The temperature of the flame is around 32000 C.
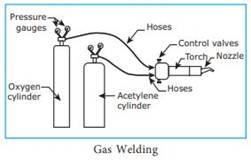
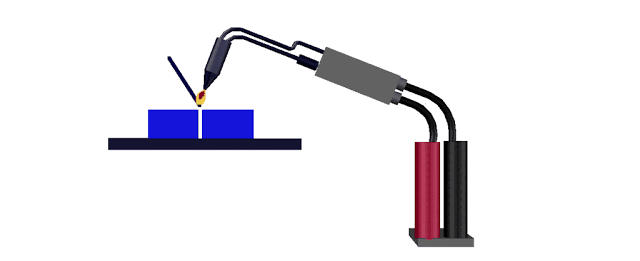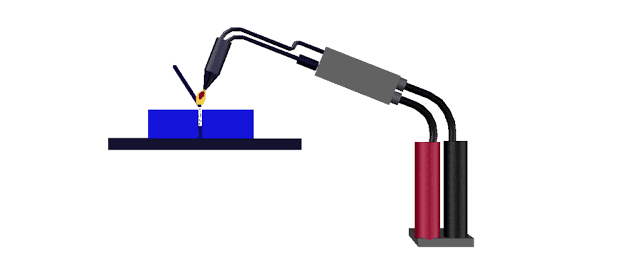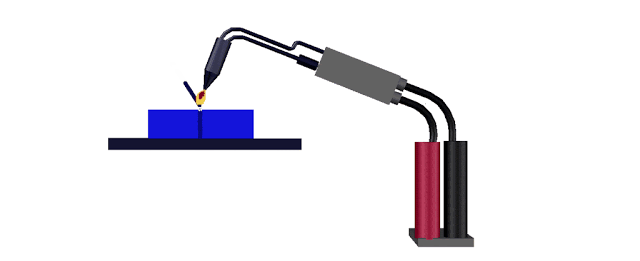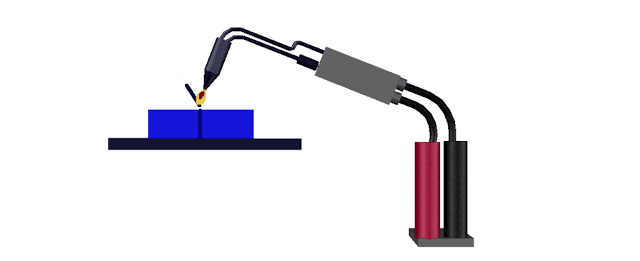
Gas welding equipments
The following equipments are necessary for gas
welding
1.
Gas cylinders
2.
Regulators
3.
Pressure gauges
4.
Rubber hoses
5.
Welding torch
6.
Safety goggles
7.
Gloves
8.
Spark lighter
9.
Wire brush
Gas cylinders
Oxygen
and acetylene gases are stored in separate cylinders and used for gas welding.
The colour of oxygen cylinder is black and the acetylene gas is stored in
maroon cylinders. Oxygen is stored at a pressure of 125kg/cm2.
Acetylene gas is stored at a pressure of 16Kg/cm2. In the cylinder.

Regulators
Separate
regulators are fitted on both the cylinders. A regulator is used to control the
working pressure of the gases. The working pressures of oxygen is 1Kg/cm2
and acetylene is 0.15Kg/cm2. Working pressure of these gases are
altered according to the thickness of the metal parts of the joint.

Two pressure gauges are fitted
each on the oxygen cylinder and on the acetylene cylinder. One of the pressure
gauges indicates the pressure of the cylinder and the other gauge indicates the
working pressure of the specific gas.
Hoses
Separate
hoses are used to connect the two cylinders with the welding torch through
regulators. The colour of the hose from the oxygen cylinder is black and the
one from the acetylene cylinder is red. These hoses carry the gases to the
welding torch.

