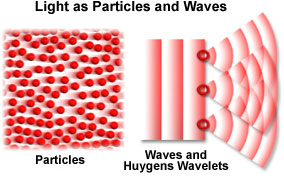
Dual Nature of Light
Light has Dual Nature:
1. Sometimes
it behaves like a particle (called a photon), which explains how light travels
in straight lines.
2.
Sometimes it behaves like a
wave, which explains how light bends (or diffracts) around an object.
3. Scientists
accept the evidence that supports this dual nature of light.
Quantum Theory:
1. Light
is thought to consist of tiny bits of energy that behave like particles called
photons.
2. Particles
explain how light travels in straight lines or reflects off of mirrors.
James
Maxwell (1870) suggested that when electrically charged particles move under
acceleration, alternating electrical and magnetic fields are produced and
transmitted. These fields are transmitted in the forms of waves called
electromagnetic waves or electromagnetic radiation.
From
further experiments we come to know about some properties of electromagnetic
waves, they are:-
1. The oscillating electric and
magnetic fields produced by oscillating charged particles are perpendicular to
each other and both are perpendicular to the direction of propagation of the
wave.
2. Unlike sound waves or water waves,
electromagnetic waves do not require medium and can move in vacuum.
3. Electromagnetic radiations differ
from one another in wavelength (or frequency) and constitute is called as
electromagnetic spectrum.
4. Different kinds of units are used
to represent electromagnetic radiation.
These radiations are characterised by the properties,
namely, frequency (ν) and wavelength (λ).
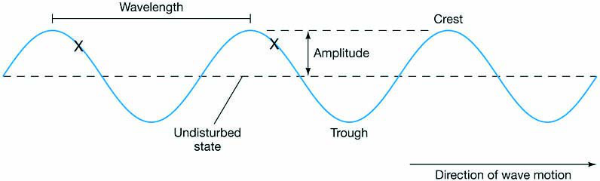
Frequency
is defined as the number of waves that pass a given point in one second. The SI
unit for frequency (ν) is hertz, Hz.
Wavelength
is the distance between one peak of a wave to the next
corresponding peak. The SI unit of wavelength is meter (m). Since
electromagnetic radiation consists of different kinds of waves of much smaller
wavelengths, smaller units are used.
The
velocity of light (c), the frequency (ν), and wavelength (λ) are
related by the equation, c
= ν λ.
Wavenumber
![]() is defined as the number of wavelengths per
unit length. Its units are reciprocal of wavelength unit, i.e., m−1.
However commonly used unit is cm-1.
is defined as the number of wavelengths per
unit length. Its units are reciprocal of wavelength unit, i.e., m−1.
However commonly used unit is cm-1.
Problems:
1. The Vividh
Bharati station of All India Radio, Delhi, broadcasts
on a frequency of 1,368 kHz (kilo hertz). Calculate the wavelength of the
electromagnetic radiation emitted by transmitter. Which part of the
electromagnetic spectrum does it belong to?
Solution:
The frequency ν = 1,368 kHz
The velocity of light c
= 3.0 × 108 m s−1
Therefore as c = ν λ
Wavelength λ = ![]()
=
![]() (1 kHz is 1 × 103 s−1)
(1 kHz is 1 × 103 s−1)
= 219.298 m
This is a characteristic radio
wave wavelength.
2. The wavelength range of the visible spectrum extends from violet (400 nm) to
red (750 nm). Express these wavelengths in frequencies (Hz). (1nm = 10−9 m)
Solution:
The
wavelength of violet light = 400 nm
=
400 × 10−9
m
The
wavelength of red light = 750 nm
=
750 × 10−9
m
The
velocity of light c =
3.0 × 108 m s−1
c = ν λ
Frequency ν = ![]()
The frequency
of violet light = ![]()
=
7.5 × 1014
s−1 or 7.5 × 1014 Hz
Similarly,
The
frequency of red light =
![]()
=
4 × 1014
s−1 or 4 × 1014 Hz
The
range of visible spectrum extends from 4 × 1014 Hz to 7.5 × 1014
Hz.
3. Calculate (a) wavenumber and (b) frequency of yellow radiation having
wavelength 5800 Å. (ångström or angstrom, Å is equal
to 10−10 m)
Solution:
The wavelength of yellow
radiation =
5800 Å
= 5800 × 10−10 m
The velocity of light c = 3.0 × 108 m s−1
a) Wavenumber (![]() ) is the number of wavelengths per
unit length, so,
) is the number of wavelengths per
unit length, so,
![]() =
= ![]()
= ![]()
= 1.724 × 106 m−1
b) The frequency of yellow
light =
![]()
=
5.172 × 1014
s−1
=
5.172 × 1014
Hz