Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics
The Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics
states that two systems in thermal equilibrium with a third system separately
are in thermal equilibrium with each other.

Application of Zeroth Law of
Thermodynamics
For example, consider two separate cups of boiling water. If
we place a thermometer into the first cup, it gets warmed up by the water until
it reads 100C. We now say that the thermometer is in thermal
equilibrium with the first cup of water. Next, we move the thermometer
into the second cup of boiling water, and it continues to read 100C. The
thermometer is therefore also in thermal equilibrium with the second cup of
water. Using the logic of the zeroth law, we can
conclude that the two separate cups of boiling water are in thermal
equilibrium with each other.
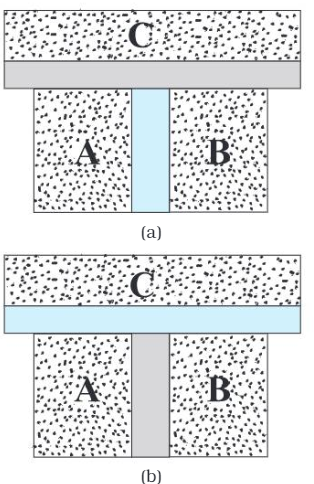
(a) Systems A and B are
separated by an adiabatic wall, while each is in contact with a third system C
via a conducting wall.
(b) The adiabatic wall between
A and B is replaced by a conducting wall, while C is insulated from A and B by
an adiabatic wall.