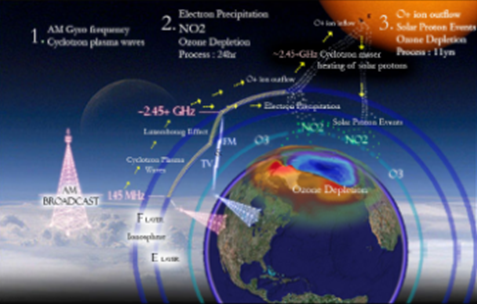
Stratospheric Pollution
The upper stratosphere consists of
considerable amount of ozone (O3), which protects us from the
harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiations (λ 255 nm) coming from the sun. These radiations
cause skin cancer (melanoma) in humans. Therefore, it is important to maintain
the ozone shield.
Ozone in the stratosphere is a product of
UV radiations acting on dioxygen (O2) molecules. The UV radiations
split apart molecular oxygen into free oxygen (O) atoms. These oxygen atoms
combine with the molecular oxygen to form ozone.
Ozone Layer
Ø
The ozone layer is
basically naturally occurring gas in the region of stratosphere where ozone
particles are accumulated.
Ø
Ozone layer is also
naturally broken down but there is a balance between its formation and natural
depletion.
Ø
As a result the total
amount of ozone remains constant. But ozone layer thickness varies with
altitude and seasonal change. Ozone concentration is highest between
19 - 23 km.
Ø
Most of ozone is formed at
equator where there is maximum sunshine but with winds it travels at high
altitude and get accumulated in stratosphere.
Causes of Ozone Layer Depletion
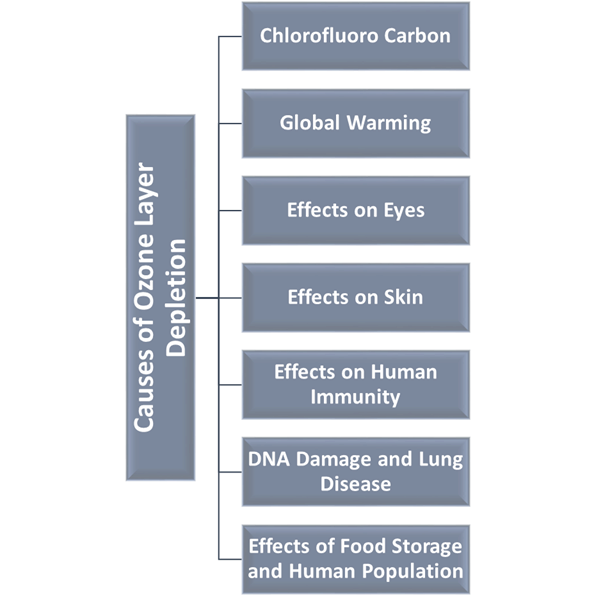
1. Chlorofluoro Carbon:
ü
Ozone depletion occurs when
the natural balance between the production and destruction of stratospheric
ozone is disturbed.
ü
Although natural phenomenon
can cause ozone depletion but human activities such as CFCs are now accepted as
major cause of depletion. All ozone depleting chemicals contain chlorine and
bromine.
ü
CFCs are highly volatile
and non-combustible so they are very quickly evaporated and can easily reach in
stratosphere where ozone is present here they start depleting ozone molecules.
ü
These CFCs have also adverse affects on human health. According to the chemical
model for ozone destruction proposed about 20 years ago, the photolysis of Cl2O2
is key to ozone depletion reaction.
ü
But now atmospheric
researchers studied that the rate of this reaction is not extremely high as it
was thought previously so we can no longer say that CFCs are the main cause of
ozone depletion.
2.
Global Warming:
ü
Global warming also leads
to ozone layer depletion. Due to global warming and greenhouse effect most of
the heat is trapped in troposphere which is the layer below the stratosphere.
ü
As we all know ozone is
present in stratosphere so heat don’t reaches troposphere and it remain cold as
recovery of ozone layer requires maximum sunlight and heat so it leads to
depletion of ozone layer.
3.
Effects on Eyes:
ü
The major cause of
blindness in this world is cataracts. There would be 0.3% - 0.6% increase in
risk of cataract if there will be 1% decrease in Ozone level. Eye lens can be
damaged by oxidative agents.
ü
Oxidative oxygen produced
by UV radiation can severely damage eye lens and cornea of eye is also badly
damaged by UV radiation. Photokeratitis, cataract,
blindness all are caused due to UV rays.
4.
Effects on Skin:
ü
Exposure to UV radiations
can cause skin cancer. UV radiations alter the structure of biomolecules and
thus lead to different diseases.
ü
Skin is the most often
exposed part of body to UV radiations
ü
There are two types of skin
cancer,
o
Melanoma
o
Non-melanoma
ü
Melanoma is most serious
form of cancer and is often fatal, while non-melanoma is most common type and
less fatal.
ü
Depletion of ozone layer
leads to both Sun burn and skin cancer. UV radiations are also responsible for
breast cancer and leukemia.
5.
Effects on Human
Immunity:
ü
Exposure to UV radiations
can also result in suppression of immune response to skin cancer, infectious
diseases and other antigens.
ü
The immune supression is due to changes in skin photoreceptors and
antigen presenting cells that are brought by UV radiations.
ü
More increase in depletion
of ozone results in more decrease in immune system.
6.
DNA Damage and Lung
Disease:
ü
Short exposure to UV-B
radiations can cause the DNA damage because UV radiations can disturb
biomolecules such as lipids, proteins and Nucliec
acids.
ü
Due to UV-B radiations there would be cryptic
transposable elements which may lead towards the mutations which is more
dangerous than the immediate DNA damage.
ü
Excessive UV-B radiation exposure results in
the basal and squamous cells carcinomas. These types of cancers are induced due
to transcriptional errors during DNA replication which are caused by changes in
pyrimidine bases.
ü
The ultimate cause of this
whole mechanism is found to be the prolonged exposure to UV radiations. It is
estimated that there is increase of 2% of incidence of these cancers by 1%
depletion of ozone layer.
ü
Exposure to UV radiations equally affects
lungs. Bronchitis, obstruction of lungs Emphysema, asthma all can be resulted
from UV radiations exposure.
7. Effects
of Food Storage and Human Population:
ü
Depletion of ozone layer is
also causing the problem of food shortage to humans. UV radiations are
disturbing developmental and physiological processes which is decreasing the
productivity of crops.
ü
As humans are heavily dependent on crops for
food so there is a great chance if depletion of ozone layer is not checked it
may cause seriously shortage of food to humans.
ü
Researches also show that
UV radiations can also be used to enhance yield of crops by the use and
application of phytohormones.