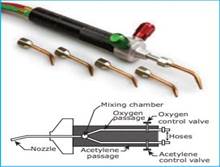
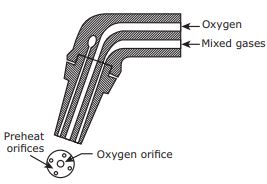
Welding torch
Oxygen
and acetylene reach the welding torch through the passages of hoses from the
respective cylinders. These gases are mixed in the mixing chamber of the
welding torch. Flame is produced at the tip of the torch when the gases are
ignited. There are two control valves present in the torch to control the
quantity of oxygen and acetylene. By this control, the grade of the flame can
be altered. The size of the flame is altered to suit the thickness of the metal
parts.
Goggles
Oxy
acetylene flame emits ultraviolet and infrared rays. These rays are highly
harmful to bare eyes. In order to protect the eyes of the welder, goggles
should be used by him.

Welding gloves
Protective
hand gloves are used by the operator to prevent possible damages that may be
caused by high temperatures and metal splashes during welding.

Spark lighter
Spark
lighter is used to ignite the oxyacetylene gas at the tip of the welding torch.

Wire brush
Wire
brushes are useful for cleaning the weld before and after the welding process.
Types of gas flame
The
size of the flame can be altered by varying the ratio of oxygen and acetylene. By
doing so, the following three types of flames are obtained.
1.
Neutral flame
2.
Carburising flame
3.
Oxidising flame
Neutral flame
The supply of equal quantities of oxygen and
acetylene produces neutral flame. There are two zones in this flame-
1.
Sharp and bright inner cone and
2.
Bluish outer cone.
The temperature of the inner cone
will be around 32000 C. This neutral flame is generally used as it will not
cause any chemical reaction upon the heated metal.
Carburising flame
This flame is also known as reducing flame. The
supply of acetylene will be more than oxygen to produce this flame. Carburising
flame consists of three zones namely,
1.
Sharp inner cone
2.
White intermediate cone
3.
Bluish outer cone
Carburising
flame is useful in welding low carbon steel and alloy steels. It is also used
to harden the outer surface of metal parts.
Oxidising flame
Oxidising
flame is obtained by supplying more oxygen than acetylene. It consists of two
zones namely bright inner cone and outer cone. This flame is useful in welding
brass and bronze.
Filler rods used in gas welding
Filler
rods used in gas welding supply the additional metal is making joints. These
rods are melted by the gas flame and deposited over the parts of the joint.
Generally the filler rods are made of the same metal as that of the parts of
the joint.
The
diameter of the filler rod depends upon the thickness of the parts to be
welded. The strength of the welding joint is increased by adding Nickel or
Chromium in filler rods. A thin coat of copper is provided on the filler rods
to prevent the molten metal from reacting with atmospheric oxygen. Flux may be
applied either in powdered form or liquid form.
Advantages of gas welding
1.
Applied for different classes of work
2.
Welding temperature is controlled easily
3.
The quantity of filler metal added in the joint
can easily be controlled
4.
The cost of the welding unit is less
5.
The cost of maintenance is less
6.
Both welding and cutting can be done
Disadvantages of gas welding
1.
Intended for welding thin work pieces only
2.
The process of welding is slow
3.
The time taken by the gas flame to heat the metal
is more when compared with electric arc.
4.
The strength of the joint is less
5.
Great care should be taken in handling and storing
gas cylinders.
Differences between arc welding and gas welding
|
Arc welding |
Gas welding |
|
The
heat is generated by the electric arc |
The required heat is provided
by the gas flame. |
|
The working
temperature is about 40000 C |
The temperature of the gas flame is about 32000
C |
|
The
filler rod is used as electrode. |
Filler rod is used separately |
|
Care
should be taken against the dangers |
The danger of the process is because of the
gases that may be caused because of electricity at high pressure |
|
The
strength of the joint is more |
The joint is not as strong as
that of arc welding |
|
Brazing
and soldering cannot be performed with the gas flame. |
The processes of brazing and soldering can be
done by the electric arc. |
|
The
filler rod metal should be selected as the joint. |
The filler rod metal can be
different from that of the the same metal as that of the parts of parts of
the joint |
Resistance
welding
The process of resistance welding
involves developing electrical resistance in the parts of the joint to bring
them into a plastic state and Applying pressure on the parts to make the joint.
