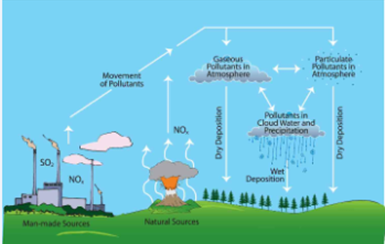
Acid Rain
ü Acid
rain caused by emission of SO2 and NOx from various sources to the
atmosphere and they dissolve in atmospheric water and produce acids in the rain
water.
ü SO2
does not react much in the atmospheric chemicals but it can travel quicker to
long distances and when get contact with ozone or hydrogen peroxide it produces
SO3, which is highly soluble in water and form sulphuric
acid.
ü Sulphur
dioxide is naturally produced by volcanic eruptions, sea spray, planktons,
rotting vegetation and forest fires.
ü Anthropogenic
sources 69.4 % of Sulphur dioxide released from industrial combustion (point
sources), house hold heating of fire wood and coal (area or non-point sources)
and 3.7% from transportation (mobile sources).
ü NOx
is naturally produced by lightening, bacterial action, forest fire and
volcanoes, manmade emission are by automobiles (43%) and fertilizer industries,
utility plants and other industrial combustion (32%) (‘Causes and Effects of
Acid Rain’)
ü Acid
rain increases nitrate levels in soil, leading to nitrogen saturation in soils.
Nitrate ions remove additional calcium and magnesium from soil, excess nitrogen
subsequently lower the frog population as well.
ü Acid
rain releases aluminum from the soil into lakes and streams which is toxic to
many aquatic organisms. According to natural surface effects of deposition
about 75% of the lakes and about 50% of the streams
ü Nitrogen
dioxide deposition in water bodies is another major reason for episodic
acidification, about 10- 45 % of the nitrogen dioxide reaching water bodies are
airborne and they are released to atmosphere mainly from anthropogenic sources.
Acid
deposition
Effects on Forest
ü Acid precipitation on vegetation
reduces the photosynthesis and growth also increase the susceptibility to
draught and disease, process called ‘dieback’ it causes browning of leaf and
fall off
ü In addition, effects such as thinning
of annual growth ring and reduction in biomass (due to reduced growth), it also
damage the fine root system, affect root mycorrhiza (due to increase in Al and
acidity) and decrease the lichens, reduction of soil fertility as potassium
leached out of the soil,
ü Phosphorus is also reduced this
reduces the fruit production, toxic metals such as zinc and aluminum
accumulates, aluminum toxicity retard root growth and causes loss of
chlorophyll.
ü Soil acidity can be overcome by
addition of lime, whereas alkalinity of limestone neutralizes the negative ions
in acid.
ü Lime
stone is added to neutralize the acid in the water body; it also facilitates the
release of locked nutrients of the acidified mud bottoms by neutralizing the
ions.
ü Essential
nutrients such as phosphorus and other limiting minerals get released and
thereby planktons and plant productivity get increased.
ü Agricultural lime (CaCO3) is recommended
type generally in use, Dolomite lime (MgCO3) is impure substance,
Quicklime (CaO) and Hydrated lime (Ca(OH)2)
are caustic, used in acidified lakes in little quantities and if applied in
high amount results fish kill and Soda ash (Na2CO3) also
usable but it is less preferred due to its high cost.
ü In addition factors such as hardness of the
water, existing pH, alkalinity, chemistry and acidity of bottom mud,
temperature and water quality, density and type of aquatic plants, targeted pH,
type, type of limestone (purity and particle size) amount and flushing rate to
be considered in liming applications.
ü Treatment can be extended in several additional
applications if required, limestone is applied by boat or barge (flushing lime
at high pressure) and by snow mobile tractor or spreader on ice covered lakes
(lime dissolved on surface ice and subsequently reaches the waters).
Health Effects
ü The
causing agents of acid rain SO2, SO3 and NOx may affect
the health particularly SO2 & SO3 effect on asthma
and emphysema patients and increase the incidence, Particulate deposition of
particles less than PM 2.5 can even reach the blood stream via lungs and cause
harmful effects such as lung cancer.
Reduce Acid Rain
ü This can be done either fuel
switching or scrubbing. Fuel switching includes limiting the use of Sulphur
containing fuels such as coal or switching to low sulphur
containing coal or oil, switching to alternative energy sources such as using
gas boilers instead of coal or oil boilers, nuclear power generation, using
renewable energy sources such as wind, air, wave and geothermal energy.
ü Use solar batteries, fuel cells, natural gas and electric motor vehicles. EPAs energy star
program, reduce carpool by using public transportation, maintain the vehicle
for low NOx emission and factory boilers such as clean the stacks and exhaust
pipes.
ü Use energy efficient boilers and
using filters or scrubbers to catch the oxides of sulphur
and Nitrogen in industrial effluents and vehicles, defining the right stack
height was 150-300m common in smelters and thermal electric generating plants.
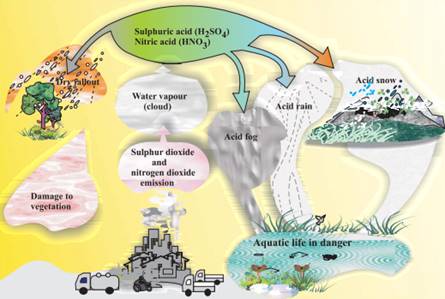
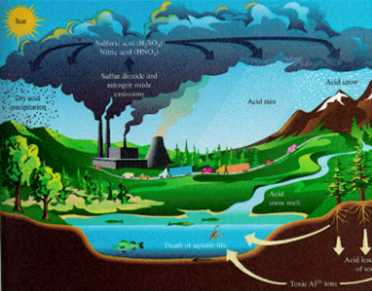
ü Acid rain is one of the world’s major
environmental problems since 19th century. Coal burning is the major cause of
SO2 production and also vehicle emission and various fossil fuel
based power generation emits NOx. Both SO2 and NOx produces sulphuric and nitric acid
ü Acid
rain affects forest trees causes yellowing and leaf fall, acidified rivers and
lakes causes fish death, loss of calcareous shell forming species (mollusks),
it also affects soil microorganisms causes increased nitrification which also
leads to eutrophication in water bodies and changes in the biodiversity.
ü Acid
rain also destroys the coral reefs. It causes leaching of metal ions including
toxic Aluminum and heavy metals such as chromium, cadmium and nickel, which
adversely affects the soil micro flora and aquatic biota.

ü Acid
rain deteriorates the marble, stone monuments and architectures, corrode metal
structures and fading paints. Liming is used to neutralize the acidity in soil
and aquatic bodies.
ü Several
methods are used to reduce the emission of SO2 and NOx such as
reducing the sulphur content in fuels, using
scrubbers such as flue gas desulphurization (FGS) lime injection multi stage
burning (LIMB) or fluidized bed combustion (FBC or circulation dry scrubber).