Computer Organisation
Explain in detail
1. Explain the characteristics
of a microprocessor.
Microprocessor's
performance depends on the following characteristics:
(I)
Clock speed
(ii)
Instruction set
(iii)
Word size
(i) Clock Speed:
ü Every
microprocessor has an internal clock that regulates the speed at which it
executes instructions.
ü The
speed at which the microprocessor executes instructions is called the clock
speed. Clock speed is measured in MHz (Mega Hertz) or in GHZ (Giga Hertz).
(ii) Instruction Set:
ü A
command which is given to a computer to perform an operation on data is called
an instruction.
ü Basic
set of machine level instructions that a microprocessor is designed to execute
is called as an instruction set.
ü This
instruction set carries out the following types of operations: Data transfer,
Arithmetic operations, Logical operations, Control flow, Input/output.
(iii) Word Size:
ü The
number of bits that can be processed by a processor in a single instruction is
called its word size. Word size determines the amount of RAM that can be
accessed by a microprocessor at one time and the total number of pins on the
microprocessor.
ü Total
number of input and output pins in turn determines the architecture of the
microprocessor.
2. How the read and write
operations are performed by a processor?
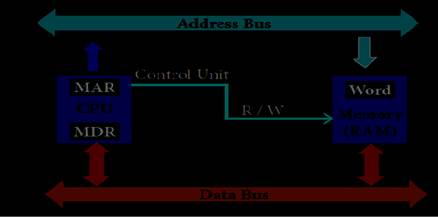
·
The read operation fetches data
from memory and transfers to MDR. A single control line performs two operations
like Read/Write using 1 or 0. Also, the write operation transfers data from the
MDR to memory.
·
This organisation is shown in
figure.
·
The word in the RAM has the
same size (no. of bits) as the Memory Data Register (MDR).
·
If the processor is an 8-bit
processor like Intel 8085, its MDR and the word in the RAM both have 8 bits.
If
the size of the MDR is eight bits, which can be connected with a word of eight
bits where the data can be stored or retrieved, the data bus has eight wires in
parallel to transfer the data in any one direction which depends on whether the
control is read or write.
·
This
control line is labelled as R/W, which becomes 1 means READ operation and 0
means WRITE operation.
·
Figure
shows the content of MDR and the Memory Word before the READ operation. Also
figure shows the content of MDR and the Memory Word after the READ operation.
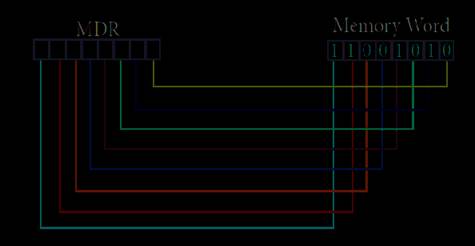
Before the READ operation
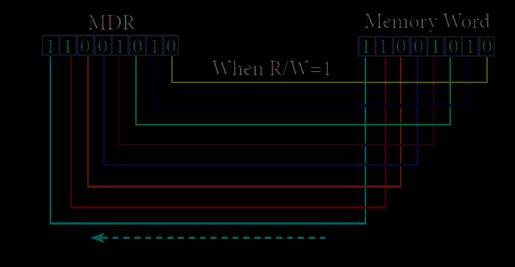
After the READ operational
The read operation transfers the data (bits) from word
to memory data register. The write operation transfers the data (bits) from
memory data register to word.
3.
Arrange the memory devices in ascending order based on the access time.
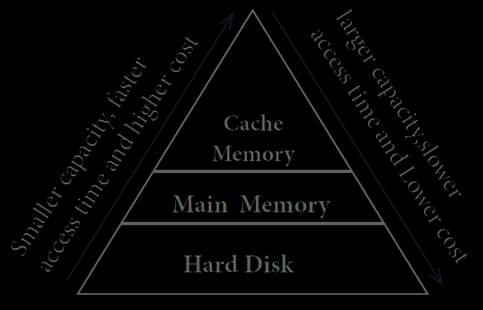
Cache
memory:
v
The
cache is a very high speed, expensive piece of memory, which is used to speed
up the memory retrieval process.
v The idea of introducing a cache is that, this
extremely fast memory would store data that is frequently accessed and if
possible, the data that is spatially closer to it. This helps to achieve the
fast response time.
Random-access memory / main memory:
v RAM
is a volatile memory, which means that the information stored in it is not
permanent.
v As
soon as the power is turned off, whatever data that resided in a RAM is lost.
It allows both read and write operations.
Hard Disk:
v Hard
disk is a magnetic disk on which we can store computer data. In general, hard disks are less portable than
floppies, although it is possible to port by removal hard disks.
v Two
types of removable hard disks are disk packs and removable cartridges.
v A
CD or CD-ROM is made from 1.2 millimetres thick, polycarbonate plastic
material. A thin layer of
aluminium or gold is applied to the surface.
v CD
data is represented as tiny indentations known as "pits",
encoded in a spiral track moulded into the top of the polycarbonate layer.
v The
areas between pits are known as “lands”. A motor within the CD player rotates
the disk. The capacity of an ordinary CD-ROM is 700MB.
v A
DVD (Digital Versatile Disc or Digital Video Disc) is an optical disc capable of storing up to 4.7
GB of data, more than six times what a CD can hold.
v DVDs
are often used to store movies at a better quality than with a VHS. DVDs can
also have interactive menus and bonus features such as deleted scenes and
commentaries. Like CDS, DVDs are read with a laser.