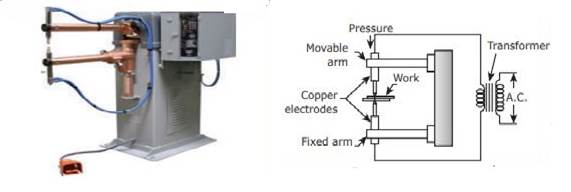
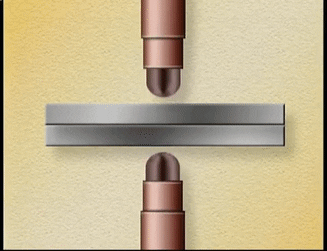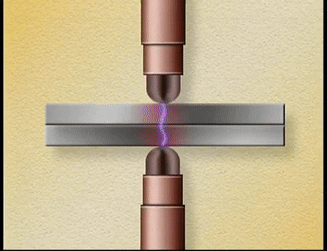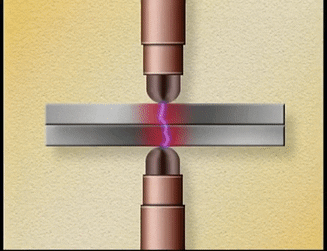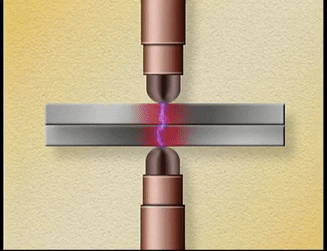
Two
copper electrodes are connected to an electric circuit of low resistance. The
parts to be welded are placed between the electrodes. When current is allowed
to pass through the electrodes, high electrical resistance is developed at the
joint. Because of the resistance, heat is generated at the joint. The metal
parts reach plastic state at this high temperature.
At
this point, pressure is applied by means of either mechanical or hydraulic or
pneumatic power source to make the joint. Current is provided by a suitable
A.C. transformer. Resistance welding is useful in welding sheet metal, bars and
pipes.
Welding related processes
Following are some important welding related
processes used in industries.
1.
O x y - a c e t y l e n e cutting
2.
Arc cutting
3.
Hard facing
4.
Soldering
5.
Brazing
Oxy-acetylene cutting
Plates
made of iron and steel are cut by oxygen, acetylene cutting torch. Oxygen and
acetylene are mixed in the cutting torch and a gas flame is generated. The
flame heats the sheets to bring them to red hot condition. High pressure oxygen
is supplied on the red hot metal through a separate central hole of the cutting
torch. Iron and steel sheets are thus cut by the jet of oxygen.

Arc cutting
In this process, the metal parts are
heated by means of carbon or metal electrodes. High pressure air is supplied on
the molten metal to remove it and cut the metal parts. Oxygen jet is supplied
along with the electrode instead of air nowadays. Arc cutting is not suitable
for accurate work.
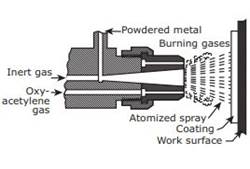
Hard facing
Hard
facing is a process of coating a hard material on soft metal parts. Powdered
coating metal is filled in the welding gun. The metal powder is melted by the
oxy-acetylene gas flame. The supply of inert gas at pressure makes the powdered
metal to split into small particles. These particles are sprayed on the
surfaces of the soft metal. Coatings of Tungsten carbide, Chromium carbide and
Aluminium oxide can be made on the surfaces of different cutting tools and
cutters.
