Computer Organisation
Explain in Brief
1.
Differentiate Computer Organisation from Computer Architecture.
|
Computer
Organisation |
Computer
Architecture |
|
Computer
organisation deals with the hardware components of a computer system. It
includes input/output devices, the central processing unit, storage and
primary memory. |
Computer
architecture deals with the engineering considerations involved in designing
a computer. |
2. Classify the microprocessor based on the size
of the data.
Depending on the data width,
microprocessors can process instructions. The microprocessor can be classified
as follows.
(2) 16-bit microprocessor
(3) 32-bit microprocessor
(4) 64-bit microprocessor
3. Write down the
classifications of microprocessors based on the instruction set.
Reduced
Instruction Set Computers (RISC): RISC stands for Reduced
Instruction Set Computers. They have a small set of highly optimized
instructions. Complex instructions are also implemented using simpler
instructions, thus reducing the size of the instruction set. Eg: RISC
processors are Intel P6, Pentium IV, AMD K6 and K7.
Complex Instruction Set Computers (CICS): CICS stands for Complex Instruction Set
Computers. Computers supporting CICS can accomplish a wide variety of tasks,
making them ideal for personal computers. E.g.: CICS processors are Intel 386
& 486, Pentium, Pentium II and III, and Motorola 68000.
4. Differentiate PROM and EPROM.
|
PROM |
EPROM |
|
PROM is a memory on which data can be written only
once. |
EPROM is a memory on
which ultra violet rays are used to clear its content and making it possible
to reprogram the memory. |
5. Write down the interfaces
and ports available in computer.
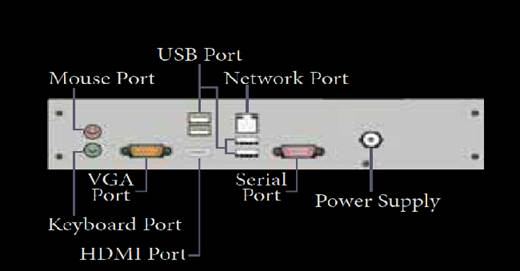
Ports and Interfaces
To connect the external devices, found in old
computers.
Parallel Port:
To
connect the printers, found in old computers.
USB Ports:
To
connect external devices like cameras, scanners, mobile phones, external hard
disks and printers to the computer.
USB 3.0
is the third major version of the Universal Serial Bus (USB) standard to
connect computers with other electronic gadgets. USB 3.0 can transfer data up
to 5 Giga byte/second. USB 3.1 and USB 3.2 are also released.
VGA Connector:
To
connect a monitor or any display device like LCD projector.
Audio Plugs:
To connect sound speakers, microphone and
headphones.
PS/2 Port:
To connect mouse and keyboard to PC.
SCSI Port:
To connect the hard disk drives and network
connectors.
High
Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI): High-Definition Multimedia Interface is
an audio/video interface which transfers the uncompressed video and audio data
from a video controller, to a compatible computer monitor, LCD projector,
digital television etc.
6. Differentiate CD and DVD.
|
CD |
DVD |
|
CD stands for Compact
Disc |
DVD stands for Digital
Versatile Disc |
|
Cd’s are made with the
purpose of holding audio files as well as program files. |
DVDs are made with the
purpose of holding video files, movies, substantial amount of programs etc. |
|
A standard CD can
store about 700 MB of data |
A standard DVD can
hold 4.7 GB of data. |
7. How will you differentiate a
flash Memory and an EPROM?
|
Flash Memory |
EPROM |
|
The flash
memory allows data to be written or erased in blocks |
The EPROM
requires data to be written or erased one byte at a time |
|
Flash
memory is fast in performance |
EPROM is
slower in performance |
8. What is
microprocessor? Draw the block diagram of microprocessor.
The
microprocessor is a programmable multipurpose silicon chip that is based on a
register. It is driven by clock pulses. It accepts input as a binary data and
after processing, it provides the output data as per the instructions stored in
the memory.
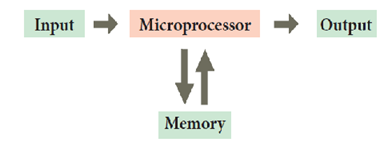
A
Microprocessor – Based System
A
DVD (Digital Versatile Disc or Digital Video Disc) is an optical disc capable
of storing up to 4.7 GB of data, more than six times what a CD can hold. DVDs
are often used to store movies at a better quality. Like CDs, DVDs are read
with a laser.
The
disc can have one or two sides, and one or two layers of data per side; the
number of sides and layers determines how much it can hold. A 12 cm diameter
disc with single sided, single layer has 4.7 GB capacity, whereas the single
sided, double layer has 8.5 GB capacity.
The 8
cm DVD has 1.5 GB capacity. The capacity of a DVD-ROM can be visually determine
noting the number of data sides of the disc. Double-layered sides are usually
gold-coloured while single-layered sides are usually silver-coloured, like a
CD.
10. Write short notes ion Disc.
Blu-ray Disc is a high-density
optical disc similar to DVD. Blu-ray is the type of disc used for Play station
games and for playing high-definition (HD) movies. A double layer Blu-ray disc
can store up to 50GB (gigabytes).
This is
more than 5 times the capacity of a DVD, and above 70 times of a CD. The format
was developed to enable recording, rewriting and playback of high-definition
videos, as well as storing large amount of data.
DVD uses a red laser to read
and write data. But, Blu-ray uses a blue-violet laser to read and write. Hence,
it is called as Blu-ray.
11. What are the methods to access the
memory?
Computer
memory is the storage space in the computer, where data and instructions are
stored. There are two
types of accessing methods to access (read or write) the memory. They are
sequential access and
random access.
In
sequential access, the memory is accessed in an orderly manner from starting to end.
But, in
random access, any byte of memory can be accessed directly without navigating through
previous bytes.
12. List down the different types of
operations in Instruction set.
A
command which is given to a computer to perform an operation on data is called an
instruction. Basic set of
machine level instructions that a microprocessor is designed to execute is called as an instruction
set. This instruction set carries out
the following types of operations:
(i) Data transfer
(ii) Arithmetic operations
(iii) Logical operations
(iv) Control flow
(v) Input/output.