Ø Read-only
memory refers to special memory in a computer with pre-recorded data at
manufacturing time which cannot be modified.
Ø The
stored programs that start the computer and perform diagnostics are available
in ROMs. ROM stores critical programs such as the program that boots the
computer.
Ø Once
the data has been written onto a ROM chip, it cannot be modified or removed and
can only be read.
Ø ROM retains its contents even when the
computer is turned off. So, ROM is called as a non-volatile memory.
Ø Programmable
read-only memory is also a non-volatile memory on which data can be written
only once. Once a program has been written onto a PROM, it remains there
forever.
Ø Unlike
the main memory, PROMs retain their contents even when the computer is turned
off.
Ø The
PROM differs from ROM. PROM is manufactured as a blank memory, whereas a ROM is
programmed during the manufacturing process itself.
Ø PROM
programmer or a PROM burner is used to write data to a PROM chip. The process
of programming a PROM is called burning the PROM.
Erasable Programmable Read-Only
Memory (EPROM):
Ø Erasable
Programmable Read-Only Memory is a special type of memory which serves as a
PROM, out the content can be erased using ultraviolet rays.
Ø EPROM
retains its contents until it is exposed to ultraviolet light. The ultraviolet
light clears its contents, making it possible to reprogram the memory.
Ø An
EPROM differs from a PROM, PROM can be written only once and cannot be erased.
Ø EPROMs
are used widely in personal computers because they enable the manufacturer to
change the contents of the PROM to replace with updated versions or erase the
contents before the computer is delivered.
Ø Electrically
Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory is a special type of PROM that can be
washed by exposing it to an electrical charge.
Ø Like
other types of PROM, EEPROM retain site Contents even when the power is turned
off. Comparing with all other types of ROM, EEPROM is slower in performance.
5. Explain in detail the various
types of storage devices.
v The
secondary storage devices are used to store data that is of larger size which
can be accessed later.
v Since
the main memory is costly, the size is generally very limited in a computer.
v A
portion of a secondary storage which can serve as an extension of the main
memory and can perform its job is called as virtual memory.
Ø Hard
disk is a magnetic disk on which you can store computer data. The term hard is
used to distinguish it from a soft, or floppy disk. Hard disks can store more
data and are faster than floppy disks.
Ø A
hard disk, for example, can store anywhere from 10 megabytes to several
gigabytes, whereas most floppies have a maximum storage capacity of 1.4
megabytes.
Ø In
general, hard disks are less portable than floppies, although it is possible to
port by removable hard disks. There are two types of removable hard disks: disk
packs and removable cartridges.
Ø A
CD or CD-ROM is made from 1.2 millimetres thick, polycarbonate plastic
material.
Ø A
thin layer of aluminium or gold is applied to the surface. CD data is
represented as tiny indentations known as “pits”, encoded in a spiral track
moulded into the top of the polycarbonate layer.
Ø The
areas between pits are known as “lands”. A motor within the CD player rotates
the disk. The capacity of an ordinary CD-ROM is 700MB.
Ø A
DVD (Digital Versatile Disc or Digital Video Disc) is an optical disc capable
of storing up to 4.7 GB of data, more than six times what a CD can hold. DVDs
are often used to store movies at a better quality than with a VHS.
Ø DVDs
can also have interactive menus and bonus features such as deleted scenes and
commentaries. Like CDs. DVDs are read with a laser.
Ø The
disc can have one or two sides, and one or two layers per side; the number of
sides and layers determines how much it can hold.
Ø A
12 cm diameter disc with single sided, single layer has 4.7 GB capacity,
whereas the single sided, double layer has 8.5 GB capacity. The 8 cm DVD has
1.5 GB capacity.
Ø The
capacity of a DVD-ROM can be visually determined by noting the number of data
sides of the disc. Double-layered sides are usually gold-coloured, while
single-layered sides are usually silver-coloured, like a CD.
Ø Flash
memory is an electronic (solid-state) non-volatile computer storage medium that
can be electrically erased and reprogrammed.
Ø They
are either EEPROM or EPROM. Examples for Flash memories are pen drives, memory
cards etc.
Ø Flash
memories can be used in personal computers, Personal Digital Assistants (PDA),
digital audio players, digital cameras and mobile phones. Flash memory offers
fast access times.
Ø The
time taken to read or write a character in memory is called access time. The
capacity of the flash memories vary from 1 Gigabytes (GB) to 2 Terabytes (TB).
Ø Blu-Ray
Disc is a high-density optical disc format similar to DVD. Blu-ray is the type
of disc used for PlayStation games and for playing high-definition (HD) movies.
Ø In
the past, there were other standards for such movies. A double-layer Blu-Ray
disc can store up to 50GB (gigabytes) of data.
Ø This
is more than 5 times the capacity of a DVD, and above 70 times of a CD.
Ø The
format was developed to enable recording, rewriting and playback of
high-definition video (HD), as well as storing large amounts of data. DVD uses
a red laser to read and write data.
Ø But,
Blu-ray uses a blue-violet laser to write. Hence, it is called as Blu-Ray.