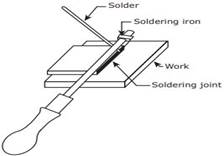
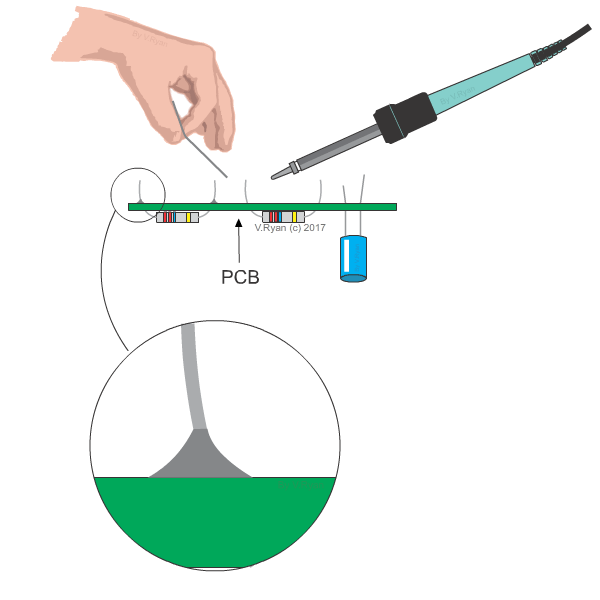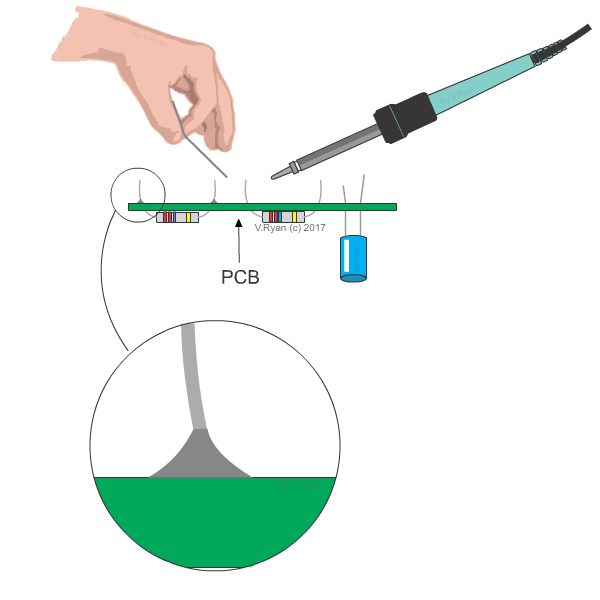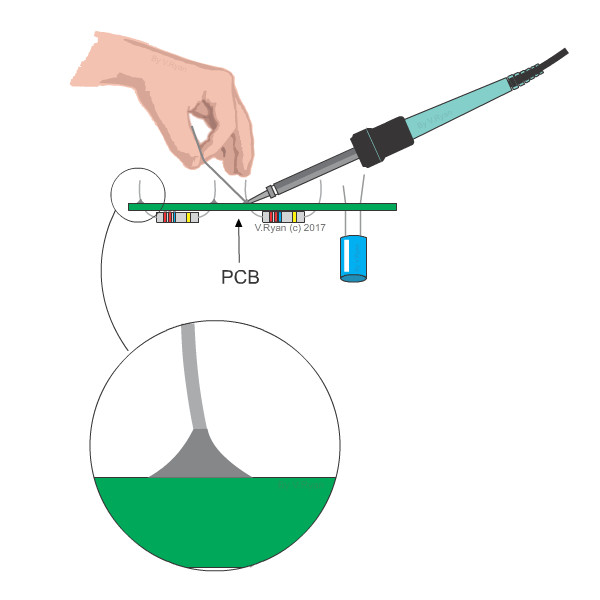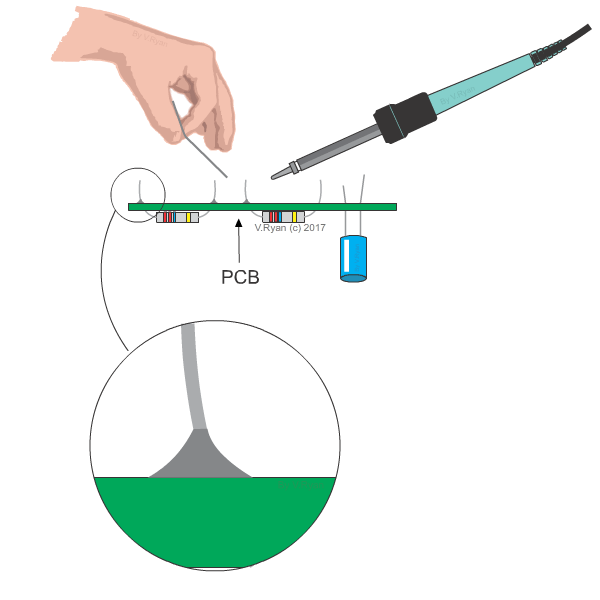
Soldering
Two
parts made of similar or dissimilar metals are joined by a solder made of a
fusible alloy. Solder is an alloy made of Tin and Lead. The melting temperature
of the solder is in the range of 1500 C to 3500 C. The
surfaces of the two metal parts are cleaned and held in correct positions. Flux
paste made of zinc chloride is applied on the parts by soldering iron.
Application of flux prevents oxidation. The solder is melted by the heat
provided by the soldering iron and filled between the metal parts. The solder
solidifies and joints the metal parts.
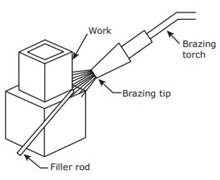
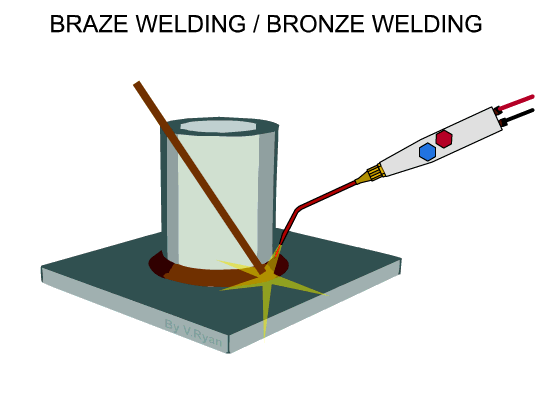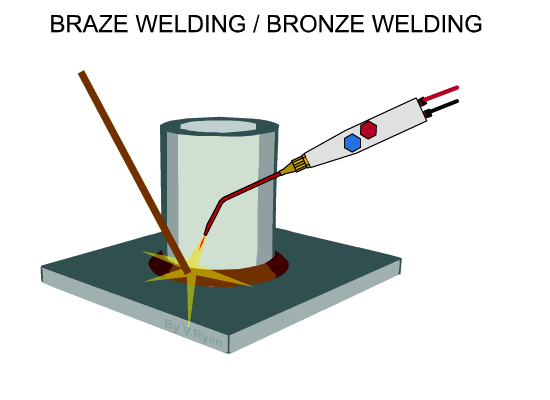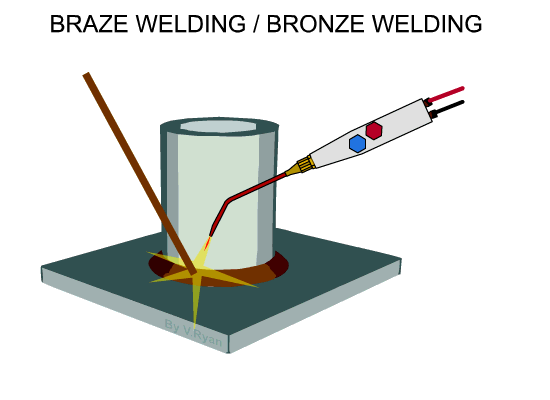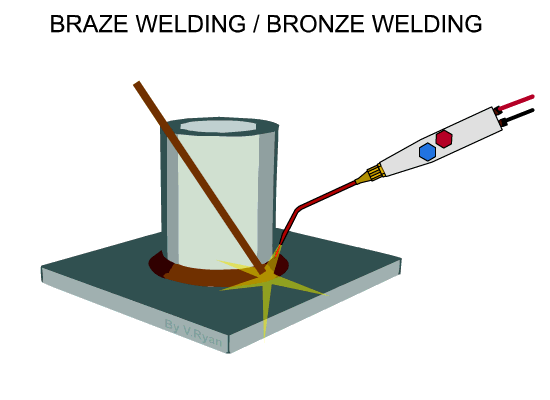
Brazing
In
brazing, filler metal in molten state is filled between the metal parts of the
joint. The filler rod is heated up to 4500 C. The parts to be joined
are cleaned and the molten filler metal is applied between the parts to make
the joint. In this method, the metal parts are not melted.
Types of welding joints
Following are the various types of welded joints
1.
Butt joint
2.
Lap joint
3.
T-joint
4.
Corner joint
5.
Flange joint
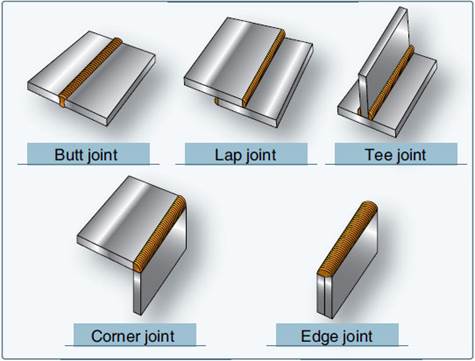
Butt joint
Butt
joint is a joint in which the corners or the edges of two metal parts are
joined. The process is done by keeping the metal parts on a same plane. The
edges of metal parts of thickness upto 5mm may be kept Open Square. If the
thickness of the metal parts exceeds 5mm, edges of the parts need to be
prepared in proper shape before welding.
Lap Joint
It
is a joint in which the metal plates are placed over lapping before welding.
The edge of one part is welded with the surface of the other plate. There are
two types of lap joint namely
(i)
single lap joint and
(ii)
Double lap joint.
T-Joint
This
joint is made by keeping the metal plates at perpendicular (900
) to each other. Sheets with thickners over
3mm only are welded by this type of joints.
Corner joint
Two
metal sheets kept at 900 to each other are welded by this joint. This method is
adopted when making boxes and tanks. Corner joints are adopted for thin and
thick sheets.
Flange joint
The
plates of the joint may be kept parallel or at 900 to each other. The edges of
the plates are bent to form the shape of a flange.
Safety precautions for welding
We
make use of electrical devices and inflammable gases like oxygen and acetylene
in welding. If proper care is not shown in handling them, there is always a
possibility of accidents taking place. So, welding process should be carried
out with due safety and caution.
Safety precautions for gas welding
1.
Gas cylinders should be kept in ventilated
locations.
2.
Cylinders should not be kept near hot locations.
They should be kept away from electrical terminals.
3.
Pressure regulators should be closed after the
welding work is completed.
4.
Regulators should be handled properly.
5.
Old and worn out regulators should be replaced
immediately.
6.
The operator should wear goggles, gloves, apron
and proper footwear.
7.
Fire extinguishers and first – aid box should be
kept ready always.
Safety precautions for arc welding
1.
The welder should always wear goggles. Gloves,
apron and proper footwear during welding
2.
Welding shop should be located properly so that it
does not cause any discomfort to others.
3.
The welder should act carefully against electric
shocks.
4.
A high quality electrode holder should be put into
use.
5.
Power supply should be provided at required voltage
and uniform current
6.
Fire extinguishers and First – aid box should
always be kept ready in a welding shop.